Comprehensive Guide to Psoriasis Treatments: Effectiveness and Side Effects
This detailed article provides an in-depth overview of effective psoriasis treatments, including biologics, oral drugs, and immunosuppressants, along with their potential side effects. It emphasizes personalized care and the importance of medical supervision to ensure safe and effective management of this chronic autoimmune skin condition, offering hope for improved quality of life for those affected.
Understanding Effective Psoriasis Treatments and Their Potential Side Effects
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune skin condition that affects millions worldwide. Characterized by red, thickened patches of skin covered with silvery-white scales, these plaques can cause significant discomfort, itching, and skin sensitivity. While there is currently no cure for psoriasis, a variety of treatments are available that aim to manage symptoms, reduce flare-ups, and improve patients’ quality of life. In this detailed guide, we explore the most effective treatment options for psoriasis, including biologics, oral medications, immunosuppressants, and supportive therapies, along with the potential side effects associated with each.
Understanding Psoriasis and Its Impact
Psoriasis arises from an overactive immune response that accelerates skin cell production, leading to the buildup of thickened plaques. The condition can manifest in various forms, including plaque psoriasis (the most common), guttate, pustular, and erythrodermic psoriasis. The severity varies from mild to debilitating, often affecting physical comfort, mental health, and social interactions. Managing psoriasis involves a personalized approach that considers disease severity, affected areas, comorbidities, and patient preference.
Biologic Therapies: Targeted Solutions for Psoriasis
Biologic therapies have revolutionized psoriasis treatment. These are advanced, targeted drugs designed to interfere with specific parts of the immune system responsible for inflammation and skin cell proliferation. They are typically used for moderate to severe cases that do not respond well to conventional treatments. Understanding how biologics work can help patients and healthcare providers make informed decisions.
Mechanism of Action: Biologics target particular immune components such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) or interleukins, which play vital roles in the inflammatory process. By inhibiting these molecules, biologics reduce inflammation, slow skin cell turnover, and alleviate symptom severity.
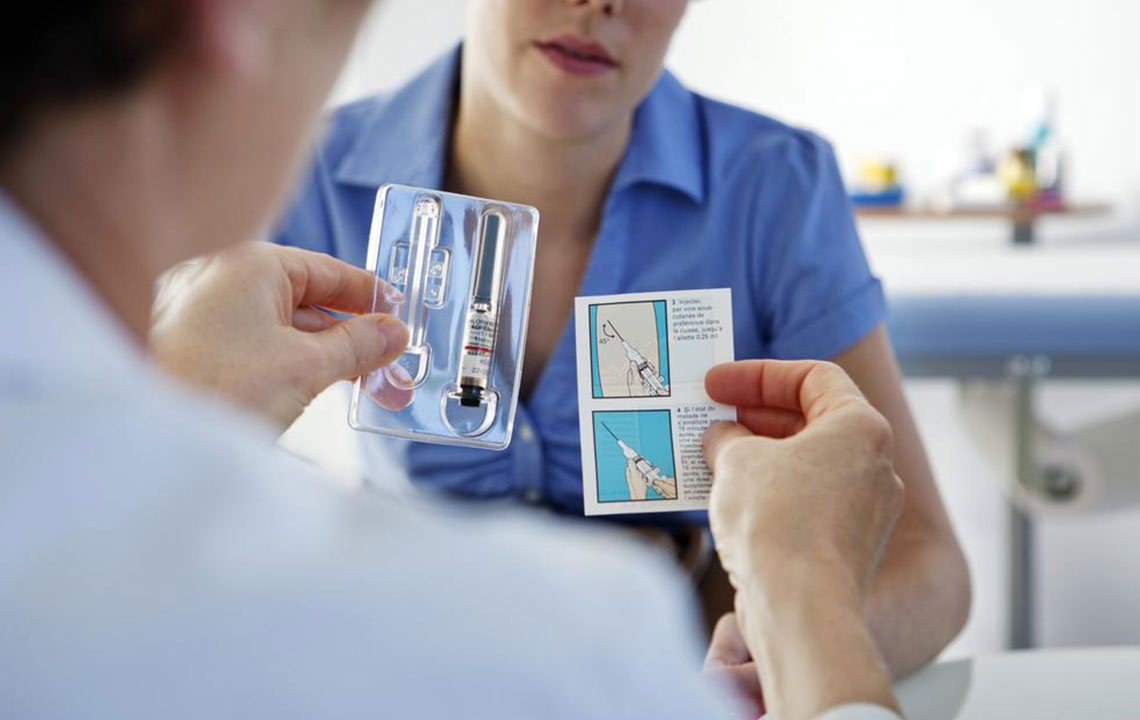
Common Biologic Medications: Examples include etanercept, infliximab, adalimumab, ustekinumab, golimumab, apremilast, secukinumab, and ixekizumab. These medications are primarily administered via injections, often on a weekly or bi-weekly schedule.
Indications and Usage: Biologics are particularly recommended for individuals with severe psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, or cases unresponsive to traditional treatments like topical agents or phototherapy.
Side Effects and Risks of Biologic Treatments
While biologics are highly effective in controlling psoriasis symptoms, they suppress parts of the immune system, potentially increasing the risk of infections and other adverse effects. Patients must be vigilant and undergo regular monitoring.
Potential Side Effects
Headaches and fatigue
Digestive disturbances such as diarrhea or nausea
Joint pain, swelling, or stiffness
Respiratory infections like sinusitis or bronchitis
Fungal infections, including oral thrush or athlete's foot
Serious infections or allergic reactions, requiring immediate medical attention
Oral Retinoids in Psoriasis Management
For severe, resistant psoriasis, oral retinoids like acitretin are often prescribed. These medications are structural derivatives of vitamin A and work by modulating skin cell growth and immune response.
Usage and Effectiveness: Primarily used in severe cases, especially when topical treatments and phototherapy are ineffective, or when psoriasis involves extensive body areas.
Common Side Effects: Dryness of skin, lips, and eyes, hair thinning, dry mouth, and mood alterations. Liver function tests are often necessary during treatment.
Serious Risks: Potential for severe side effects, including vision disturbances, persistent headaches, nausea, breathing difficulties, swelling, chest pain, fatigue, and jaundice (yellowing of skin and eyes). Due to these risks, retinoids require careful medical supervision.
Immunosuppressants: Cyclosporine
Cyclosporine is an immunosuppressant drug used for controlling severe psoriasis, especially in cases where other therapies have failed. It works by inhibiting the immune response, reducing inflammation and skin cell proliferation.
Application and Monitoring: Prescribed in short-term courses or intermittent use, with regular blood pressure and kidney function tests to detect adverse effects early.
Potential Side Effects: Headaches, hypertension, kidney problems, increased hair growth, susceptibility to infections, and fluid retention. Long-term use requires cautious monitoring due to these risks.
Methotrexate: An Antimetabolite for Severe Psoriasis
Methotrexate, marketed as Trexall, is a powerful systemic medication that slows down skin cell production and suppresses inflammation. It is often reserved for patients with extensive or refractory psoriasis.
Usage Guidelines: Administered weekly under strict medical supervision, with regular blood work to monitor liver function and blood cell counts.
Common Side Effects: Fatigue, nausea, hair loss, conjunctivitis, fever, and increased risk of infections. Liver toxicity is a significant concern, necessitating periodic liver function tests.
Precautions: Methotrexate is contraindicated in pregnant women and requires effective contraception during therapy due to teratogenic risks.
Summary and Future Outlook
Managing psoriasis effectively involves a comprehensive understanding of available treatments and their potential risks. Advances in biologics, immunosuppressants, and targeted therapies have significantly improved outcomes for many patients. However, all treatments carry some risk of side effects, highlighting the importance of personalized treatment plans and regular medical supervision. Ongoing research continues to develop new therapies aimed at improving efficacy while minimizing adverse effects, offering hope for more effective and safer psoriasis management in the future.