Comprehensive Approaches to Managing Psoriatic Arthritis: Combining Traditional and Advanced Treatments
Explore the comprehensive management strategies for psoriatic arthritis, including traditional medications, cutting-edge biologics, and supportive home remedies. Early diagnosis and personalized treatment plans are crucial to preventing joint damage and maintaining quality of life in this chronic autoimmune condition.
Exploring Innovative and Conventional Strategies for Psoriatic Arthritis Management
In-Depth Overview of Modern and Traditional Treatments for Psoriatic Arthritis
Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is a chronic autoimmune disease that causes inflammation in one or more joints, leading to pain, stiffness, swelling, and potential joint destruction if left untreated. This condition often develops in individuals with psoriasis—an inflammatory skin disorder characterized by scaly patches—though it's important to note that not everyone with psoriasis will develop PsA. Accurate diagnosis and early intervention are critical to managing symptoms effectively and preventing irreversible joint damage.
Psoriatic arthritis can affect any joint in the body, including the spine, where it manifests as spondylitis, leading to stiffness and reduced mobility. It can also cause tenderness and inflammation in tendons, resulting in heel pain, back pain, or other localized discomforts. Because of its variable presentation, early recognition of symptoms is vital for effective management.
Many individuals fear the prospect of permanent joint damage, but with early diagnosis and appropriate treatment, it is possible to control the disease and maintain quality of life. This article explores the wide range of treatment options available today—from traditional medications to cutting-edge biologics—and discusses emerging therapies that promise improved outcomes for patients.
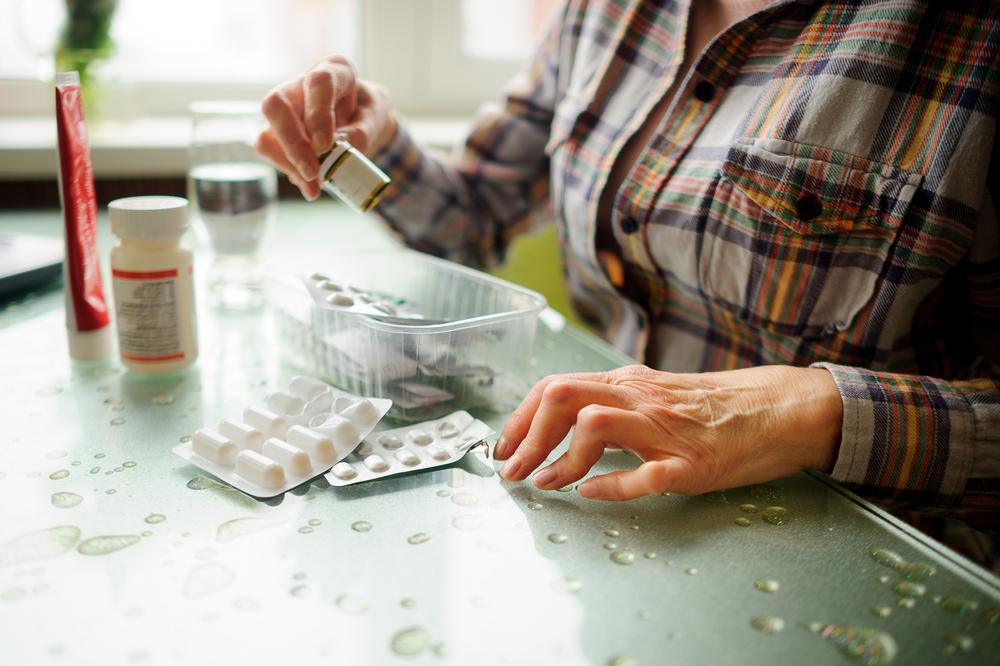
Current treatment modalities for psoriatic arthritis include a diverse spectrum of medications designed to alleviate symptoms, reduce inflammation, and mitigate joint damage. These treatments can be over-the-counter, prescription-only, or biologic agents administered under medical supervision. The goal is to tailor therapy to each patient's disease severity, symptoms, and overall health status.
Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): NSAIDs such as ibuprofen and naproxen are often the first line of defense. They help decrease pain, inflammation, and swelling, providing symptomatic relief. Both oral forms and topical gels or creams are used depending on the extent of skin involvement and joint pain.
Corticosteroids: These powerful anti-inflammatory agents are used for short-term flare management, either orally or via injections directly into affected joints. While effective, long-term use is limited due to potential side effects, including weight gain and osteoporosis.
Topical Agents: For skin symptoms alongside joint issues, topical treatments like corticosteroid creams, vitamin D analogs, or coal tar preparations may be prescribed to improve skin lesions and reduce associated inflammation.
DMARDs (Disease-Modifying Anti-Rheumatic Drugs): These medications, including methotrexate, sulfasalazine, and leflunomide, work by suppressing immune-mediated inflammation. They are central to preventing joint erosion and preserving function, especially in moderate to severe cases.
Biologic Therapies: Advanced biologic drugs target specific components of the immune system driving inflammation. Agents such as TNF-alpha inhibitors (e.g., etanercept, adalimumab), interleukin inhibitors (e.g., secukinumab, ixekizumab), and T-cell modulators have transformed disease management. Administered via injections or infusions, these drugs can significantly improve symptoms and prevent joint damage.
Phototherapy and Light-Based Treatments: Controlled exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light, mainly ultraviolet B (UVB), can reduce psoriasis severity and alleviate joint inflammation when used under dermatologist supervision.
Ongoing research continually introduces new options for psoriatic arthritis treatment. Recently approved medications, such as ixekizumab and tofacitinib, enhance therapeutic outcomes when combined with traditional DMARDs. However, because these drugs suppress immune functions, they carry an increased risk of infections. For instance, tuberculosis screening is mandatory before initiating biologic therapy to prevent serious complications.
In addition to pharmaceutical treatments, many patients find supportive home remedies beneficial in managing symptoms. Herbal supplements like turmeric, renowned for its potent anti-inflammatory properties, have gained popularity. Similarly, magnesium-rich Epsom salt baths may help soothe joint and skin discomfort. Nevertheless, it is crucial to consult healthcare professionals before starting any supplementary therapies to ensure safety and compatibility with existing treatments.
Understanding that psoriatic arthritis is a complex disease requiring comprehensive management strategies is vital. Combining traditional medications, emerging biologic therapies, lifestyle modifications, and supportive home remedies can lead to optimal disease control and enhance quality of life. Patients should work closely with their healthcare providers to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses their unique needs and health conditions. Early diagnosis paired with a proactive treatment approach remains key to preventing long-term joint damage and improving functional outcomes.





