Comprehensive Insights into the Causes and Management of Atopic Dermatitis
Discover comprehensive insights into the causes, triggers, and management strategies for atopic dermatitis. Learn how genetics, environment, and lifestyle influence this common chronic skin condition and explore effective treatment options for better skin health and quality of life.
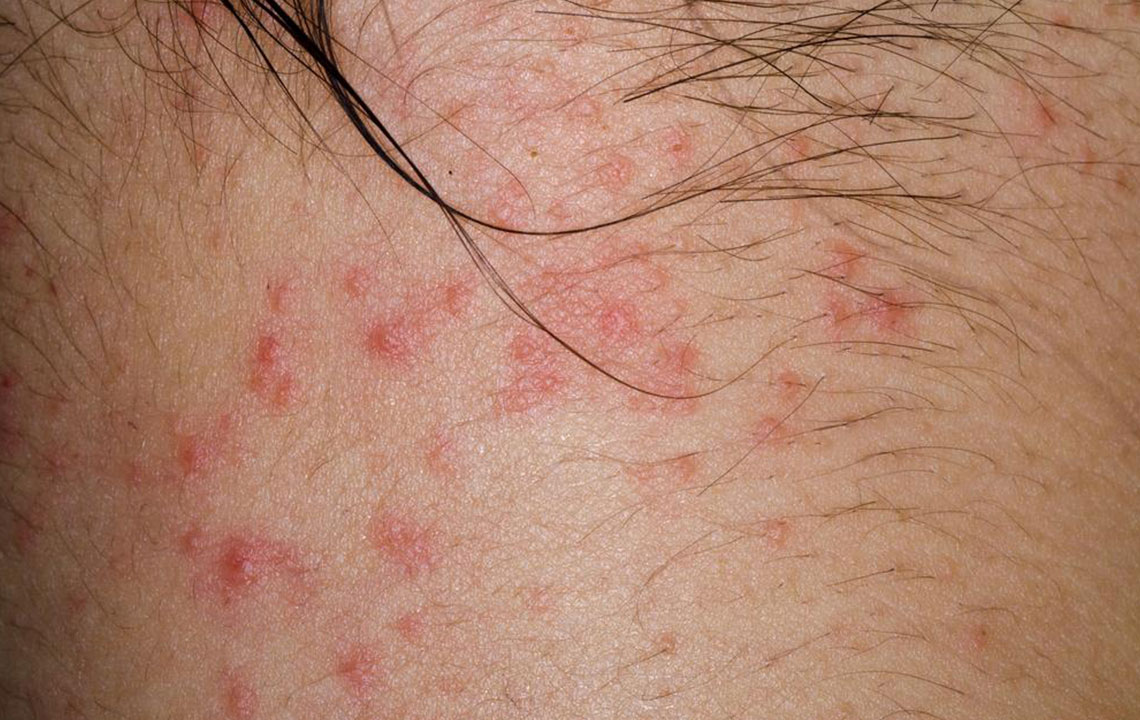
Comprehensive Insights into the Causes and Management of Atopic Dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis, often referred to as eczema, is one of the most common chronic skin conditions affecting millions worldwide. In the United States alone, it impacts approximately 17.8 million individuals, cutting across age groups but predominantly beginning in early childhood. This skin disorder is characterized by persistent and relapsing episodes of red, itchy, and inflamed patches. These patches commonly appear on the cheeks, arms, legs, and other flexible skin areas, causing discomfort and affecting the quality of life of those affected. Understanding the underlying causes, triggers, and management strategies is crucial for effective control and improved skin health.
While the exact etiology of atopic dermatitis remains elusive, extensive research suggests a complex interplay between genetic predispositions, immune system dysfunction, and environmental factors. Individuals with a family history of allergies or atopic conditions such as asthma and hay fever are at a higher risk of developing the condition. This hereditary component indicates that genetics play a pivotal role in determining skin barrier integrity and immune responses. Damaged or weakened skin barriers allow irritants and allergens to penetrate more easily, triggering inflammatory responses that manifest as dermatitis.
Environmental influences significantly contribute to the frequency and severity of flare-ups. Common external triggers include harsh soaps, detergents, environmental allergens like pollen, pet dander, dust mites, and even climatic factors such as dry or cold weather. Exposure to these triggers can cause the immune system to overreact, leading to increased inflammation, redness, and itchiness. Certain foods may also act as allergens in some individuals, prompting rash outbreaks after meals. Identifying personal triggers through diligent monitoring and allergy testing is a fundamental part of managing atopic dermatitis effectively.
Management of atopic dermatitis involves a multifaceted approach tailored to an individual’s specific triggers and severity of symptoms. Topical therapies, primarily moisturizers and corticosteroid creams, are the mainstays of treatment. Moisturizers help restore and maintain the skin's protective barrier, reducing vulnerability to irritants, while corticosteroids decrease localized inflammation. Additionally, newer treatment options like calcineurin inhibitors offer alternatives for sensitive skin areas. Beyond medications, lifestyle modifications such as avoiding known triggers, wearing soft fabrics like cotton, and maintaining proper skin hydration are essential for controlling ongoing symptoms and preventing exacerbations.
For severe or refractory cases, healthcare providers might recommend phototherapy or systemic medications that modulate the immune response. These treatments are typically prescribed after comprehensive evaluation and are aimed at reducing the frequency and intensity of flare-ups. Education about skin care routines, early detection of flare signs, and stress management can significantly improve disease outcomes. Living with atopic dermatitis requires ongoing attention, but with the right combination of treatments and lifestyle adjustments, most individuals can achieve significant relief and maintain healthy skin.