Complete Guide to Piriformis Syndrome: Causes, Recognizing Symptoms, and Effective Treatment Options
This comprehensive guide explores piriformis syndrome, highlighting its causes, symptoms, and the most effective treatment methods. Understanding this condition can help sufferers recognize early signs, seek timely medical care, and adopt lifestyle habits to prevent recurrence. The article provides detailed strategies including physical therapy, injections, and self-care tips, emphasizing the importance of proactive management for long-term relief and improved mobility.

Complete Guide to Piriformis Syndrome: Causes, Recognizing Symptoms, and Effective Treatment Options
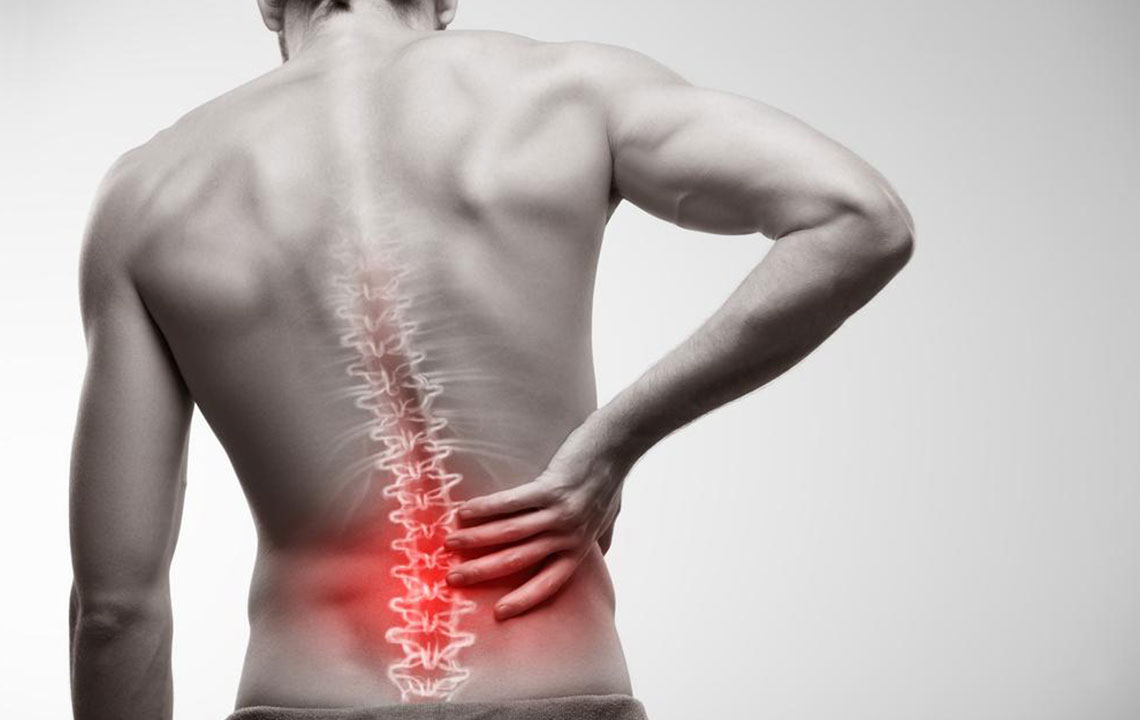
Piriformis syndrome is a neuromuscular condition triggered when the piriformis muscle becomes inflamed, tight, or spasms, leading to compression or irritation of the sciatic nerve. This particular syndrome, though relatively uncommon, can cause significant discomfort and mobility issues if left untreated. The piriformis muscle is located deep within the buttocks, near the top of the hip joint, and plays a vital role in hip stabilization, thigh rotation, and overall lower limb movement. When dysfunctional, it can lead to radiating pain, tingling, and weakness, impacting daily activities such as walking, sitting, or climbing stairs.
Understanding the Symptoms of Piriformis Syndrome
Individuals experiencing piriformis syndrome often report sudden or gradual onset of pain in the buttocks. This discomfort frequently radiates down the back of the thigh and can extend into the calf or foot, mimicking sciatic nerve pain. Recognizing these symptoms is essential for early intervention. Typical signs include:
Persistent, dull or sharp pain in the buttocks that worsens with activity
Radiating pain along the sciatic nerve pathway, commonly down the leg, calf, and foot
Increased pain when sitting for extended periods or during activities like climbing stairs and running
Pain that intensifies after prolonged sitting or remaining stationary
Limited hip mobility, stiffness, and difficulty in movements like hip rotation or flexion
Using Symptoms as Clues: How to Identify Piriformis Syndrome
Given the overlap of symptoms with other common musculoskeletal conditions such as herniated discs or arthritis, differentiating piriformis syndrome requires careful evaluation. If buttock or leg discomfort persists beyond several weeks and is not relieved by rest, consulting a healthcare practitioner is crucial. Diagnostic procedures include physical examination, where specific maneuvers may reproduce symptoms, and imaging tests like Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) or Computed Tomography (CT) scans to rule out disc herniations, spinal stenosis, or joint degeneration. Sometimes, ultrasound imaging can assist in visualizing muscle inflammation and ruling out other pathologies, providing a more accurate diagnosis.
Comprehensive Treatment Strategies for Piriformis Syndrome
Effective management of piriformis syndrome involves a combination of lifestyle adjustments, therapeutic interventions, and sometimes medications to alleviate symptoms and address underlying causes. Treatment options include:
Ice and Thermotherapy: Applying ice packs immediately after activity helps reduce inflammation and numb nerve endings, providing quick relief. An ice massage, where a small ice cube is gently massaged over the affected area for up to 10 minutes, can diminish muscle spasm and pain. Conversely, heat therapy, such as using a heating pad or taking warm baths, relaxes tight muscles and improves blood flow, which supports tissue healing.
Medications and Injections: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help manage pain and swelling. In more severe or persistent cases, corticosteroid injections or botulinum toxin (Botox) injections into the piriformis muscle are effective in reducing muscle spasms and nerve compression, thereby providing symptom relief and facilitating physical therapy.
Physical Therapy and Targeted Exercises: Tailored physical therapy routines are fundamental. Stretching exercises focusing on the piriformis, hip flexors, and surrounding muscles improve flexibility and reduce spasm-inducing tightness. Strengthening core and hip muscles stabilizes the pelvis and minimizes undue stress on the piriformis. Techniques like deep tissue massage, myofascial release, and range-of-motion exercises enhance healing and restore mobility.
Gradual Return to Activity and Lifestyle Modifications: Activity modification is important to prevent aggravating the condition. Patients are advised to avoid prolonged sitting, wear supportive footwear, and lift objects correctly. Incorporating regular breaks, stretching routines, and low-impact aerobic exercises such as swimming or walking can maintain flexibility and promote overall musculoskeletal health.
Preventive Measures to Minimize Recurrence
Prevention starts with habits that promote muscular health and proper body mechanics. Maintaining good posture during sitting and standing reduces undue pressure on the buttocks and lower back. Regular stretching routines targeting the piriformis, hip flexors, and hamstrings can prevent muscle tightness. Warming up adequately before physical activity and avoiding sudden, intense movements help avoid injuries. Using ergonomic furniture, especially in workplaces, and practicing correct lifting techniques further contribute to the prevention of piriformis syndrome. Staying active and maintaining a balanced fitness regimen helps keep muscles flexible and less prone to spasms or overuse injuries.
Long-term Management and Lifestyle Adjustments
Persistent or recurrent piriformis syndrome requires ongoing management. Recognizing and avoiding activities that trigger symptoms is key. Incorporating daily stretching and strength exercises into routines supports long-term relief. Learning to listen to your body and avoiding overexertion can prevent flare-ups. Additionally, maintaining a healthy weight reduces stress on the hips and lower back, decreasing the risk of developing or worsening sciatica symptoms. Consistent medical follow-up and physical therapy sessions are often recommended for chronic cases, ensuring that underlying issues are addressed and symptoms kept under control.
In conclusion, although piriformis syndrome can be challenging to diagnose due to its symptom overlap with other conditions, timely treatment and proper lifestyle modifications significantly improve quality of life. Emphasizing active living, targeted stretching, and medical intervention when necessary can effectively alleviate pain, restore mobility, and prevent future episodes. Awareness and early intervention are vital in managing this condition successfully.