Comprehensive Guide to Effectively Managing Fever Symptoms for Better Health
This comprehensive guide offers effective strategies for managing fever symptoms, emphasizing when to seek medical care, proper temperature measurement, and home care tips. Suitable for caregivers and individuals, it aims to improve comfort and promote recovery, especially in children and vulnerable populations. Understanding fever management is key to preventing complications and supporting overall health during illness.

Comprehensive Strategies for Managing Fever Symptoms to Promote Recovery and Comfort
Fever, medically known as pyrexia, is a common response of the body to various infections and illnesses. It is characterized by an elevation in core body temperature beyond the normal range, typically as a natural defense mechanism against pathogens. While often perceived as a sign of illness, fever can sometimes be beneficial, helping the immune system to fight off infections more effectively. However, managing fever symptoms appropriately is crucial to ensuring comfort and preventing potential complications, especially in vulnerable populations like children and the elderly.
Understanding When Treatment Is Necessary for a Fever
The primary objective in managing a fever is to alleviate discomfort and support the body's natural healing process. Many cases of mild fever do not require pharmacological treatment, as they tend to resolve on their own as the immune system combats the underlying cause. Nonetheless, recognizing when intervention is necessary can prevent complications and ease symptoms. Generally, a fever is considered significant when body temperature reaches 100.4°F (38°C) or higher, measured through ear, rectal, or temporal artery thermometers.
Normal Body Temperature and Variations
The average normal body temperature is approximately 98.6°F (37°C), but it can vary between 97°F (36.1°C) and 99°F (37.2°C) depending on factors like physical activity, time of day, and individual differences. For example, older adults tend to have lower baseline temperatures, which means their fever thresholds might differ slightly. Understanding these nuances helps in accurately assessing whether a temperature reading indicates a fever.
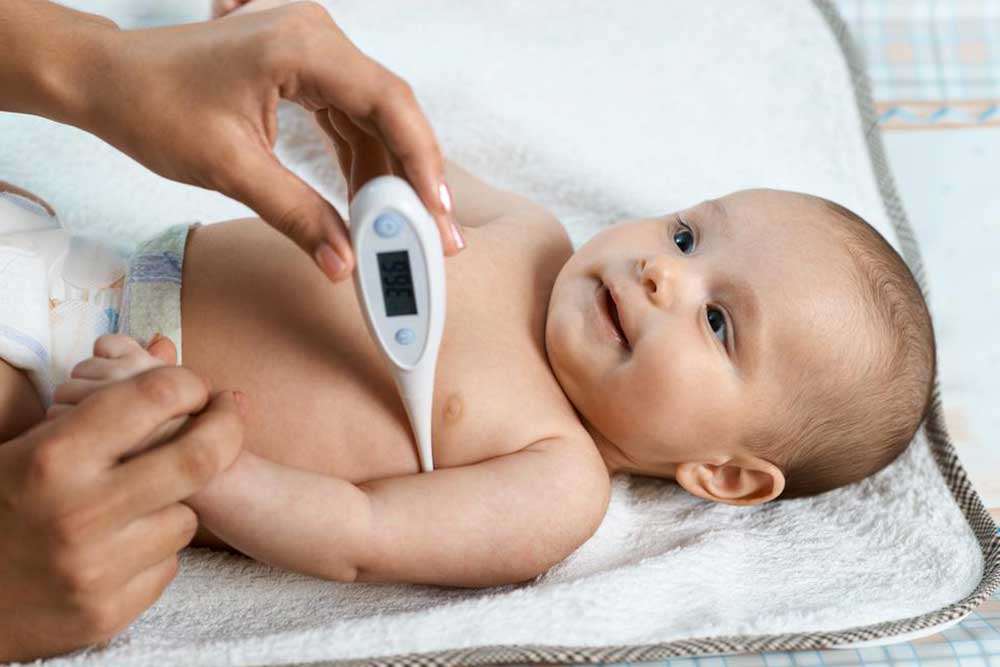
Effective Fever Care for Children
Children often exhibit high temperatures without appearing very ill, but parental reassurance and proper care are essential. Comforting measures include ensuring adequate hydration through fluids like water, oral rehydration solutions, or electrolyte drinks. Dressing children in lightweight, breathable clothing, and using a light blanket if chills are present can help regulate body temperature. Over-the-counter medications such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen at appropriate doses can provide relief from discomfort and reduce fever, but it's critical to adhere strictly to dosing guidelines. For infants under six weeks, medical consultation is vital before administering any medication, as their immune systems are more vulnerable to complications.
Fever Management Strategies for Adults
For adult patients, fever management depends on specific symptoms, temperature severity, and overall health status. A fever exceeding 103°F (39.4°C) may leave individuals feeling extremely fatigued, weak, or disoriented. Rest, hydration, and over-the-counter medications like ibuprofen or acetaminophen are the mainstays of targeted treatment to alleviate symptoms and bring comfort. Adults should monitor their temperature regularly and seek medical attention if symptoms worsen or if the fever persists beyond a few days.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Prompt medical evaluation is crucial in certain situations. Infants younger than three months with any fever should be assessed by healthcare professionals immediately. For children aged 3-6 months, a fever over 102°F (38.9°C) accompanied by irritability, lethargy, or persistent discomfort warrants medical advice. In children aged 2 to 17 years, a fever exceeding 102°F (38.9°C) that persists for more than three days or is associated with other concerning symptoms should prompt consultation. Emergency care becomes imperative if the fever accompanies severe symptoms such as seizures, stiff neck, persistent vomiting, confusion, difficulty breathing, or if the fever remains high despite medication.
Monitoring and Measuring Body Temperature Accurately
To properly assess and manage a fever, accurate measurement is essential. Digital thermometers—whether oral, ear (tympanic), or temporal artery types—are highly effective and user-friendly. Proper technique includes following the manufacturer’s instructions, cleaning the device after each use, and taking multiple readings to confirm consistency. Comparing these measurements against a fever chart helps determine the severity of the condition and guides subsequent steps in care.
Frequency of Temperature Checks During Illness
Maintaining regular temperature monitoring provides valuable insight into illness progression and recovery. Especially in children or vulnerable individuals, checking the temperature hourly during acute phases can help identify worsening symptoms early. Advanced digital thermometers can provide fast and gentle readings without disturbing sleep, offering comfort and precision. Increased frequency of measurement helps both caregivers and patients make informed decisions about seeking further care or continuing home management.
In conclusion, fever is a common physiological response that, when carefully managed, can facilitate recovery. Recognizing symptoms, understanding when to treat or seek professional help, and maintaining accurate temperature tracking are critical steps toward effective fever management. Proper care not only alleviates discomfort but also ensures early detection of potential complications, ultimately supporting health and well-being during illness recovery.