Comprehensive Guide to Managing and Lowering Blood Glucose Naturally
This comprehensive guide offers practical strategies for managing and lowering blood glucose levels naturally. It covers symptom recognition, dietary modifications, lifestyle adjustments, and home remedies to help prevent diabetes and related health complications. By adopting these evidence-based tips, individuals can maintain healthy blood sugar levels, improve insulin sensitivity, and boost overall well-being through sustainable habits and proactive health management.
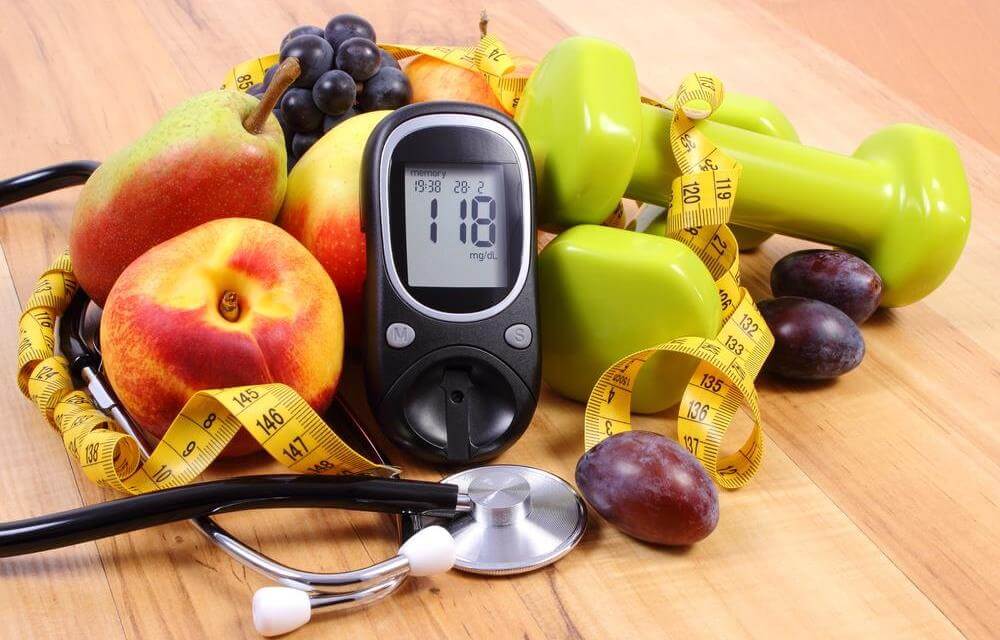

Comprehensive Guide to Managing and Lowering Blood Glucose Naturally
Effective strategies for maintaining healthy blood sugar levels
Maintaining optimal blood glucose levels is crucial for overall health and long-term wellness. When the body encounters difficulty in effectively transporting glucose from the bloodstream into cells, blood sugar levels rise abnormally, leading to a variety of health concerns such as insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Persistent hyperglycemia can cause damage to vital organs, nerves, and blood vessels if not properly managed. While emergency interventions are necessary in cases of severely high blood sugar, adopting consistent lifestyle changes can significantly help prevent and control elevated blood sugar levels over time.
People with prediabetes or those at risk of developing diabetes often seek natural and sustainable methods to regulate their blood sugar. Making informed choices in diet, physical activity, and daily habits can influence blood glucose readings positively. Several home remedies and dietary adjustments can effectively contribute to lowering blood glucose levels, positioning individuals to take proactive steps toward their health management. Recognizing early signs of high blood sugar and understanding how to address them is vital for preventing complications and fostering overall well-being.
Here's an in-depth overview of blood sugar management strategies.
Common symptoms indicating elevated blood sugar
Excessive thirst that feels unquenchable
Frequent urination, especially during the day
Persistent dry mouth and dehydration
Unusual fatigue or sluggishness
Irritability, mood swings, and general discomfort
Foods and dietary choices to limit for better blood sugar control
Refined grains such as white bread, white rice, and processed cereals
Fruits high in sugar, sweet desserts, and candies
Full-fat dairy products and sugary snacks
Refined pasta and baked goods with added sugars
Limit consumption of starchy vegetables like potatoes and corn
While no specific foods can instantly lower blood sugar, selecting low glycemic index (GI) foods helps prevent spikes and maintains steady glucose levels. Prioritizing whole, unprocessed foods is essential.
Dietary strategies to effectively lower blood glucose levels
Decrease carbohydrate intake and shift focus to low-GI foods rich in soluble fiber like oats, beans, and lentils.
Control portion sizes through careful measurement to avoid overeating and unnecessary glucose surges.
Incorporate more protein-rich snacks (nuts, seeds, eggs, lean meats) to stabilize blood sugar between meals.
Natural methods for lowering blood sugar without medication
Consult healthcare professionals about natural approaches suitable for mildly elevated blood sugar levels.
Engage in regular physical activity—such as brisk walking, swimming, cycling, or dance—to enhance insulin sensitivity and glucose uptake.
Stay properly hydrated to assist in flushing excess sugar through urine.
Practice stress-reducing techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises to prevent stress-induced hormonal spikes.
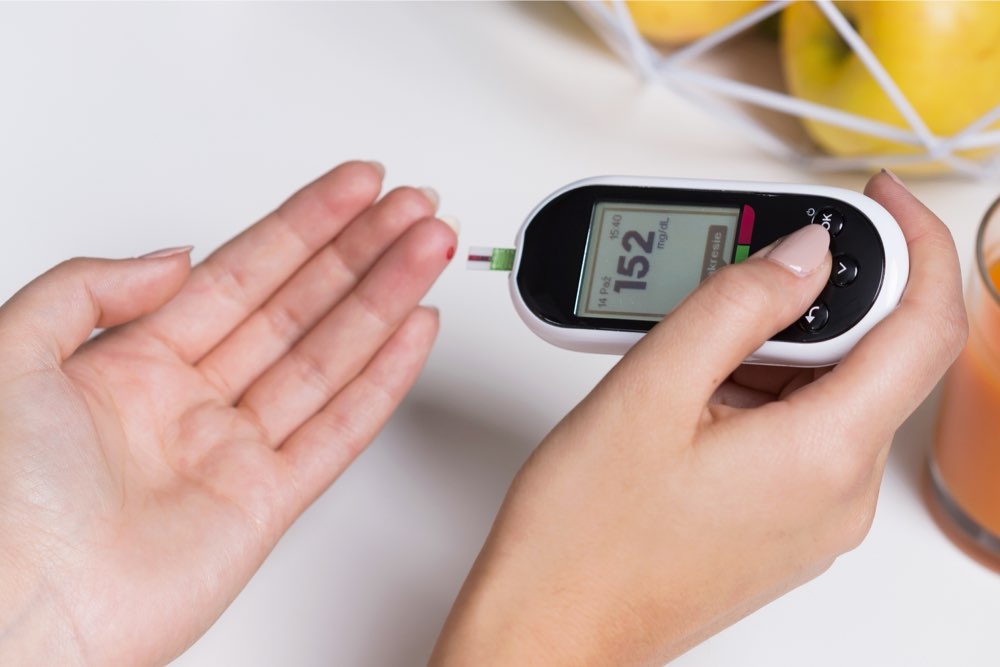
Consistent blood sugar monitoring helps tailor lifestyle adjustments and identify patterns or triggers.
Foods that support balanced blood glucose levels
Healthy fats such as avocados, olive oil, and nuts improve insulin response.
Omega-3 fatty acids from fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines help regulate blood sugar and improve insulin sensitivity.
Other beneficial foods include sour cherries, apple cider vinegar, garlic, leafy greens, dark chocolate (in moderation), chia seeds, and whole grains like oats and quinoa.
After adopting these comprehensive strategies, individuals can better manage their blood glucose levels, reduce health risks, and enhance their overall quality of life. Building habits around proper diet, regular movement, stress management, and health monitoring forms the foundation of effective blood sugar control. Remember, consistent care and personalized guidance from healthcare providers are essential for achieving long-term success in blood glucose management.