Comprehensive Guide to Managing Fever Naturally and with Medical Support
Learn comprehensive strategies to manage fever naturally and medically. This guide covers home remedies, hydration tips, clothing advice, and when to seek professional healthcare. Proper management of fever is essential for quick recovery and preventing complications, whether using simple home treatments or medical interventions. Prioritize hydration, rest, and timely medical attention for severe or persistent fevers to safeguard your health effectively.

Comprehensive Strategies for Effectively Managing Fever Through Natural and Medical Approaches
Maintaining a normal body temperature is crucial for overall health, with an average of approximately 98.4°F (37°C). When body temperature rises above this baseline, it indicates a fever, which is a common response of the immune system to infections such as bacteria, viruses, or other pathogens. Understanding when and how to manage a fever is vital for effective recovery and to prevent complications.
A fever often presents with symptoms like sore throat, nasal congestion, persistent cough, muscle aches, fatigue, and nausea. The severity and accompanying symptoms can vary depending on the underlying cause and the individual’s health condition.
In cases where the fever exceeds 104°F (40°C), immediate medical attention is necessary. Such high temperatures can lead to dangerous complications like seizures, dehydration, and organ stress. Recognizing symptoms early and responding appropriately can make a significant difference in outcomes.
While mild fevers can often be managed at home, persistent or extreme temperatures require professional medical evaluation. It is essential to balance effective relief with caution to avoid excessive medication intake, which can lead to adverse effects.
Natural Remedies for Fever Relief
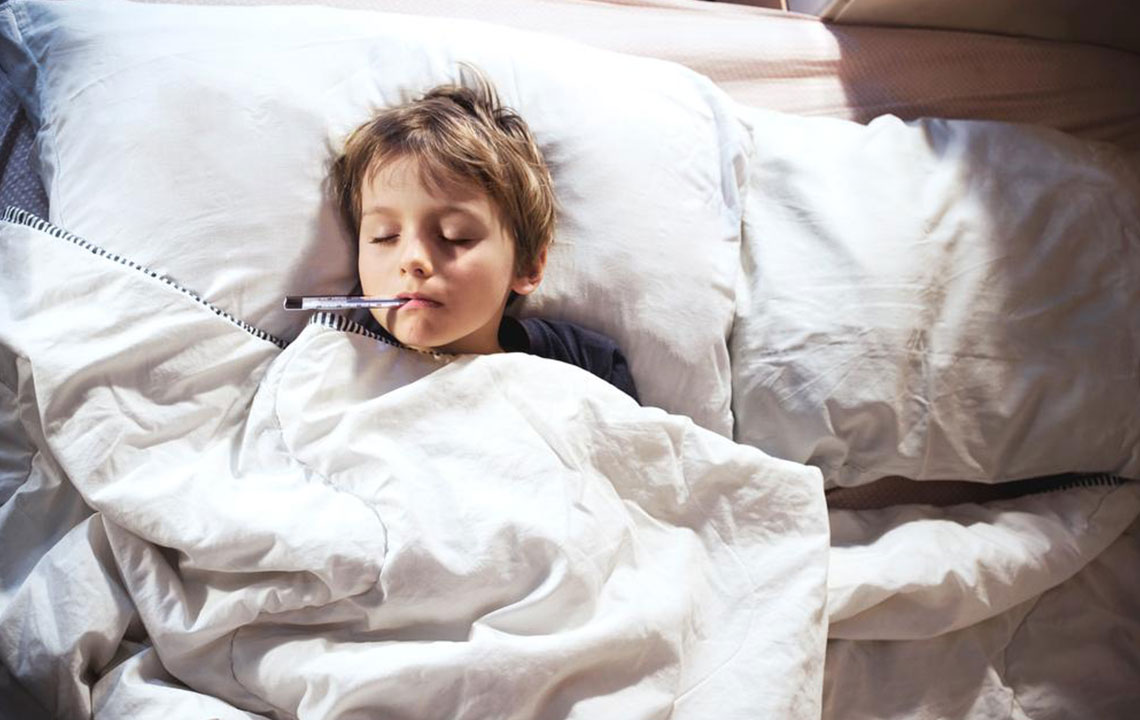
Monitoring your temperature accurately is the first step—note that a reading above 100.4°F (38°C) signifies a fever. During fever episodes, prioritize rest as it aids your immune system in fighting off infections. Resting in a comfortable, quiet environment enhances recovery.
Hydration is paramount. Consume plenty of fluids such as water, herbal teas, fresh fruit juices, and broth-based soups. Hydration helps prevent dehydration and assists in temperature regulation. Cold ice chips and chilled beverages can soothe the throat and provide some cooling effect.
Keeping cool is vital. Dress in lightweight, breathable clothing, and use light blankets if chills are present. Avoid overdressing or overheating, as this can worsen the fever. Conversely, if experiencing chills, adding a layer can help you feel more comfortable.
Warm baths with lukewarm water can be soothing. Avoid cold showers or icy baths, which might cause shivering and increase core temperature. Maintain a comfortable, cool environment to facilitate natural cooling of the body.
For sore throats or throat discomfort associated with fever, warm beverages such as herbal teas, warm water with honey, or broths can provide relief. These drinks soothe inflamed tissues and assist with hydration.
Eat small, nutritious meals that are easy to digest. Soups, stews, fruits, and light grains support energy levels without taxing the digestive system. Proper nutrition aids your body in fighting infections and recovering faster.
Gently moving or stretching your limbs can prevent stiffness and promote circulation. Avoid vigorous activity that could exacerbate fatigue. Listen to your body and rest as needed.
Regularly check your temperature and be attentive to any worsening symptoms like dizziness, weakness, or difficulty breathing. Seek immediate medical care if symptoms become severe or if the fever persists beyond a few days.
Applying a cool, damp cloth or sponge to the forehead, neck, or wrists can help lower body temperature temporarily. Use cool water and dry the skin afterward to prevent discomfort.
Medical Treatments for Fever
When home remedies are insufficient, over-the-counter (OTC) medications can effectively reduce fever and discomfort. However, it is important to adhere strictly to dosing instructions and avoid overuse or mixing multiple medications without medical advice.
Common OTC options include acetaminophen (paracetamol), ibuprofen, and naproxen—each with specific indications and safety considerations.
Acetaminophen
This medication is suitable for children and adults without liver issues. It can be taken every 4 to 6 hours, with a maximum daily dose. For those who cannot swallow pills, suppositories provide an alternative.
Ibuprofen
Particularly effective for reducing fever and alleviating pain. Recommended for children over six months and adults, with dosages based on weight or age. Typically, 200-400 mg every 6-8 hours is effective, but always follow medical guidance.
Naproxen
Effective for short-term fever reduction in adults, generally taking 220 mg (two tablets) every 12 hours. Not recommended for children due to safety concerns.
Additionally, aspirin should be avoided in children and teenagers with fever because of the risk of Reye’s syndrome—a rare but serious condition.
In cases of persistent or very high fever, or when OTC medications do not bring relief, consult a healthcare professional promptly. Prescription medications, including antibiotics (if bacterial infection is diagnosed), or injections might be necessary for thorough treatment.
Remember, maintaining proper hydration and nutrition, alongside medication, supports your body's immune response and speeds recovery.
Understanding the appropriate ways to manage fever—whether through home remedies or medical intervention—is crucial for effective health management. Recognizing warning signs and seeking timely medical care can prevent complications and promote quicker recovery.