Comprehensive Guide to Probiotic Treatments for IBS Symptom Relief
This comprehensive guide explores the vital role of probiotics in managing IBS symptoms. It details how specific probiotic strains and fermented foods can restore gut health, reduce inflammation, and alleviate discomfort. Learn about effective probiotic strategies, top strains, and dietary tips to improve your digestive wellbeing naturally. Perfect for individuals seeking non-invasive treatment options, this article emphasizes the importance of personalized care and patience in achieving long-term symptom relief.
In-Depth Strategies Using Probiotics to Manage Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) remains one of the most common gastrointestinal disorders worldwide, impacting millions of individuals with symptoms such as persistent abdominal pain, irregular bowel habits—which may include diarrhea, constipation, or alternating patterns—bloating, and cramps. Managing IBS effectively often requires a multifaceted approach, and among the various treatments available, probiotic supplementation has garnered significant attention for its potential benefits in alleviating symptoms and promoting gut health.
Probiotics, which comprise live beneficial bacteria, play a vital role in supporting gut microbiota balance. These microorganisms enhance overall digestive health by encouraging the growth of healthy bacteria while suppressing pathogenic organisms. Proper selection of probiotic supplements tailored to individual needs is essential for maximizing therapeutic effects.
Understanding the Role of Probiotics in Gut Health Probiotics are friendly bacteria naturally present in the human gut. They assist in digestion, bolster immune defenses, and aid in the elimination of harmful bacteria, thereby maintaining a healthy and balanced intestinal environment. When the gut microbiota is disrupted, which often occurs in IBS, introducing beneficial bacteria through supplements or fermented foods can help restore equilibrium.
These resilient microorganisms fortify the intestinal lining, serving as a barrier against pathogenic invasion and reducing inflammation. Incorporating probiotics into your daily routine can be a game-changer in managing IBS symptoms effectively, especially when combined with dietary modifications and lifestyle changes.
How Probiotics Contribute to IBS Symptom Relief Probiotics help mitigate IBS symptoms by fostering a healthy microbial environment within the gut. They work through multiple mechanisms, providing comprehensive relief and supporting long-term gut health:
Combatting Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth (SIBO), a common factor in IBS pathology
Reducing levels of harmful bacteria that contribute to inflammation and discomfort
Enhancing intestinal motility and regularity
Strengthening the intestinal lining to prevent leaky gut syndrome
Boosting immune response to fight off infections and reduce inflammation
Lowering intestinal permeability, which is associated with many IBS-related symptoms
Reducing visceral hypersensitivity that causes pain and discomfort
Supporting the integrity of the bowel wall to minimize bloating and cramps
Maintaining a balanced gut microbiota for optimal digestion and overall health
Popular Probiotic Strains for Managing IBS Research has identified several probiotic strains with promising therapeutic potential for IBS. These strains, when chosen appropriately, can significantly improve gut function and alleviate symptoms:
Popular probiotic strains include:
Lactobacillus strains: Known for supporting bowel health, these strains are generally dairy-free and gluten-free, making them suitable for individuals with sensitivities.
Bifidobacterium strains: Often effective in reducing pain, bloating, urgency, and other digestive complaints associated with IBS.
Saccharomyces Boulardii: A beneficial probiotic yeast that reduces inflammation and enhances recovery in IBS sufferers.
Multi-strain formulations: Combining various probiotic strains can create a synergistic effect, improving the diversity of gut flora and providing more comprehensive symptom relief.
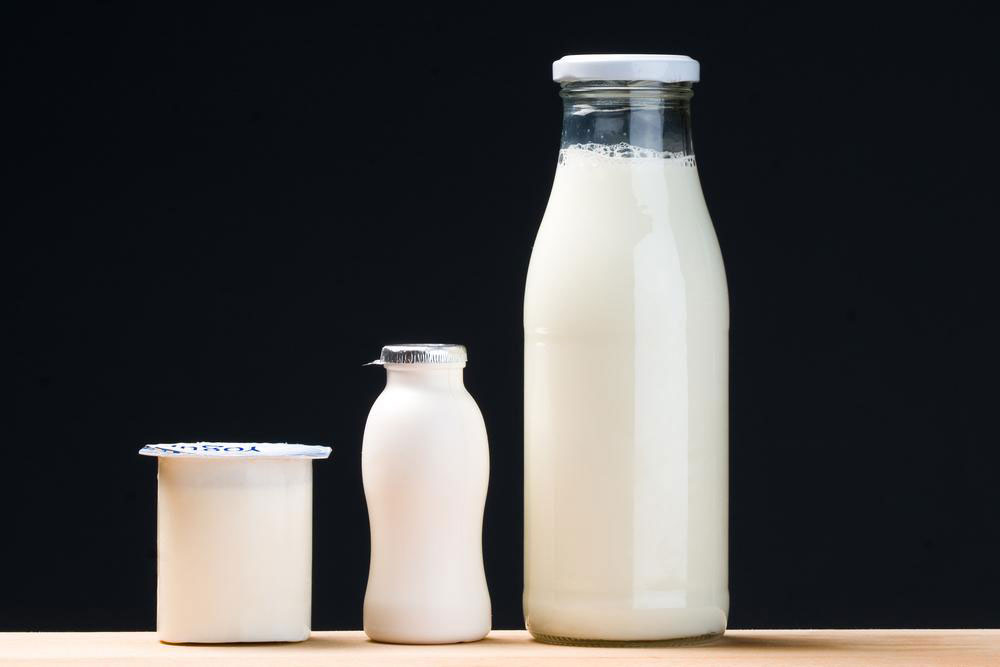
Fermented Foods as Natural Probiotics: Integrating fermented foods such as yogurt, sauerkraut, kimchi, kefir, and other probiotic-rich products into your diet offers a natural and tasty way to support your gut health. These foods contain beneficial bacteria that can complement probiotic supplements. For best results, consume these foods along with water or non-hot dishes to preserve their probiotic bacteria. It’s advisable to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement or dietary regimen, particularly if you have underlying health issues or are pregnant. Remember, patience is key; probiotic benefits often take at least four weeks of consistent use to become noticeable, and longer-term adherence is recommended for sustained relief.





