Comprehensive Guide to Liver Cancer: Causes, Symptoms, and Modern Treatment Options
This comprehensive guide explores liver cancer's causes, symptoms, risk factors, and the latest treatment options available. It highlights the importance of early detection and advances in medical therapies that can improve patient outcomes. Understanding these aspects helps individuals at risk and healthcare providers take proactive steps to manage and treat this serious liver disease effectively.
Comprehensive Guide to Liver Cancer: Causes, Symptoms, and Modern Treatment Options
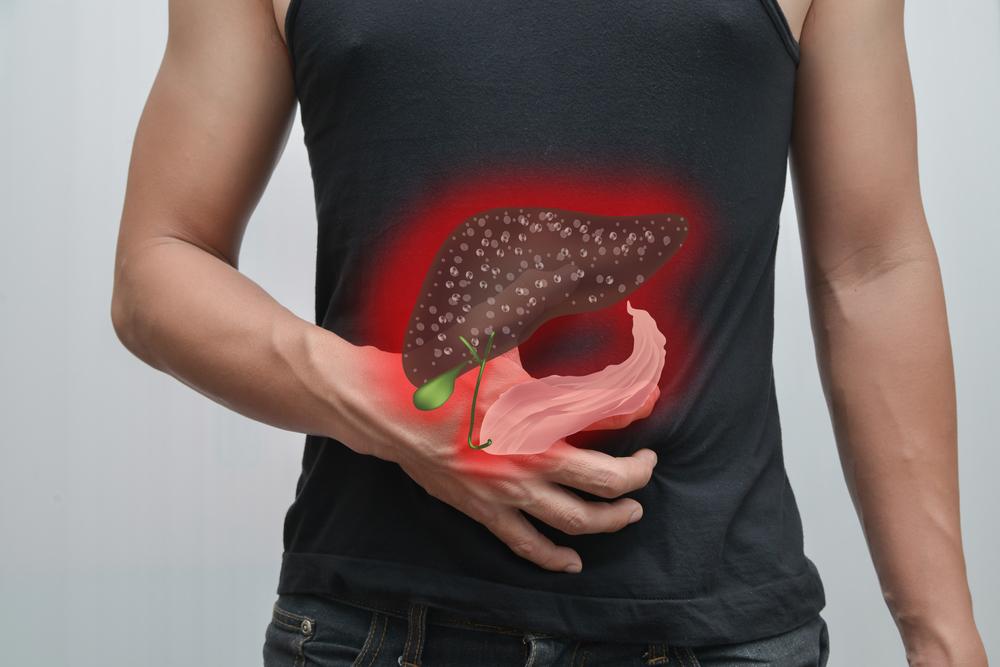
Liver cancer, also known as hepatic cancer, represents a serious and often rapidly progressing malignancy that originates in the liver tissue. It is characterized by the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells within the liver, which can severely impair organ function and pose significant health risks. Understanding the nuances of liver cancer, including its causes, early signs, risk factors, and available treatment methods, is essential for early detection and effective management. This article provides an in-depth exploration of liver cancer, covering key information that can help patients, caregivers, and healthcare professionals better understand this complex disease.
Types of Liver Cancer: An Overview
Primarily, liver cancer can be classified into two categories: primary and secondary. Primary liver cancer originates directly within the liver itself, while secondary liver cancer, also known as metastatic liver cancer, occurs when cancer cells spread to the liver from other parts of the body such as the colon, lung, or breast. Accurate diagnosis of the type of liver cancer is critical for determining an appropriate treatment plan.
The most prevalent form of primary liver cancer is hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), which accounts for approximately 80-85% of cases. HCC develops from the hepatocytes, the main type of liver cells responsible for processing nutrients and chemicals. Alongside HCC, other less common primary liver cancers include cholangiocarcinoma, arising from the bile ducts within the liver, representing roughly 10% of cases, and angiosarcoma, a rare vascular tumor originating from the blood vessel lining in the liver, comprising about 2% of cases.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Liver Cancer
In its early stages, liver cancer often remains asymptomatic, making early detection challenging. As the disease progresses, various signs and symptoms may become evident. These include unexplained weight loss, persistent loss of appetite, discomfort or pain in the upper right abdomen, nausea, fatigue, abdominal bloating, and jaundice, which manifests as yellowing of the skin and eyes. Additionally, patients may observe pale or clay-colored stools, dark urine, and a generalized feeling of weakness. Recognizing these symptoms early can be lifesaving, emphasizing the need for regular medical checkups for individuals at risk.
Key Risk Factors Associated with Liver Cancer
Understanding the risk factors that contribute to liver cancer development is vital for prevention and early intervention. Major factors include:
Hepatitis B and C Virus Infections: Chronic infections with hepatitis B virus (HBV) and hepatitis C virus (HCV) are among the leading causes of liver cancer worldwide. These infectious agents damage the liver tissue over time, leading to inflammation, cirrhosis, and increased cancer risk. They can be transmitted through contaminated blood, unsterilized medical equipment, or unprotected sexual contact.
Cirrhosis: This condition involves extensive scarring of liver tissue resulting from chronic hepatitis, alcohol abuse, or other liver diseases. Cirrhotic changes impair liver function and create an environment conducive to carcinogenesis.
Type 2 Diabetes and Obesity: Metabolic disorders, particularly when combined with other risk factors, significantly raise the susceptibility to liver cancer by promoting fatty liver disease and chronic inflammation.
Other Factors: Excessive alcohol consumption, exposure to aflatoxins (toxins produced by certain molds on food), inherited liver diseases such as hemochromatosis, and environmental toxins also increase the risk of developing liver cancer.
Advancements in Liver Cancer Treatment: Modern Strategies and Approaches
Managing liver cancer effectively often hinges on early diagnosis and the selection of suitable treatment options tailored to the individual patient's condition. The choice of therapy depends on factors such as tumor size and location, liver function, overall health, and disease stage. Modern medical advancements have expanded the treatment landscape, offering hope for improved survival rates and quality of life. The main treatment options include:
Partial Liver Resection: Surgical removal of the tumor is viable when the cancer is localized and the patient’s liver function remains adequate. In early-stage lesions, partial resection can be curative.
Liver Transplantation: Replacing the diseased liver with a healthy donor organ offers a potential cure, especially for patients with small tumors and underlying liver cirrhosis. Restrictions on tumor size and number apply.
Ablation Techniques: Procedures like radiofrequency ablation (RFA), microwave ablation (MWA), and cryoablation use heat or cold to destroy cancer cells. These minimally invasive techniques are effective for small tumors and can be performed under local anesthesia.
Radiation Therapy: Advanced techniques like stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) deliver high-energy beams precisely to tumor sites, minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissue.
Embolization Procedures: Transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) and transarterial embolization (TAE) block blood flow to the tumor, starving cancer cells of essential nutrients and oxygen, thereby halting tumor growth.
Chemotherapy: Systemic or targeted chemotherapy employs anti-cancer drugs to destroy tumorous cells. In recent years, targeted therapies like sorafenib and lenvatinib have shown promising results in managing advanced cases.
Immunotherapy: Novel treatments harness the patient’s immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells, representing an emerging frontier in liver cancer management.
Early detection remains critical for successful treatment outcomes. Patients at high risk should undergo routine screening, including ultrasound imaging and alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) testing, to catch the disease at an early, treatable stage. Continued research strives to improve existing therapies and discover new possibilities to combat liver cancer more effectively.
In conclusion, liver cancer is a complex and often aggressive disease that requires prompt diagnosis and personalized treatment strategies. Advances in medical technology and increased awareness are crucial in improving prognosis and survival rates. Individuals with risk factors should seek regular medical checkups and adopt healthy lifestyle choices to reduce their chances of developing this formidable disease.