Comprehensive Guide to Psoriasis: Symptoms, Causes, and Modern Treatment Options
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune skin condition characterized by red, scaly patches and joint pain. This comprehensive guide explores its symptoms, causes, triggers, and the most effective modern treatments, including topical therapies, phototherapy, and biologic medications. Understanding these aspects helps patients manage the disease better and improve quality of life through personalized care and lifestyle modifications.

Comprehensive Guide to Psoriasis: Symptoms, Causes, and Modern Treatment Options
Psoriasis is a complex and persistent autoimmune skin condition that affects millions worldwide. Characterized by abnormal skin cell production, psoriasis leads to the development of red, flaky, and scaly patches that can appear on various parts of the body. This chronic disorder not only affects physical appearance but can also significantly impact an individual's quality of life, causing discomfort, itching, and emotional distress. Understanding the nuances of this disease, including its symptoms, causes, and the latest treatment options, is essential for effective management and improving patient outcomes.
Identifying the Symptoms of Psoriasis
Psoriasis presents with a wide range of clinical manifestations, making it sometimes challenging to diagnose correctly. The symptoms can vary based on the type of psoriasis and its severity, but common signs include:
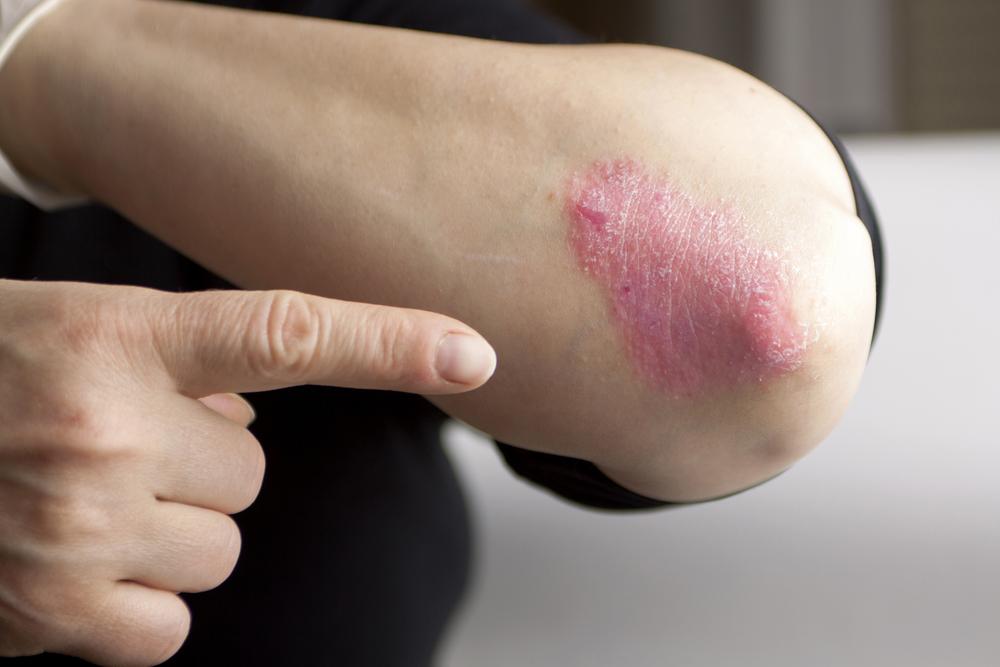
Small, silver-white, scaly patches on the skin, often known as plaques
Thickened, ridged, or pitted nails, which can be painful or unsightly
Persistent itching, soreness, and burning sensations in affected areas
Swelling, stiffness, or pain in joints, referred to as psoriatic arthritis, which may lead to joint damage if untreated
Dry, cracked skin that may bleed and cause secondary infections or discomfort
These symptoms may flare up periodically, sometimes triggered by external factors or internal health changes. Recognizing early signs can facilitate prompt treatment to control the progression of the disease.
Exploring the Causes and Triggers of Psoriasis
While the precise etiology of psoriasis remains elusive, extensive research points toward a combination of genetic, immunological, and environmental factors. It is classified as an autoimmune condition where the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells, prompting excessive cell production. Several factors are known to trigger or exacerbate psoriasis episodes:
Genetic predisposition: A family history significantly increases susceptibility
Infections: Streptococcal pharyngitis (strep throat) or skin infections can activate immune responses
Environmental triggers: Cold, dry weather conditions are notorious for worsening symptoms
Psychological stress: Both mental and physical stressors have been linked to flare-ups
Unhealthy lifestyle habits: Excessive alcohol consumption and smoking are common aggravators
Skin traumas: Cuts, scrapes, bug bites, or sunburns can trigger the Koebner phenomenon, leading to new lesions
Medications: Beta-blockers, lithium, and antimalarial drugs are known to influence psoriasis development
Understanding these triggers is crucial for managing and preventing flare-ups through lifestyle adjustments and medical interventions.
Modern and Traditional Treatment Strategies for Psoriasis
Although a definitive cure for psoriasis remains undiscovered, a variety of therapies are available to control symptoms and improve patient quality of life. The selection of treatment depends on disease severity, lesion location, patient preferences, and response to previous therapies.
Topical Therapies
These are typically the first line of treatment, especially for mild to moderate psoriasis, and include:
Corticosteroid creams and ointments: These are powerful anti-inflammatory agents that reduce redness, scaling, and itching. Available in various potencies, they should be used under medical supervision to avoid side effects like skin thinning.
Vitamin D analogs: Synthetic derivatives such as calcipotriene and calcitriol help regulate skin cell growth and promote skin normalization when used alone or with corticosteroids.
Coal tar products: Over-the-counter formulations that help decrease scaling and inflammation, though they may have a characteristic odor and can stain clothing.
Salicylic acid: A keratolytic agent that aids in softening and removing scales, facilitating better absorption of other topical medications.
Phototherapy and Systemic Treatments
For moderate to severe cases, healthcare providers may recommend phototherapy or systemic medications:
Ultraviolet B (UVB) light therapy: Exposing the skin to UVB light can reduce psoriasis plaques effectively.
Psoralen plus ultraviolet A (PUVA): A combination therapy involving a photosensitizing agent and UVA light
Oral or injectable systemic drugs: These include biologics, methotrexate, cyclosporine, and acitretin that modulate the immune response, targeting the root cause of the disease.
While systemic therapies are more potent, they also carry higher risks of side effects, requiring close medical supervision. Recent advancements in biologic treatments have revolutionized psoriasis management, offering targeted approaches that specifically inhibit immune pathways involved in disease progression.
Lifestyle Modifications and Complementary Approaches
In addition to medical treatments, patients are encouraged to adopt lifestyle habits that reduce flare-up risks. These include maintaining a healthy weight, managing stress through relaxation techniques, avoiding known triggers, and moisturizing regularly to prevent skin dryness. Some patients find relief through alternative therapies like acupuncture, dietary supplements, or herbal remedies, but these should always be discussed with healthcare providers to ensure safety and efficacy.
Conclusion: Managing Psoriasis Effectively
While psoriasis remains a lifelong condition with no current cure, advances in understanding its pathophysiology have significantly improved treatment options. Early diagnosis, personalized therapy plans, lifestyle adjustments, and ongoing medical care can help individuals manage symptoms effectively and enjoy a better quality of life. Whether through topical medications, phototherapy, or biologic agents, patients can find an approach that suits their needs and minimizes discomfort.