Comprehensive Guide to Liver Diseases: Causes, Symptoms, and Health Risks
Discover in-depth insights into liver diseases, their causes, symptoms, and health risks. Learn how early detection, proper management, and lifestyle changes can prevent serious complications like liver failure and improve quality of life. This comprehensive guide aims to raise awareness about liver health and the importance of proactive medical care for maintaining overall well-being.
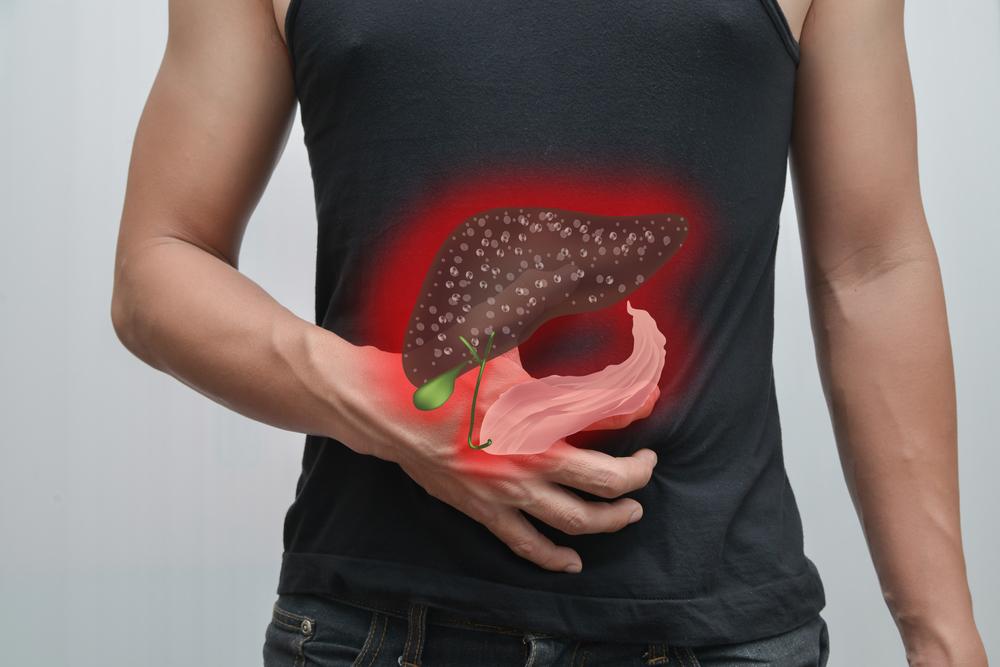
An In-Depth Exploration of Liver Diseases and Their Impact on Overall Health
The liver is a vital organ responsible for numerous critical functions, including detoxification, metabolism, storage of nutrients, and blood regulation. When the liver faces damage or dysfunction due to various medical conditions, it can lead to serious health consequences. Liver diseases encompass a wide range of conditions, from infections and autoimmune diseases to lifestyle-related issues and genetic disorders. Understanding these diseases, their causes, symptoms, and potential health risks is essential for early detection, effective management, and prevention.
Across different types of liver ailments, there are common symptoms that often serve as warning signs. These include persistent fatigue, abdominal discomfort, swelling, jaundice (yellowing of skin and eyes), easy bruising, and anemia. One of the liver’s primary functions is detoxification—filtering harmful substances such as toxins, chemicals, alcohol, and drugs from the bloodstream. When this function is impaired, toxins can accumulate, adversely affecting multiple organs and leading to a cascade of health issues.
Chronic liver disease can significantly impair health, leading to complications like fluid retention, bleeding problems, and even liver failure. One notable aspect of liver health is its remarkable ability to regenerate tissue; however, prolonged or severe damage can overwhelm this capacity. In cases such as liver cancer or cirrhosis, understanding the signs and seeking timely medical intervention are critical for improving prognosis. The sooner liver issues are detected, the better the chances of successful treatment and management.
Many liver conditions stem from infections, with hepatitis B and hepatitis C viruses being some of the most common culprits. Autoimmune disorders and genetic factors can also contribute to liver damage. Additionally, lifestyle choices, such as excessive alcohol consumption, unhealthy diet, and exposure to toxins, play significant roles in the development of liver disease. Regular health check-ups and liver function tests can help identify problems early, potentially preventing irreversible damage.
The liver's role extends beyond detoxification; it also manages blood sugar levels by storing excess glucose as glycogen. During fasting or periods of increased energy demand, the liver converts this stored glycogen back into glucose, supplying energy to the body. Impairment of this process due to liver disease can lead to hyperglycemia, characterized by symptoms such as increased thirst, frequent urination, hunger, fatigue, weight loss, dry skin, and cardiovascular irregularities. Such symptoms necessitate prompt medical evaluation to prevent severe complications like diabetes mellitus.
Further, liver failure can have widespread effects on other vital organs, resulting in complications such as bleeding tendencies, hepatic encephalopathy (confusion and mental disturbances), and kidney dysfunction. Early diagnosis and treatment are key to managing liver health, preventing disease progression, and improving quality of life.
If you experience persistent symptoms that may indicate liver problems, such as jaundice, unexplained fatigue, unusual swelling, or changes in skin or eye color, seeking medical advice promptly is essential. Diagnostic tests like blood panels, imaging studies, and liver biopsies help determine the extent and cause of liver damage. Lifestyle modifications, antiviral therapies, medications, and in some cases, surgical interventions are used to treat various liver diseases effectively. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, avoiding hepatotoxins, and getting regular check-ups can dramatically reduce your risk of developing serious liver conditions and ensure long-term health and well-being.