Comprehensive Guide to Maintaining Healthy Blood Glucose Levels for Better Wellbeing
This comprehensive guide offers essential insights into maintaining healthy blood glucose levels for overall wellness. Learn about normal ranges, monitoring methods, and lifestyle strategies including diet, exercise, and medication to keep blood sugar stable. Whether diabetic or not, managing blood glucose is vital for preventing serious health issues and enhancing quality of life. Discover tips on effective monitoring, understanding your body’s signals, and making informed choices for better health through consistent habits.

Effective Strategies for Managing Your Blood Sugar Levels
Achieve and maintain balanced blood glucose through proven methods
Maintaining optimal blood sugar levels is a critical aspect of overall health that applies to everyone, regardless of whether they have diabetes or not. Stabilizing blood glucose not only helps prevent chronic diseases but also enhances your daily vitality and longevity. When blood sugar levels fluctuate excessively, it can lead to severe health risks, including cardiovascular issues, nerve damage, kidney disease, and vision problems. Recognizing the importance of blood sugar regulation is the first step toward better health. Fortunately, a combination of healthy lifestyle habits, proper monitoring, and medical guidance can enable you to keep your blood glucose within the ideal range effectively.
Understanding what constitutes normal blood glucose levels
Knowing the normal ranges for blood sugar is fundamental for anyone interested in managing their health better. Blood glucose levels naturally fluctuate throughout the day, being lowest in the early morning after fasting, rising after meals due to digestion and carbohydrate absorption, and stabilizing again during fasting periods. Typically, healthy fasting (pre-meal) blood sugar levels should be between 4 and 7 mmol/l. Post-meal levels, usually measured about 90 minutes after eating, should be below 10 mmol/l to be considered within safe limits. Bedtime blood sugar levels tend to hover around 8 mmol/l, and maintaining this stability is essential for overall health. Recognizing these ranges helps you gauge your health status and provides guidance in your management plan.
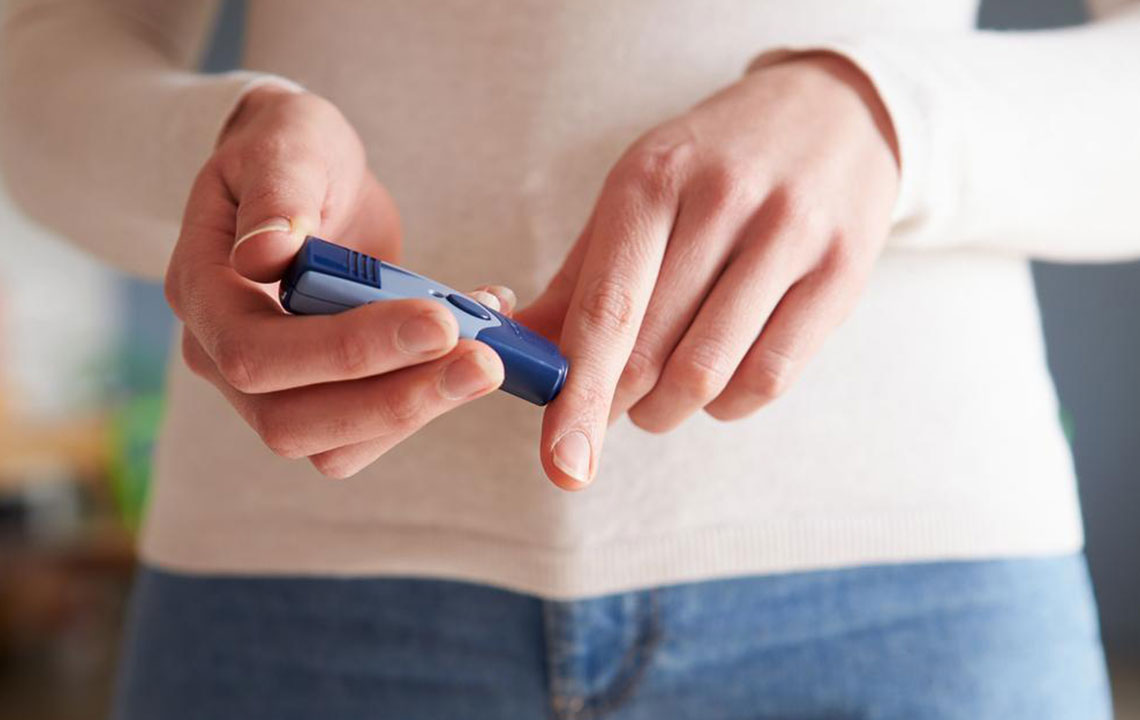
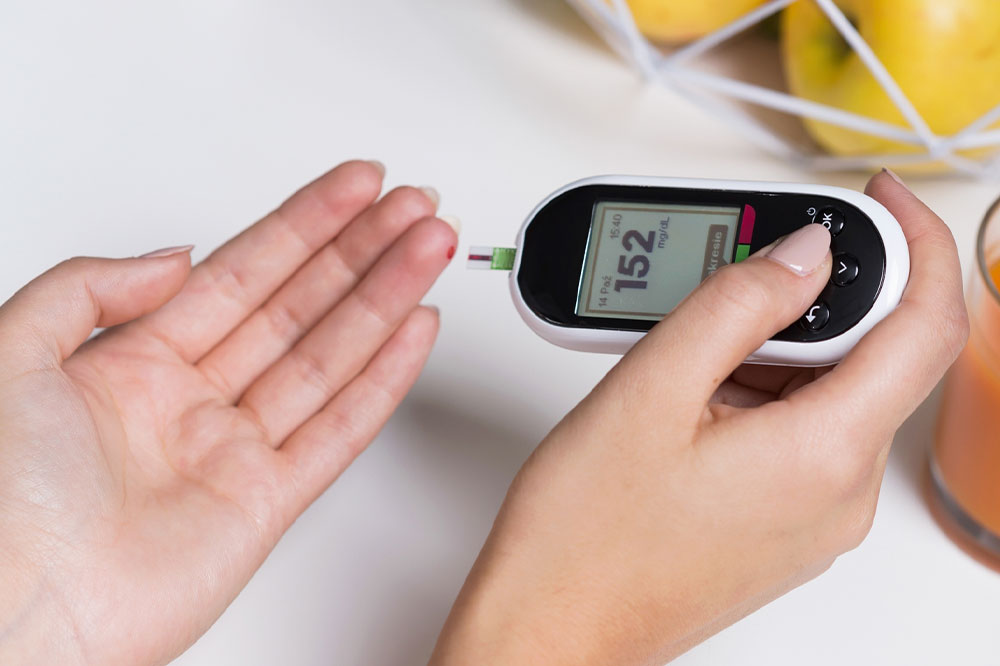
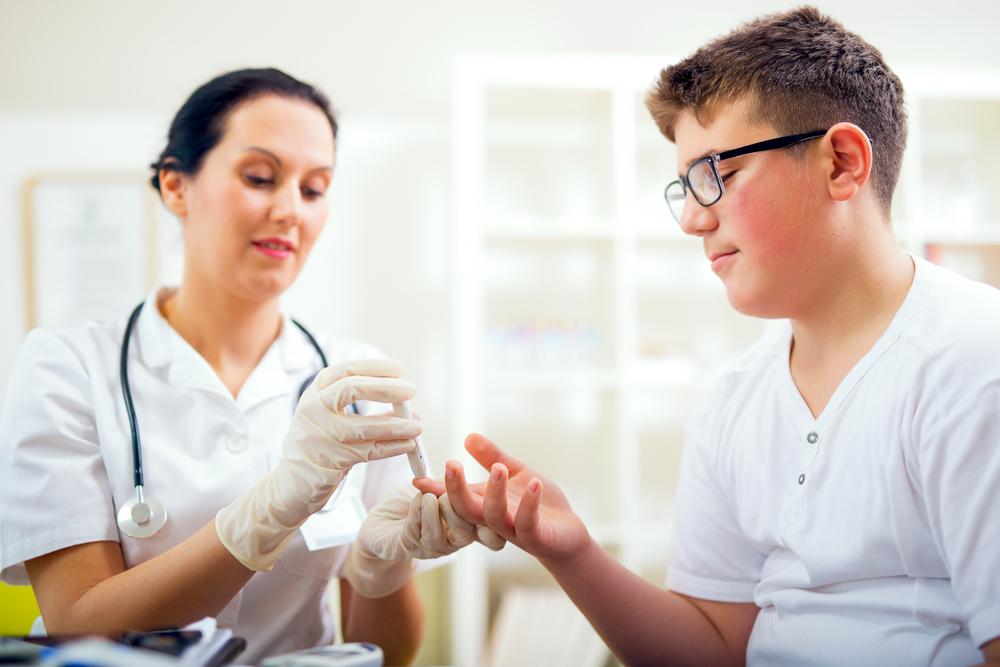
For effective self-monitoring, home glucose testing kits are invaluable tools. These kits are user-friendly and designed for regular use, allowing individuals to measure their blood sugar levels conveniently. They typically involve a small finger prick to obtain a blood sample, which is then analyzed by a portable device using test strips. Results are displayed within seconds, giving immediate insight into your glucose levels. Leading brands such as OneTouch, Accu-Chek, FreeStyle, TrueMetrix, Contour Next, TrueTrack, and GE 100 are widely trusted and recommended for accurate and easy monitoring. Regular testing helps identify patterns, triggers, and trends, enabling better management and early detection of potential issues.
Why maintaining proper blood glucose levels is vital for your health
Consistently keeping blood sugar within normal parameters is especially important for individuals with diabetes to prevent complications like vascular damage, neuropathy, kidney failure, and vision loss. High blood glucose over time damages small blood vessels, leading to serious health problems. However, even people without diabetes benefit from stable blood sugar levels, as fluctuations can contribute to an increased risk of metabolic syndrome, heart disease, and other chronic conditions. Stable blood glucose levels promote optimal organ function, reduce inflammation, and support the immune system, ultimately enhancing your quality of life and longevity. It’s also associated with improved energy levels, better mood, and overall well-being.
Strategies to maintain stability in blood glucose levels
Because blood sugar instability can have profound health implications, adopting habits that promote glycemic stability should be a priority for everyone. Diet plays a crucial role; consuming balanced meals rich in fiber, healthy fats, and lean proteins helps slow carbohydrate absorption and flatten blood sugar spikes. For diabetics, following the guidance of healthcare professionals on suitable foods and portion sizes is essential. Non-diabetics should minimize intake of refined sugars and processed foods that can cause rapid sugar surges. Regular physical activity is equally important, as exercise increases insulin sensitivity and helps muscles absorb glucose more effectively.
When lifestyle changes are insufficient to control blood glucose, medications might be prescribed by healthcare providers. These drugs assist in maintaining levels but are not standalone cures; they should be combined with diet, exercise, and routine monitoring. Always consult with healthcare professionals before starting or adjusting medications. Long-term health management involves disciplined routines, stress management, adequate sleep, and avoiding harmful habits such as smoking or excessive alcohol consumption. By integrating these strategies, you can effectively prevent complications and promote a healthier, more energetic life.