Top Probiotic-Rich Foods to Enhance Your Digestive Wellness
Discover a comprehensive guide to probiotic-rich foods that can significantly improve your digestive health. From yogurt and kefir to kimchi and sauerkraut, learn how incorporating these foods into your diet supports a balanced gut microbiome, boosts immunity, and enhances overall wellness. This detailed article provides practical tips and nutritional insights to help you embrace a probiotic-friendly lifestyle for better health.

Top Probiotic-Rich Foods to Enhance Your Digestive Wellness
Probiotics are live beneficial microorganisms that play a crucial role in maintaining a healthy gut microbiome, supporting our immune system, and promoting efficient digestion. While many people assume that all bacteria are harmful, the truth is that our bodies host a complex ecosystem of both beneficial and harmful bacteria. Scientific studies reveal that over 70% of our immune cells are located within the gut, underscoring its vital importance to overall health. To sustain a balanced and healthy gut environment, incorporating probiotic-rich foods into your diet is essential. These foods not only promote gut health but also bolster immune defenses, improve nutrient absorption, and enhance overall wellness.
Integrating a variety of probiotic foods into your daily meals can profoundly impact your health. Some of the most effective and delicious probiotic-rich foods include yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, and other fermented products. Regular consumption of these foods supports digestion, strengthens immune function, and contributes to long-term health benefits. Let’s explore in detail the most beneficial probiotic foods and the reasons why they should find a regular place on your plate.
Essential probiotic foods for digestive health include:
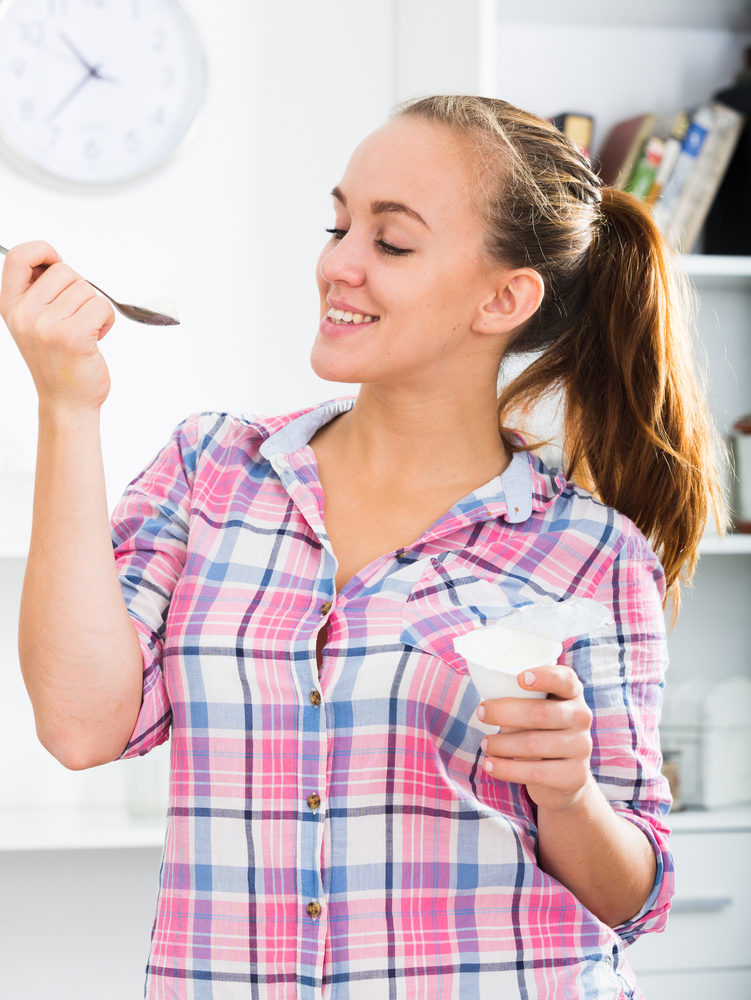
Yogurt: A popular probiotic source made through bacterial fermentation of milk, yogurt is rich in live cultures like Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium. These bacteria are known to help restore gut flora balance, especially for individuals with lactose intolerance, as some yogurts contain enzymes that aid lactose digestion. Choosing plain, unsweetened yogurt ensures maximum probiotic benefit without added sugars.
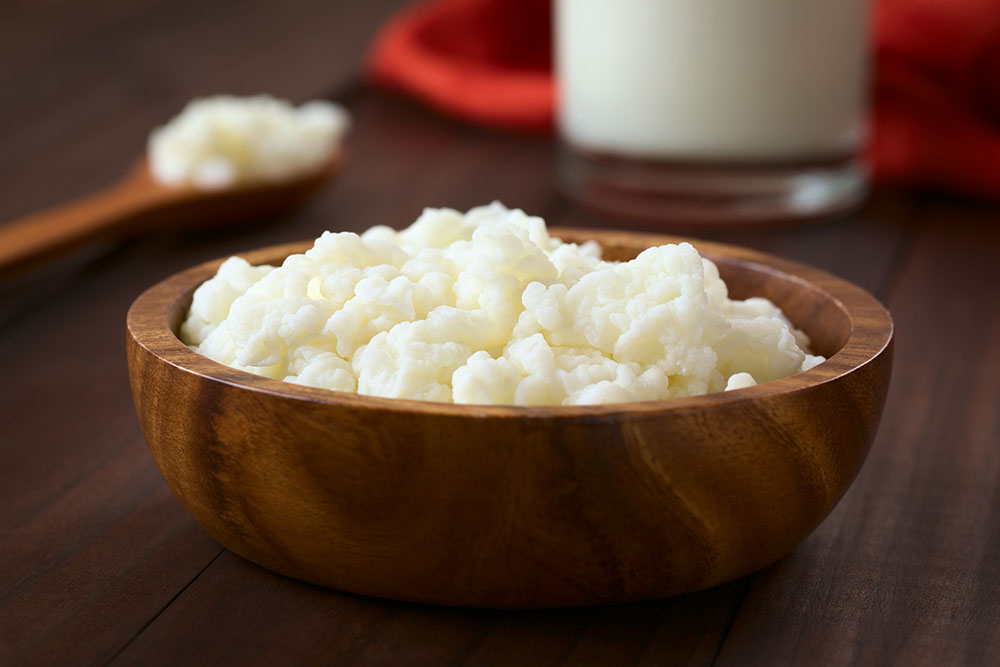
Kefir: This fermented milk drink resembles thin yogurt and is loaded with diverse probiotic strains. Rich in calcium and vitamins, kefir is generally easier to digest than regular milk, making it suitable for people with lactose sensitivities. Its potent probiotic profile supports gut health, enhances immune responses, and aids in the maintenance of healthy gut flora.
Sauerkraut: Fermented cabbage that undergoes lactic acid fermentation, sauerkraut is a potent source of probiotics, vitamins C and K, minerals, and antioxidants. To maximize probiotic content, opt for unpasteurized, refrigerated sauerkraut, as the pasteurization process destroys live cultures. It can be added to salads, sandwiches, and side dishes.
Tempeh: A fermented soybean product originating from Indonesia, tempeh is an excellent source of plant-based protein and vitamin B12 — nutrients often lacking in vegetarian diets. Its fermentation process promotes beneficial bacteria, supporting gut health and providing a versatile meat substitute in various recipes.
Kimchi: A spicy Korean fermented vegetable dish, kimchi typically contains cabbage, radishes, and seasonings. Rich in probiotics, vitamins, and minerals, kimchi is known for its flavorful profile and health benefits. Incorporating kimchi into meals can enhance digestion and boost immune health.
Miso: A Japanese fermented soybean paste, miso adds savory umami flavor to soups and dressings. It contains probiotics and is associated with antioxidant properties that may protect cells from damage, improve gut flora, and potentially lower risks of certain diseases.
Kombucha: A tangy, fizzy fermented tea brewed from green or black tea, kombucha is a popular probiotic beverage. Rich in beneficial bacteria and organic acids, kombucha supports digestion and immune function when consumed in moderation.
Resistant potatoes: These contain resistant starch, a type of carbohydrate that resists digestion in the small intestine. Resistant starch acts as a prebiotic, feeding beneficial gut bacteria, and may improve insulin sensitivity and aid in weight management.
Raw garlic: Known for its antimicrobial properties, raw garlic promotes gut health by fostering the growth of beneficial bacteria. Adding raw garlic to salads, spreads, or dressings is an easy way to enhance gut flora.
Cheeses: Certain types of cheese, such as cheddar, mozzarella, and Gouda, contain live probiotics. They can support not only gut health but also contribute to heart and bone health through their nutrient profiles.
To optimize your gut microbiome, consider integrating these probiotic foods into your daily diet. Enjoy options like creamy yogurt topped with fresh berries and nuts, hearty miso soups, refreshing probiotic drinks, or flavorful side dishes featuring sauerkraut and kimchi. Always read labels to verify the presence of live cultures or consider taking high-quality probiotic supplements — but remember, whole foods are often the most natural and effective way to support your gut health.