Comprehensive Guide to Atopic Dermatitis: Causes, Symptoms, & Effective Management Strategies
This comprehensive guide explores atopic dermatitis, detailing its causes, symptoms, potential complications, and effective management strategies. It emphasizes the importance of skin care routines, trigger avoidance, and proper medical treatment to improve quality of life. Suitable for patients, caregivers, and healthcare providers, this article offers in-depth insights into managing this chronic skin condition and preventing associated health issues.
Comprehensive Guide to Atopic Dermatitis: Causes, Symptoms, & Effective Management Strategies
Atopic dermatitis, commonly known as eczema, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that affects a significant portion of the population worldwide. It manifests as persistent skin redness, severe itching, and dry patches that can significantly impact quality of life. While it is most prevalent in children, atopic dermatitis can develop at any age, affecting both infants and adults. Understanding its triggers, symptoms, and the best management practices is crucial for those affected and their caregivers.
Understanding the Symptoms and Visual Signs of Atopic Dermatitis
Persistent Dryness and Itching: One of the hallmark signs is relentless dry skin accompanied by intense itching, often worsening during nighttime. This itching can become so severe that it disrupts sleep and daily activities.
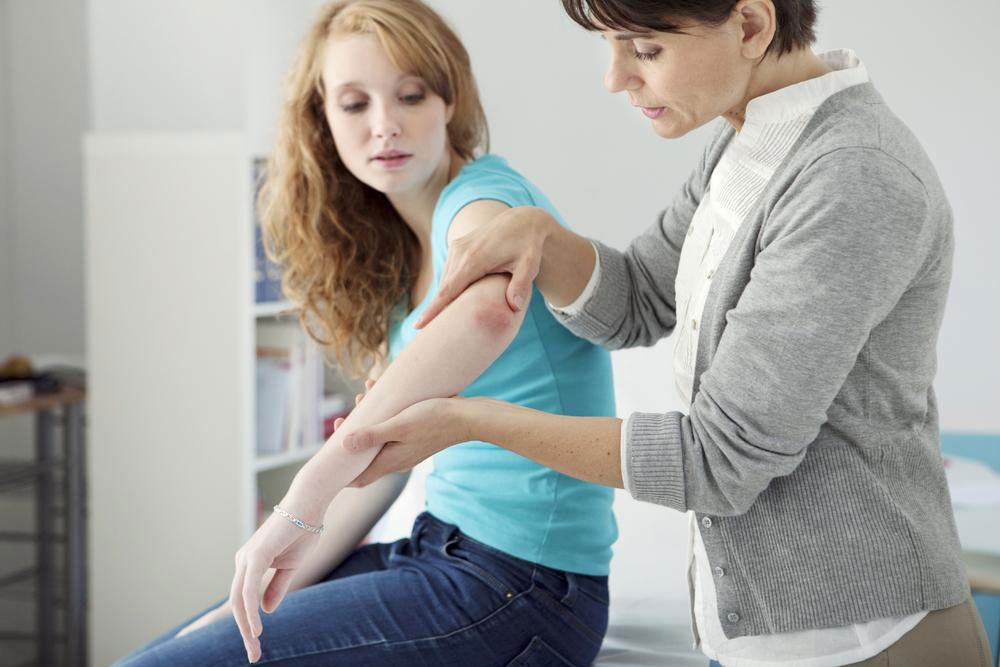
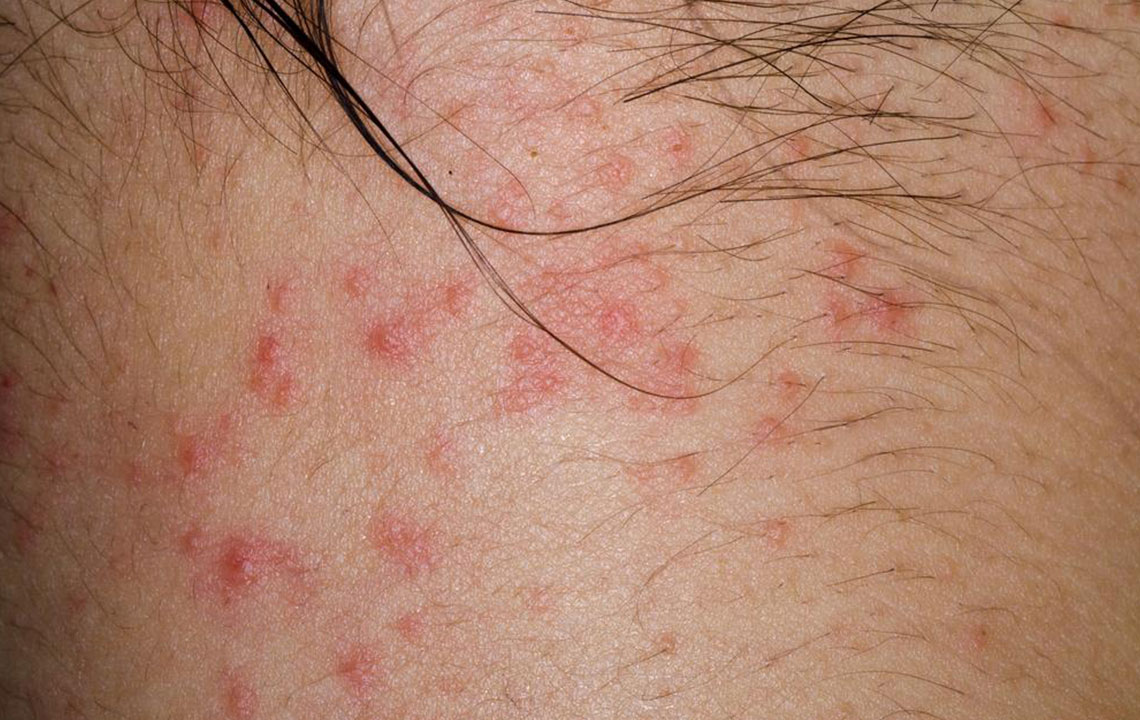
Characteristic Skin Lesions: The skin affected by atopic dermatitis typically exhibits red to brownish patches. These patches are most common on the hands, feet, ankles, wrists, eyelids, neck, and upper chest. In infants, patches frequently appear on the face and scalp. Over time, these areas may develop small, raised bumps, become swollen, or form open sores due to scratching.
Localized and Symmetrical Distribution: The rash often appears symmetrically and can be exacerbated by environmental factors, irritants, or allergens present in the surroundings.
Infants frequently develop eczema patches on their face and scalp, which can be distressing for parents. As children grow, the affected areas may shift or expand, and the severity can vary over time.
The affected skin can become sensitive, swollen, and prone to scratching, aggravating the inflammation and discomfort.
Repeated scratching increases the risk of secondary infections, complicating the condition further.
While the precise cause of atopic dermatitis remains elusive, scientific research indicates that genetic predispositions significantly influence its development. Individuals with a family history of eczema, asthma, or hay fever are at higher risk. The condition is linked to dysfunctions in the skin's protective barrier, making it more susceptible to irritants, allergens, and microbial invasion.
Potential Complications Arising from Untreated Atopic Dermatitis
Asthma and Allergic Conditions: Many children with eczema eventually develop respiratory allergies, including asthma and hay fever, often by the age of 13. These conditions tend to run in families with allergic histories and require integrated management.
Skin Infections: Persistent scratching causes skin breaches, increasing vulnerability to bacterial and viral infections such as impetigo, herpes simplex virus, and candidiasis. These complicate eczema management and may lead to further inflammation and scarring.
Despite the lack of a definitive cure, advances in dermatology have provided effective management strategies that significantly improve patient outcomes. Maintaining a regular skin care routine, avoiding known irritants, and using targeted medications during flare-ups are keys to controlling symptoms. Proper hydration with moisturizers, gentle skin cleansers, and avoidance of harsh soaps help restore and maintain the skin barrier.
Pharmacological treatments often include topical corticosteroids, antihistamines, and sometimes immunomodulators for severe cases. For individuals with frequent or severe episodes, a comprehensive approach including allergy testing and environmental modifications may be necessary. Education about trigger avoidance and proper skincare techniques plays a vital role in reducing the frequency and severity of flare-ups.
In conclusion, understanding atopic dermatitis is essential for effective management. Recognizing early signs, identifying triggers, and adhering to a personalized treatment plan can lead to better quality of life and minimize complications associated with this chronic skin condition.