Comprehensive Guide to Osteoporosis: Nutrition, Symptoms, and Natural Remedies for Stronger Bones
Discover comprehensive nutritional tips, natural strategies, and early signs of osteoporosis. Learn how diet, lifestyle, and home remedies can help strengthen bones, alleviate symptoms, and prevent fractures. Essential for those at risk or looking to improve bone health naturally.

Comprehensive Guide to Osteoporosis: Nutrition, Symptoms, and Natural Remedies for Stronger Bones
Osteoporosis is a prevalent condition that gradually weakens bones, making them fragile and more susceptible to fractures. This silent disease often progresses without noticeable symptoms until a fracture occurs, significantly affecting quality of life. In the United States alone, nearly 54 million individuals are impacted by osteoporosis and low bone mass, emphasizing the importance of understanding its causes, prevention strategies, and management options. While age and gender are major risk factors, lifestyle choices such as diet, physical activity, and home remedies play a crucial role in strengthening bones and preventing the progression of this condition.
Understanding Osteoporosis
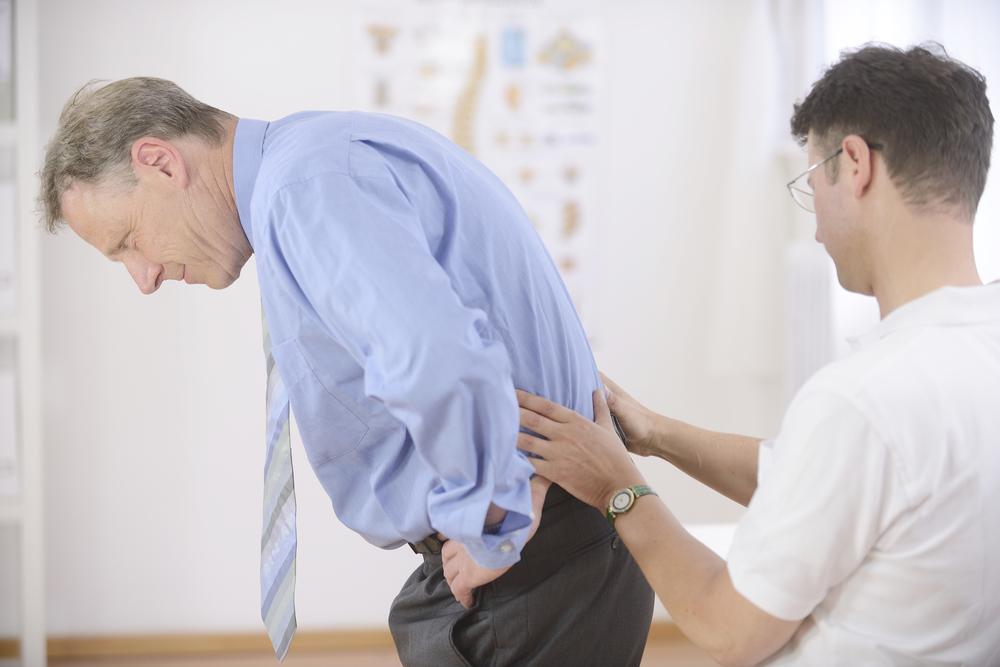
Osteoporosis is characterized by decreased bone density and deterioration of bone tissue, resulting in bones that are porous, brittle, and more prone to fractures. The disease is often called the "silent thief" because it quietly weakens bones over many years, often without symptoms until a fracture occurs. Common fracture sites include the hips, spine, and wrists.
The primary cause is an imbalance between bone resorption and bone formation, where the body loses too much bone or fails to produce enough new bone tissue. Factors contributing to osteoporosis include aging, hormonal changes (especially in postmenopausal women), inadequate calcium and vitamin D intake, lack of physical activity, smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and certain medications.
Crucial Nutritional Tips for Healthy Bones
Proper nutrition is foundational for maintaining bone density and preventing osteoporosis. A well-balanced diet rich in specific nutrients can significantly reduce risk. Here's a detailed look at key foods that promote bone strength:
Dark Leafy Greens
Vegetables such as kale, collard greens, cabbage, and Brussels sprouts are excellent sources of calcium, magnesium, and vitamin K—three nutrients essential for building and maintaining strong bones. Incorporating these greens into daily meals can provide a natural boost to bone health. Spinach also offers beneficial minerals but contains oxalates that may inhibit calcium absorption, so moderation is recommended.
Eggs and Vitamin D
Eggs are a rich source of vitamin D, which plays a critical role in calcium absorption and bone mineralization. Including eggs regularly in your diet supports the body’s ability to utilize calcium effectively. Vitamin D can also be obtained through sunlight exposure and fortified foods, but dietary intake remains essential, especially in regions with limited sun exposure.
Dairy and Plant-Based Alternatives
Milk, cheese, and yogurt are classic sources of calcium vital for bone density. For those who are lactose intolerant or prefer plant-based options, fortified soy milk, almond milk, tofu, and other calcium-rich plant foods serve as excellent substitutes. Consuming adequate calcium through various sources ensures the body maintains optimal bone strength over time.
Fruits Rich in Bone-Boosting Nutrients
Fruits such as figs, kiwis, papayas, oranges, and bananas provide vital vitamins A, C, and K. These nutrients support collagen formation, enhance calcium absorption, and reinforce bone matrix. Additionally, fruits high in potassium help neutralize acids that can leach calcium from bones, thereby protecting against bone loss.
Foods to Limit or Avoid for Bone Health
Alcohol Consumption
Excessive alcohol intake impairs bone formation and increases fracture risk. The National Osteoporosis Foundation recommends limiting alcohol consumption to no more than two drinks per day to minimize its detrimental effects on bone health.
High Sodium Foods
A diet high in salt causes increased calcium excretion through urine, weakening bones over time. Reducing salt intake to below 2,300 mg daily helps preserve calcium stores and maintain bone integrity.
Caffeinated Beverages
Consuming large amounts of caffeine from coffee, tea, energy drinks, and sodas can interfere with calcium absorption. To support bone health, it is advisable to limit caffeine consumption and balance it with calcium-rich foods.
Vitamin A and Bone Health
While vitamin A is essential for bone growth, excess intake—especially from supplements—may lead to bone weakening and increased fracture risk. It’s important to consume vitamin A in moderation and focus on obtaining it from balanced dietary sources.
Natural Strategies to Support Bone Strength
Regular Exercise
Engaging in weight-bearing and resistance exercises, such as walking, jogging, tennis, and stair climbing, stimulates bone formation and increases bone density. Regular physical activity is one of the most effective natural ways to prevent osteoporosis and maintain skeletal strength.
Lifestyle Changes: Quit Smoking
Smoking significantly accelerates bone loss, especially in women. Quitting smoking can improve bone mineral density and reduce fracture risk, contributing to overall skeletal health.
Balanced Diet and Nutrient Intake
Consuming a nutrient-rich diet with adequate levels of calcium, vitamin D, magnesium, and vitamin K supports ongoing bone maintenance. Including a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, and lean proteins aligns with strong bone health and can prevent further deterioration.
Recognizing Early Signs and Symptoms
Early detection of osteoporosis is crucial to prevent severe fractures and disabilities. Watch for signs such as:
Chronic back pain, especially in the lower back
Difficulty breathing or discomfort due to compressed spinal fractures
Postural changes, including a hunched back or stooped posture
Unexplained fractures following minor falls or injuries
Regular screenings and bone density tests are recommended, especially for postmenopausal women and older adults, to monitor bone health and initiate early interventions.