Comprehensive Guide to Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema): Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Management Strategies
This comprehensive article explores atopic dermatitis (eczema), detailing its causes, symptoms, severity, and management tips. It emphasizes the importance of early detection, accurate diagnosis, and personalized treatment plans. The guide provides practical advice on skincare, trigger avoidance, and medical treatments, helping sufferers reduce flare-ups and improve quality of life. With insightful information and visual tools, this resource is valuable for anyone looking to understand and effectively manage chronic eczema for healthier skin.

Comprehensive Guide to Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema): Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Management Strategies
Atopic dermatitis, more commonly known as eczema, is a persistent and often relapsing skin condition that affects millions worldwide. Characterized by inflammation, dryness, redness, and flaky patches of skin, eczema can significantly impact quality of life, especially when it leads to frequent flare-ups and discomfort. Understanding the intricacies of this condition, including its causes, symptoms, and management techniques, is essential for those affected and their caregivers. This extensive guide delves into the essential aspects of atopic dermatitis, offering practical tips and insights to help manage symptoms effectively and prevent flare-ups.
What is Atopic Dermatitis? An Overview
Atopic dermatitis is a chronic inflammatory skin disorder that tends to develop in early childhood but can also affect adults at any stage of life. It is part of a group of allergic conditions often linked to a family history of eczema, asthma, or hay fever. The condition manifests as itchy, red, and sometimes swollen patches on the skin, which can become dry, cracked, and prone to infection if left untreated. Eczema is a complex condition influenced by genetic, environmental, and immune factors, making it multifaceted in its presentation and management.
Understanding the detailed mechanisms behind eczema reveals how it affects the skin barrier, disrupts normal immune responses, and reacts to various triggers. This comprehensive understanding is key to developing effective prevention and treatment strategies tailored to individual needs.
Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms of Eczema
Early Signs: Although eczema can develop at any age, it predominantly affects children under five years old. Initial signs often appear as dry, sensitive skin that becomes itchy and irritated. These symptoms may be subtle initially but tend to intensify over time.
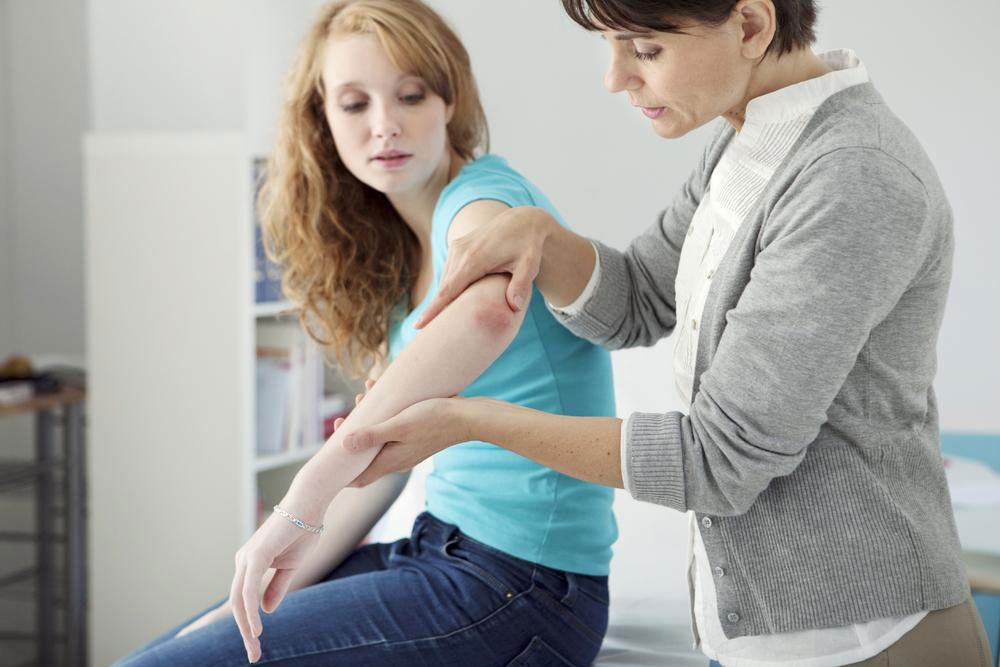
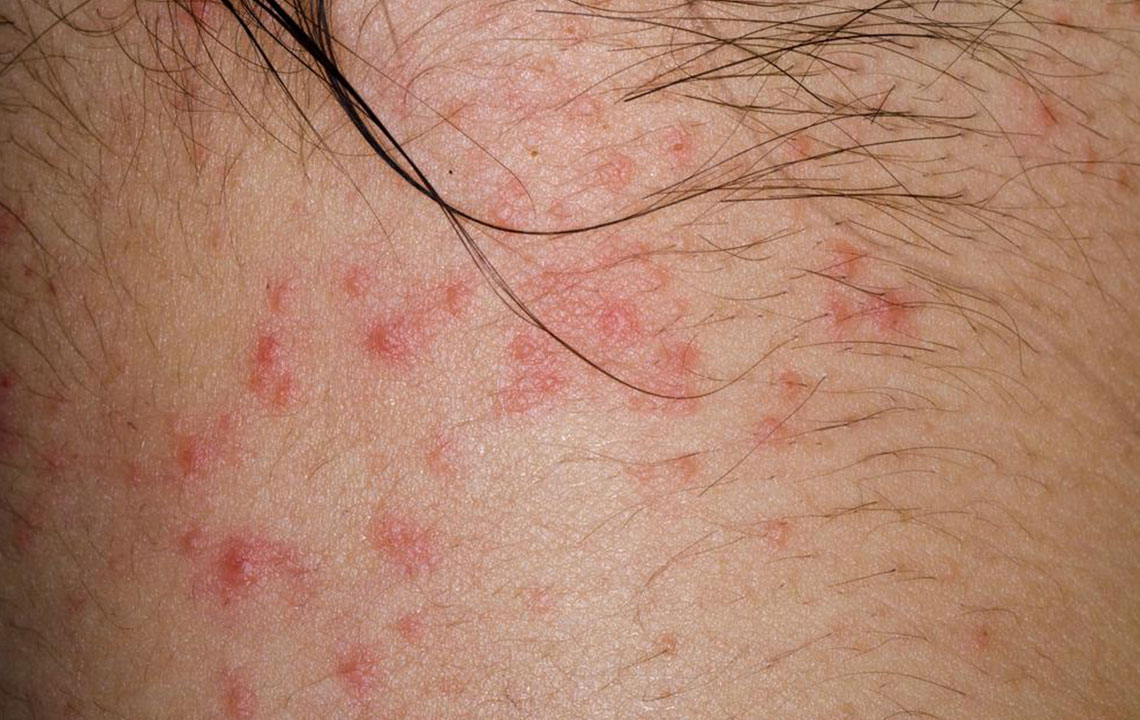
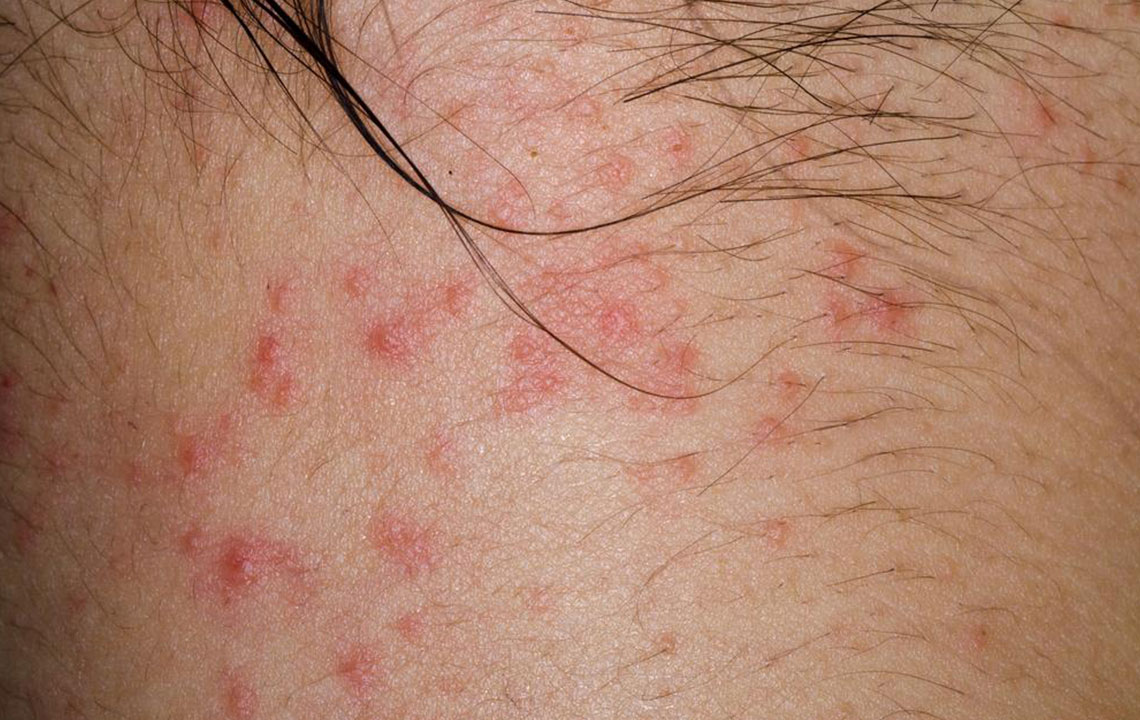
Classic Visible Signs: The hallmark of eczema includes red, inflamed patches that itch intensely. These patches are often located on the hands, feet, elbows, knees, neck, and facial areas. The skin may appear dry, scaly, or flaky, with some areas developing thickened or leathery skin due to chronic scratching.
Persistent Symptoms: Over time, eczema patches can crack, bleed, or develop crusts. In cases where scratching becomes severe, the skin may become raw and more susceptible to bacterial, viral, or fungal infections. These secondary infections can further complicate management and prolong symptoms.
Understanding these signs helps in early detection and prompt management, reducing the risk of complications and improving long-term skin health.
The Severity and Potential Complications of Eczema
Chronic and Severe Nature: Eczema is often a lifelong condition characterized by episodic flare-ups and periods of remission. Its severity varies among individuals, ranging from mild irritation to extensive skin involvement.
Impact on Quality of Life: Severe eczema can cause significant discomfort, leading to sleep disturbances, emotional distress, and social stigma. The persistent itchiness can be debilitating, affecting daily activities and mental health.
Associated Allergic Conditions: Children with eczema frequently develop other allergic conditions like asthma, hay fever, or allergic rhinitis. This allergic diathesis underscores the importance of a comprehensive approach to managing eczema and related ailments.
Possible Complications: Long-standing or untreated eczema can lead to further skin damage, including infections, which may require antibiotics or antifungal treatments. Chronic scratching can cause thickening of the skin (lichenification), which is more resistant to treatment.
Impact on Sleep and Wellbeing: Nighttime itching is a common problem that significantly disrupts sleep, leading to fatigue and decreased quality of life.
Effective Prevention and Management Tactics
Staying Hydrated and Moisturizing: Regular moisturizing is the cornerstone of eczema management. Applying emollients like creams, ointments, lotions, or petroleum jelly at least twice daily helps restore and maintain the skin barrier, reducing dryness and flare-ups.
Avoiding Triggers: Identifying and minimizing exposure to triggers such as dust mites, pet dander, pollen, harsh soaps, detergents, and certain fabrics can significantly reduce flare-ups. Keeping living environments clean and allergen-free is crucial.
Bathing Habits and Skin Care: Short, lukewarm baths or showers followed by gentle patting and immediate application of moisturizer help keep the skin hydrated. Occasionally, bleach baths under medical supervision can help reduce bacterial colonization and inflammation.
Choosing the Right Products: Utilizing mild, fragrance-free soaps and skincare products minimizes irritation. Avoiding harsh chemicals and opting for gentle cleansers are vital steps.
Medication and Medical Advice: Topical corticosteroids and calcineurin inhibitors can control inflammation during flare-ups. In severe cases, a healthcare provider may recommend systemic treatments like antihistamines or immunosuppressants.
Implementing Home Remedies: Home care strategies, such as applying cool compresses, using oat-based lotions, or taking herbal supplements (under medical guidance), may provide additional relief.
Understanding the Nature of Eczema and Its Management
Beyond Visible Symptoms: The outer appearance may not reveal the full extent of internal skin damage. Chronic eczema can cause the skin to become increasingly fragile, dry, and prone to irritation even when symptoms seem controlled.
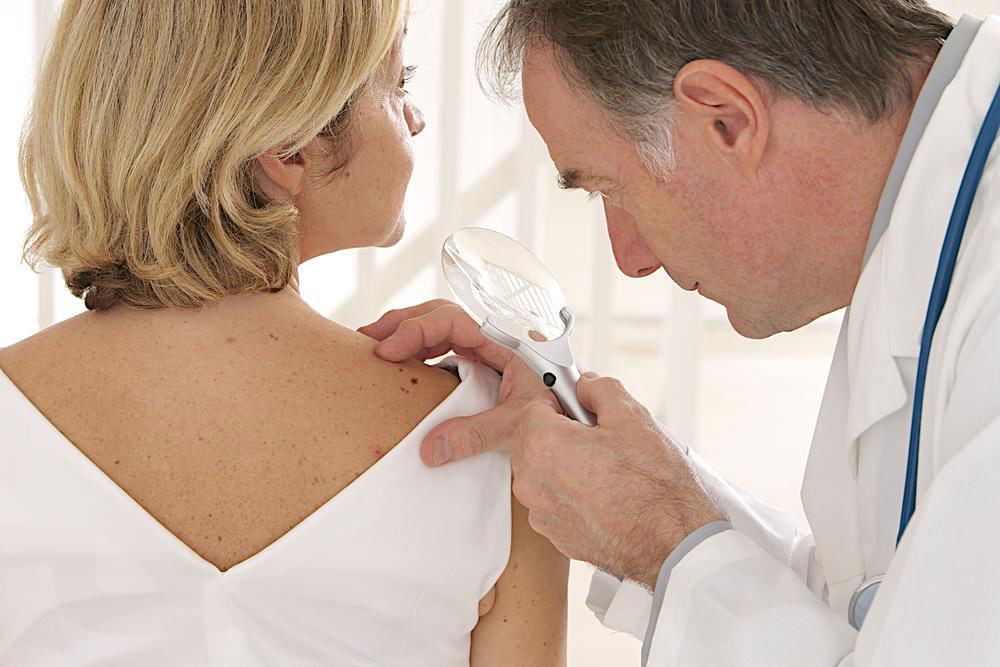
Distinguishing from Other Skin Conditions: Eczema shares symptoms with conditions like psoriasis, chickenpox, or contact dermatitis. Proper diagnosis by a dermatologist is essential for appropriate treatment.
Contagion Myths: Eczema is a non-contagious condition and cannot be transmitted through skin contact. Misconceptions can lead to social isolation; education helps dispel these myths.
Seeking Professional Help: Personalized treatment plans designed by dermatologists are pivotal for effective management. Regular follow-ups ensure tailored care and adaptations as needed.
Combining Therapy and Lifestyle Changes: Long-term relief often requires a combination of topical treatments, lifestyle modifications, and environmental controls.
Visual Insights: Using Eczema Photos for Better Understanding
Recognizable Signs: Images illustrating redness, inflammation, dryness, and flaky skin help patients and caregivers identify eczema early.
Assessing Severity: Comparing photographs over time aids in monitoring disease progression and evaluating the effectiveness of treatment strategies.
Educational Tool: Online images serve to educate patients about typical eczema presentations, aiding in prompt recognition and care.
In conclusion, atopic dermatitis is a complex yet manageable skin condition. With the right knowledge, proactive skincare, and consultation with healthcare professionals, individuals can significantly reduce the frequency of flare-ups, enhance skin health, and improve their overall quality of life.