Complete Guide to Identifying and Understanding Sarcoidosis Symptoms
Sarcoidosis is a long-term inflammatory condition affecting multiple organs, primarily the lungs. This comprehensive guide helps identify symptoms like cough, skin lesions, swollen lymph nodes, and eye discomfort, emphasizing the importance of early diagnosis and effective management. Learn about risk factors and treatment options to improve quality of life for affected individuals.

Complete Guide to Identifying and Understanding Sarcoidosis Symptoms
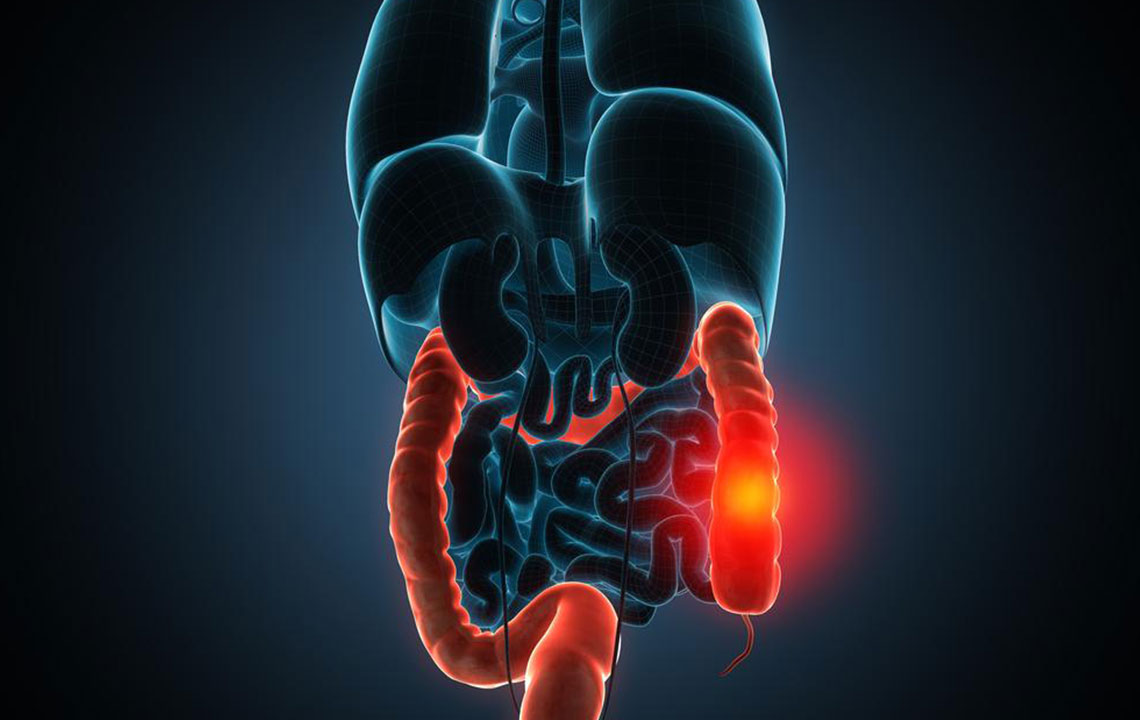
Sarcoidosis is a complex, long-lasting inflammatory disease that affects multiple organs in the body by forming granulomas—small clusters of inflammatory cells. Although it can involve any organ, it predominantly targets the lungs, with approximately 90% of cases involving pulmonary tissues. The disease arises when the immune system overreacts to environmental triggers such as bacteria, viruses, dust particles, or certain chemicals, resulting in persistent inflammation that leads to granuloma formation. This immune response is not infectious, which means sarcoidosis is not contagious, but its symptoms can develop gradually over several years, often making diagnosis challenging.
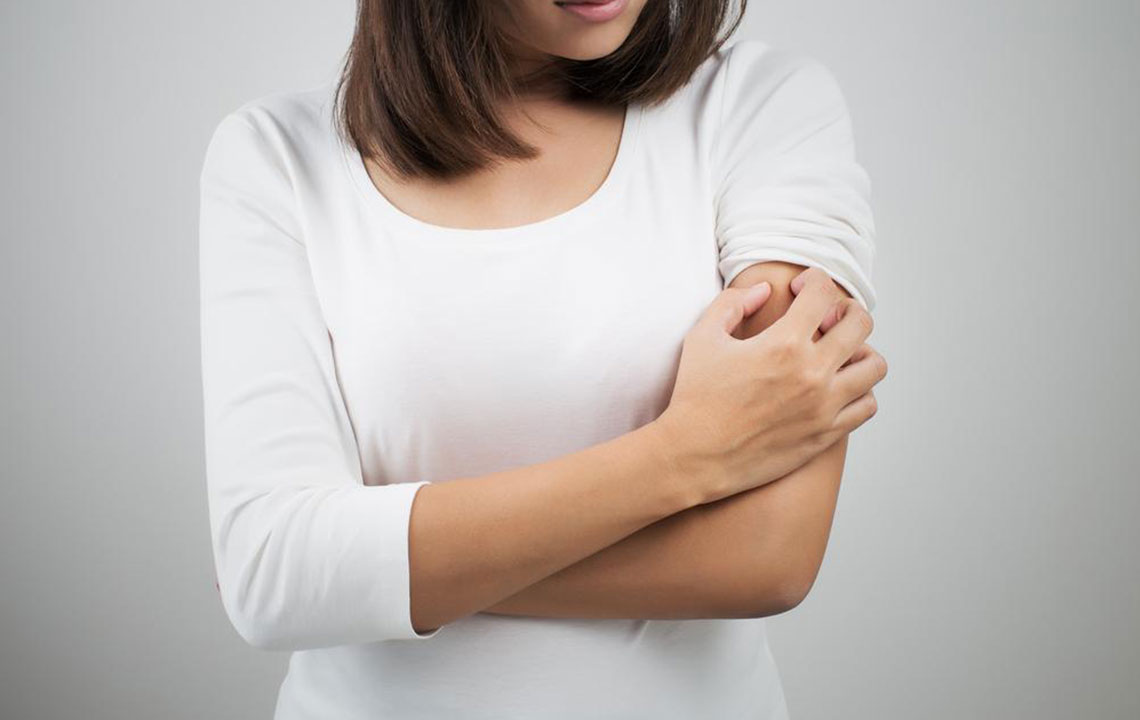
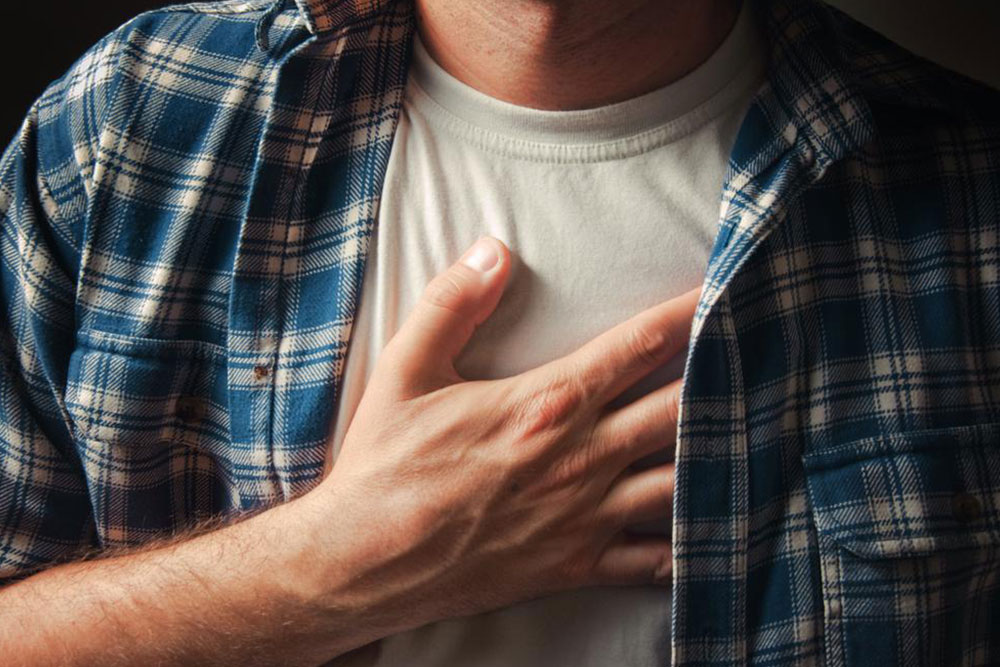
The presentation of sarcoidosis varies greatly depending on which organs are affected. Commonly, it manifests in the lungs with symptoms like a persistent dry cough, wheezing, shortness of breath, and chest discomfort. Patients may also notice enlarged lymph nodes, especially in the neck, chest, armpits, chin, and groin areas, which often become tender or swollen. Skin manifestations are frequent and can include painless bumps, ulcers, or discolored patches, typically around the face, especially near the nose and eyes, as well as on the limbs. The eyes are also commonly involved, with symptoms such as redness, sensitivity to light, dry eyes, blurred vision, and general discomfort.
Early detection and proper management are crucial in controlling the disease and preventing long-term complications. Diagnosis often involves a combination of medical history review, physical examinations, imaging tests such as chest X-rays or CT scans, and tissue biopsies to confirm granuloma presence. Treatment strategies typically aim to reduce inflammation and suppress immune activity, often involving corticosteroids or other immunosuppressive medications. Patients are strongly advised to avoid smoking and exposure to environmental pollutants, chemicals, and allergens, which can exacerbate symptoms or trigger disease progression. Regular follow-up with healthcare professionals ensures optimal disease management and a better quality of life for affected individuals.
Understanding the symptoms of sarcoidosis is vital for early diagnosis and effective treatment. Since the disease can impact multiple organs with diverse presentations, awareness of common signs such as fatigue, unexplained weight loss, respiratory issues, skin lesions, and eye problems helps patients seek medical attention promptly. Recognizing the disease early allows healthcare providers to initiate appropriate therapies, reduce the risk of permanent organ damage, and improve overall outcomes. Lifestyle modifications, including avoiding smoking and environmental toxins, also play a critical role in managing sarcoidosis effectively.