Comprehensive Guide to Liver Cancer: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Prevention Strategies
This comprehensive guide explores liver cancer in detail, covering its causes, symptoms, diagnostic methods, and prevention strategies. With insights into risk factors such as hepatitis infections, alcohol consumption, and environmental toxins, the article emphasizes the importance of early detection and lifestyle modifications. Understanding these aspects can help reduce the global burden of liver cancer and improve patient outcomes through timely intervention and preventive measures.
Comprehensive Guide to Liver Cancer: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Prevention Strategies
The human liver is a remarkably vital organ, occupying a central role in maintaining overall health and metabolic balance. Its functions include detoxifying harmful substances from the blood, producing essential proteins, and aiding in digestion through bile production. Despite its resilience, the liver is susceptible to various diseases, with liver cancer being one of the most serious and deadly conditions affecting millions worldwide. According to global health statistics, liver cancer affects approximately 30 out of every 100,000 people, making it a significant health concern, especially in regions with high hepatitis prevalence.
Liver cancer primarily occurs as Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC), which accounts for the majority of cases. However, other less common types include intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma and mixed types. It is important to understand that liver cancer can be classified into two main categories: primary, originating within the liver itself, and secondary, resulting from metastasis of tumors originating elsewhere in the body. Early detection and understanding of the causes, symptoms, and preventive measures are critical for improving survival rates and quality of life.
Understanding the Causes of Liver Cancer
The development of liver cancer involves complex interactions between genetic factors and environmental exposures. The liver’s essential functions make it particularly vulnerable to damage from various external and internal sources. Here, we detail the primary causes that increase susceptibility to liver cancer:
Chronic Viral Infections: Hepatitis B virus (HBV) and Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infections are leading causes worldwide. Chronic infection with these viruses causes persistent inflammation, leading to liver cirrhosis, which significantly elevates cancer risk.
Alcohol Abuse: Excessive alcohol consumption causes liver inflammation and cirrhosis over time, creating a fertile environment for malignant transformation of liver cells.
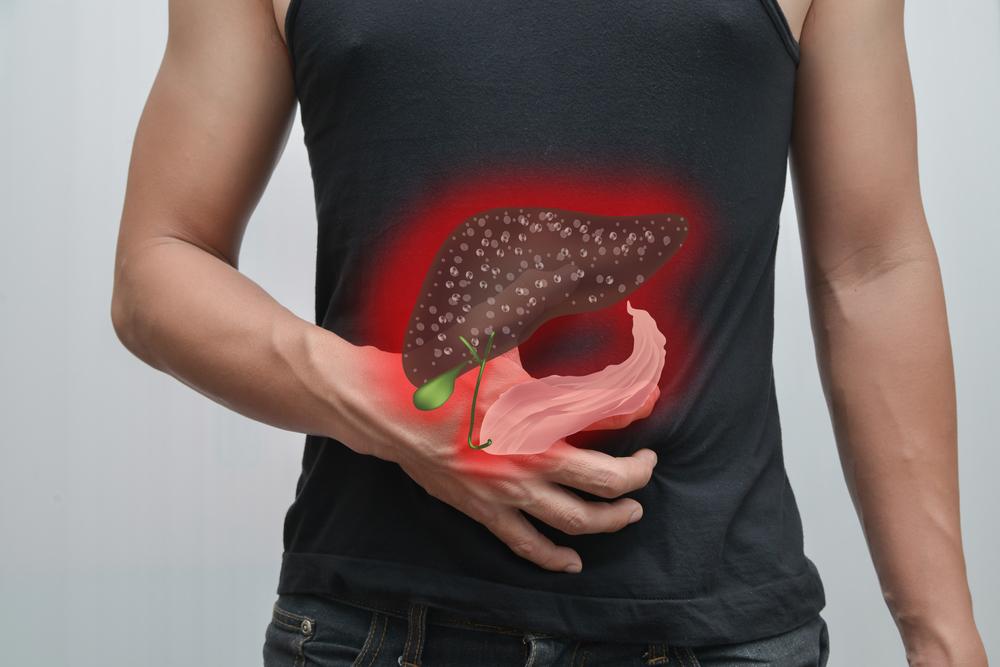
Cirrhosis: This is the advanced scarring process of the liver caused by long-term injury from various sources such as viral hepatitis and alcohol, serving as a major risk factor for hepatocellular carcinoma.
Genetic and Metabolic Disorders: Conditions like hemochromatosis (iron overload), alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency, and Wilson’s disease predispose individuals to liver damage and eventual cancer development.
Exposure to Aflatoxins: These carcinogenic toxins, produced by fungi on stored grains and nuts, are prevalent in certain developing regions and significantly contribute to liver carcinogenesis.
Obesity and Diabetes: Obesity increases fatty liver disease, which can progress to cirrhosis and increase the cancer risk. Similarly, insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes are associated with higher liver cancer incidence.
Environmental Toxins and Chemicals: Prolonged exposure to chemicals like aflatoxins, industrial chemicals, and tobacco smoke compounds amplifies the risk, especially when combined with other factors.
Understanding the multifaceted causes of liver cancer underscores the importance of preventive measures and early intervention. The role of viral hepatitis cannot be overstated, as vaccination against hepatitis B offers a powerful tool in reducing incidence in high-risk populations. Lifestyle choices, such as limiting alcohol intake and maintaining a healthy weight, are vital for lowering the risk. Moreover, avoiding exposure to known carcinogens like aflatoxins and chemicals in the environment is crucial for susceptible groups.
The demographic profile of liver cancer patients varies, with higher prevalence among men than women and notably higher rates in Asian-American populations. This disparity is linked to factors such as infection prevalence, cultural habits, and genetic predispositions.
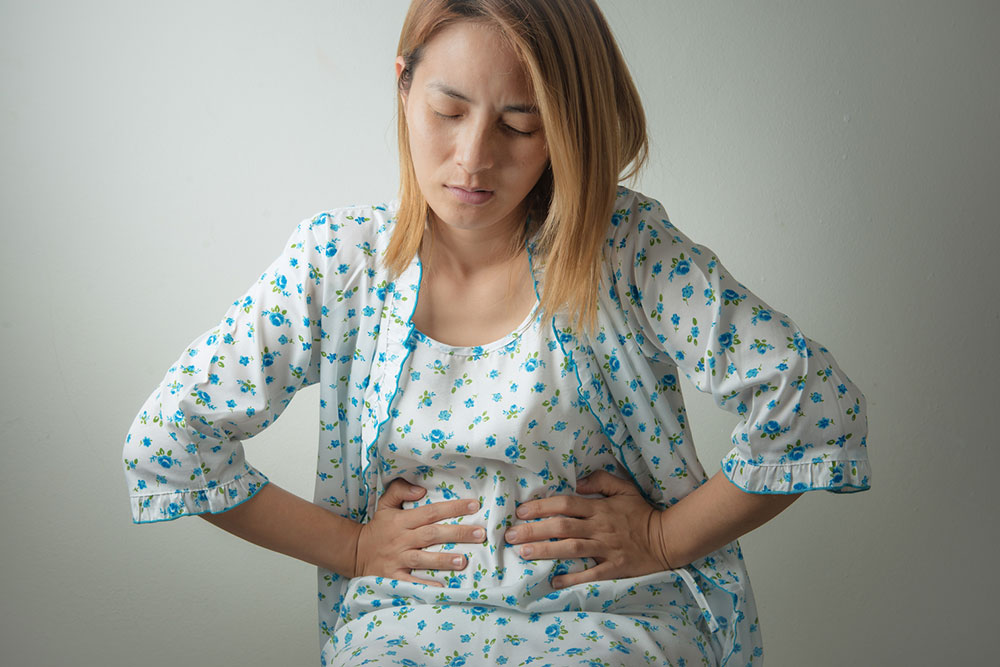
Recognizing the symptoms of liver cancer is essential for early detection. Symptoms often include persistent abdominal pain or swelling, unexplained weight loss, jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), enlarged liver, easy bruising, nausea, and fatigue. Because early-stage liver cancer may not produce noticeable symptoms, screening in high-risk groups is highly recommended.
Diagnosis involves a combination of blood tests measuring levels of alpha-fetoprotein (AFP), imaging exams using CT scans, MRI, or ultrasounds, and confirmatory tissue biopsies. These diagnostic tools help determine the presence, location, and extent of tumors, guiding treatment decisions.
Staging of liver cancer is a crucial step, typically divided into four stages, from localized tumors amenable to surgical removal or transplantation to widespread metastasis requiring palliative care. Treatment options vary based on the stage, patient health, and liver function, with early-stage cases often treatable through surgery, liver transplantation, or ablative therapies. Advanced cases may require chemotherapy, targeted therapy, or radiation therapy. Innovations in immunotherapy are also emerging as promising options.
Preventive strategies focus on lifestyle modifications, vaccination, proper management of hepatitis infections, and regular health screenings. Avoiding excessive alcohol, practicing safe injection techniques, and ensuring food safety to prevent exposure to carcinogenic aflatoxins are all critical steps. Public health initiatives aimed at hepatitis vaccination and awareness campaigns are vital for reducing the global burden of liver cancer.
In conclusion, understanding liver cancer—its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and prevention—is key to reducing its impact. Early detection and proactive lifestyle choices can significantly improve outcomes, emphasizing the importance of awareness and intervention in high-risk populations.