The Comprehensive Guide to Using Probiotics for Managing Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
Explore the comprehensive role of probiotics in managing Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS). Learn how specific strains reduce symptoms like diarrhea, constipation, and bloating, and discover targeted strategies for different IBS types. This guide emphasizes natural approaches and personalized probiotic therapy to promote gut health and improve quality of life for IBS sufferers.
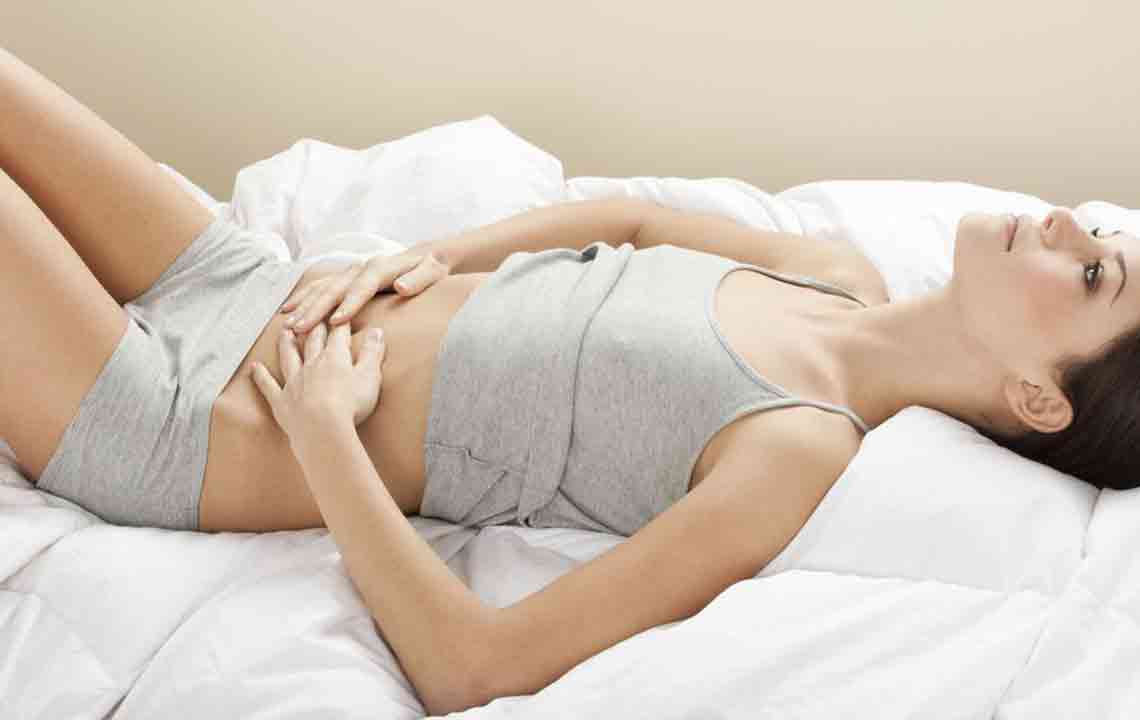

The Role of Probiotics in Easing Symptoms of Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) is a chronic gastrointestinal disorder that affects millions worldwide. Characterized by a variety of uncomfortable symptoms such as abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhea, and constipation. Unlike infections or structural abnormalities, IBS is considered a functional disorder, meaning changes in gut motility and sensitivity play significant roles. Although the precise cause of IBS remains elusive, recent scientific research highlights the potential benefits of probiotics as a natural and effective treatment option. Incorporating probiotic-rich foods and supplements into daily routines can significantly improve gut health, alleviate symptoms, and enhance overall quality of life.
Probiotics are live beneficial microorganisms that, when consumed in adequate amounts, confer health benefits to the host. They are especially valuable in restoring the natural balance of bacteria within the gut—an essential factor in maintaining digestive harmony. An imbalance of gut bacteria, known as dysbiosis, often correlates with IBS symptoms. Probiotics work by introducing friendly bacteria that outcompete harmful microbes, reducing inflammation, and supporting healthy digestion. This microbial balance can help ease common IBS symptoms like diarrhea, constipation, and abdominal bloating, contributing to a healthier gut environment.
Consuming probiotic-rich foods such as yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, and aged cheeses is an effective and natural way to boost beneficial bacteria levels. Additionally, probiotic supplements formulated with specific strains enable targeted treatment for diverse IBS symptoms. Several strains have demonstrated efficacy in clinical trials, making personalized probiotic therapy an emerging trend in managing this complex disorder.
How Probiotics Support IBS Symptom Relief
Stimulate growth of beneficial bacteria to suppress harmful microbes, leading to reduced gas, bloating, and discomfort
Assist in digesting food more efficiently, lessening IBS flare-ups caused by food intolerance or poor digestion
Enhance the health of the gut's nervous system, decreasing stress-related gastrointestinal symptoms
Targeted Probiotic Strategies for Different Types of IBS
Different subtypes of IBS require tailored probiotic approaches for effective symptom management.
IBS-D (Diarrhea-predominant): The yeast Saccharomyces boulardii has gained popularity for its ability to modulate gut flora and reduce the frequency and severity of diarrhea episodes. When used alongside long-term probiotic strains, it can help restore gut stability and prevent excessive fluid loss during flare-ups. Its gentle yet effective action makes it a preferred choice for many seeking relief from rapid transit issues.
IBS-C (Constipation-predominant): Bifidobacteria strains such as Bifidobacteria lactis BB-12, combined with dietary fiber supplements, have shown considerable promise in promoting regular bowel movements. These probiotics enhance gut motility, soften stools, and reduce discomfort associated with chronic constipation. Alongside fiber, they help create a balanced microbial environment conducive to healthy gut function.
Bloating and Gas Relief: A carefully administered seven-day course of Lactococcus lactis Rosell-52 has demonstrated effectiveness in aiding digestion of gaseous foods. Additional strains like Lactobacillus acidophilus Rosell-52 also contribute to reducing stress-related gastrointestinal symptoms, which often exacerbate bloating and cramping.
Managing Mixed IBS (IBS-M): Since this form alternates between diarrhea and constipation, a combination of probiotics such as Bifidobacteria strains, Saccharomyces boulardii, and fiber supplementation often provides the most comprehensive relief. Strains like Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium infantis have also been linked to reductions in abdominal cramps, bloating, and overall discomfort. It is essential to consult with healthcare professionals to tailor probiotic regimens based on individual symptoms and health conditions, ensuring a personalized approach to IBS management.
In conclusion, probiotics represent a promising avenue for managing IBS symptoms naturally. Beyond symptom relief, they help restore the microbial balance crucial for long-term gut health. Starting with dietary sources or specialized supplements, individuals can work with healthcare providers to develop an effective probiotic strategy tailored to their specific needs, leading to improved digestive comfort and quality of life.