Comprehensive Guide to Managing Fever in Young Children: Symptoms, Prevention, and Care Strategies
This comprehensive article offers in-depth insights into managing fever in young children, covering causes, accurate measurement techniques, preventive strategies, and when to seek medical help. It emphasizes the importance of understanding normal body temperatures, maintaining proper hygiene, and keeping detailed records of fever episodes. Parents and caregivers will learn effective ways to monitor and care for children with fever, ensuring their health and comfort while minimizing unnecessary panic or medical visits. A valuable resource for fostering healthier, resilient children from infancy through childhood.

Comprehensive Guide to Managing Fever in Young Children: Symptoms, Prevention, and Care Strategies
Understanding Fever in Children: An Essential Overview
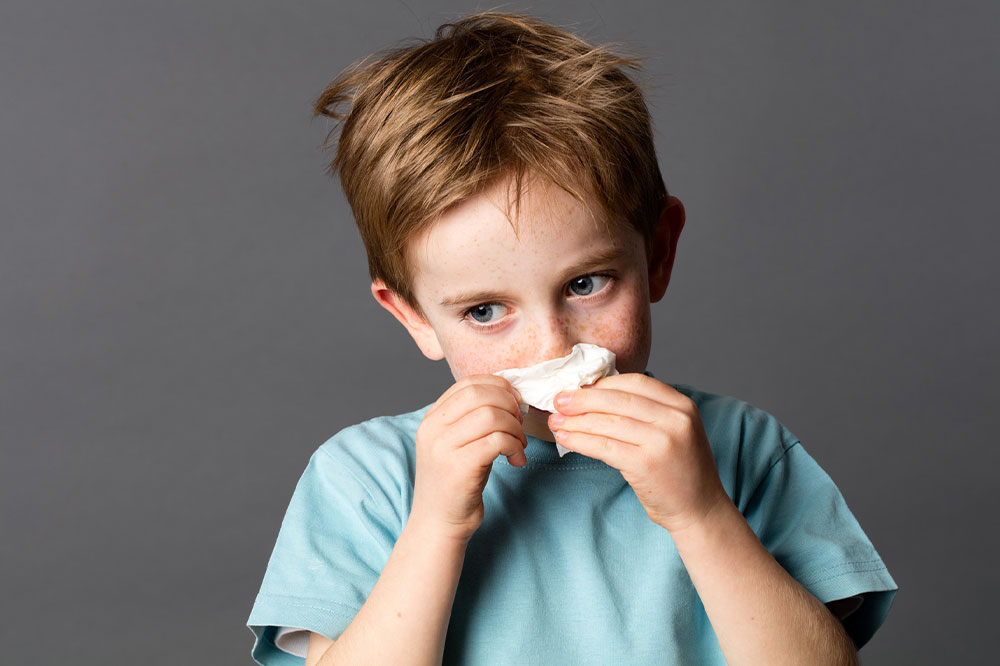
Fever is one of the most common health conditions affecting young children worldwide. It manifests as an elevation in body temperature beyond the normal range, typically caused by the immune system responding to various infections. While most fevers are benign and resolve without complications, understanding how to monitor, manage, and prevent fever is crucial for parents and caregivers. Proper knowledge ensures prompt response to serious symptoms and helps maintain the child's comfort and health.
Fever usually indicates that the body is fighting off an illness, often caused by viruses, bacteria, or other triggers like heat exposure and allergic reactions. Especially in infants and toddlers, frequent or persistent fever may signal underlying health issues that require medical attention. Implementing preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk of recurrent illnesses. These include practicing good hygiene, ensuring timely vaccinations, and maintaining a clean environment. Additionally, providing children with safe foods and nutritious water supports a robust immune response.
Fever in children may originate from various causes, including bacterial infections, viral illnesses, heat exposure, allergic reactions, or rarer conditions like juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Certain medications can also induce fever as a side effect. Typically, fever lasts for a few days and gradually subsides as the immune system overcomes the infection. Nonetheless, parents should be vigilant and seek medical care if they notice symptoms such as rash, seizures, difficulty breathing, unresponsiveness, or if the fever occurs in a child under two months of age—these are signs that warrant immediate medical attention.
Normal Body Temperature and Accurate Measurement
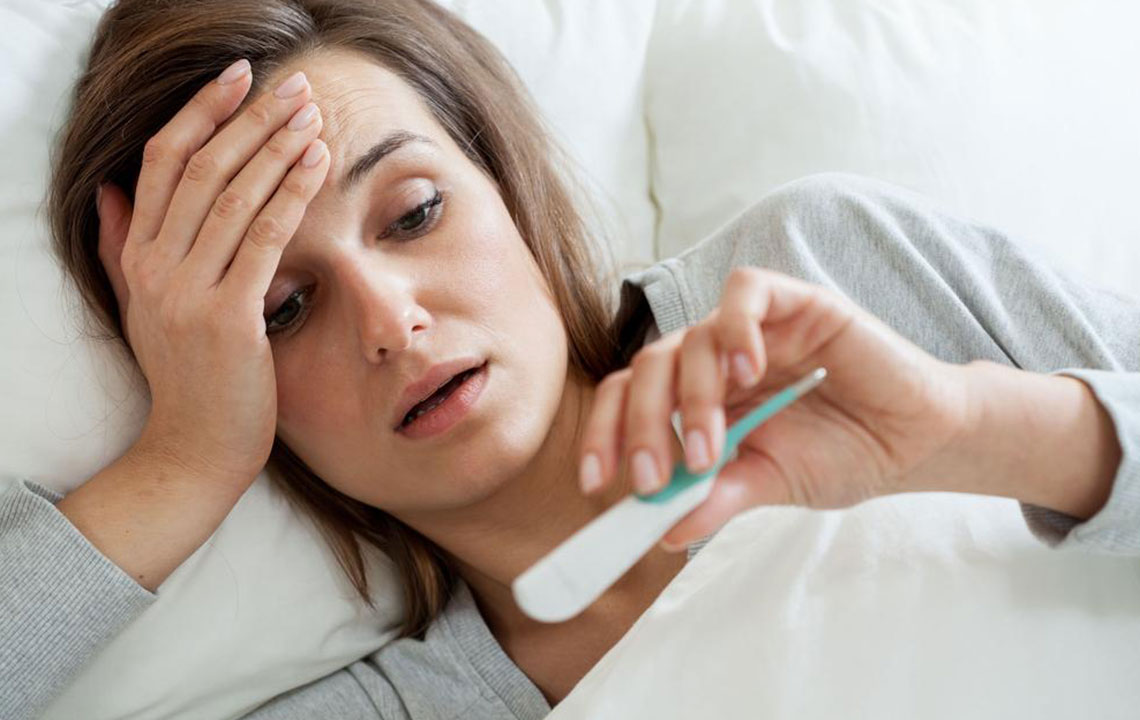
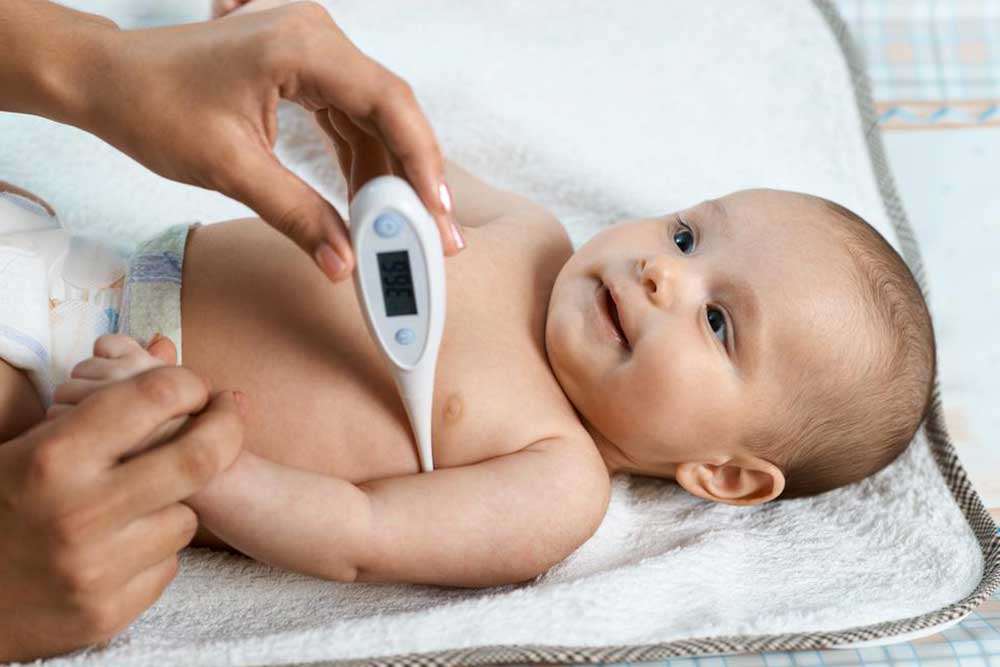
Understanding normal body temperature ranges in children is fundamental for assessing fever. On average, a child's normal temperature is approximately 36.4°C (97.5°F). A temperature reading of 38°C (100.4°F) or higher generally indicates a fever. It is important to recognize that body temperature can vary with age, activity level, and measurement site. Infants tend to have slightly higher normal temperatures around 37°C (98.6°F). Accurate measurement devices such as digital thermometers should be used, with methods including rectal, oral, ear, or underarm readings. Proper sterilization of the thermometer after each use is essential to prevent infections.
Monitoring Fever with a Temperature Log
Maintaining a detailed temperature chart is an effective way to monitor the progression of a child's fever. Recording the time and temperature measurements helps healthcare providers make accurate diagnoses and assess the severity of the illness. When tracking fever, note any additional symptoms like rash, vomiting, lethargy, or irritability. This documentation can aid in determining whether the fever needs further medical evaluation or if it is resolving independently.
Proactive Prevention Strategies for Fever
Preventing recurring fever involves comprehensive strategies aimed at bolstering the child’s immune defenses and reducing exposure to infectious agents. Parents should focus on maintaining a hygienic environment—regular handwashing, sanitizing surfaces, and avoiding contact with sick individuals. Ensuring children receive all recommended vaccinations is critical in preventing vaccine-preventable diseases. Encouraging physical activity promotes overall health and immune resilience. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, proteins, and whole grains provides necessary nutrients that support immune function. Safe water intake and proper sanitation also play roles in minimizing infection risks, ultimately reducing the incidence of fever and illness in young children.