Comprehensive Guide to Frozen Shoulder: Recognizing Symptoms and Exploring Effective Treatments
Frozen shoulder, or adhesive capsulitis, is a common condition causing shoulder pain and limited mobility, mostly affecting adults aged 40 to 60. It develops gradually due to inflammation and scar tissue formation around the joint capsule. This article explores the causes, symptoms, diagnostic methods, and various effective treatments including physical therapy, medications, home remedies, and surgical options. Timely management can significantly improve recovery outcomes. Understanding the signs and seeking prompt medical care are essential for restoring shoulder function and reducing long-term disability.
Comprehensive Guide to Frozen Shoulder: Recognizing Symptoms and Exploring Effective Treatments
Frozen shoulder, scientifically known as adhesive capsulitis, is a condition characterized by stiffness and limited range of motion in the shoulder joint. It often leads to significant pain and functional impairment, affecting many adults, particularly those aged 40 to 60. This condition develops gradually and can persist for months or even years if left untreated. Understanding the underlying causes, clear symptoms, and available treatment options is crucial for effective management and swift recovery.
Understanding the Causes of Frozen Shoulder
The development of frozen shoulder is typically linked to prolonged periods of shoulder immobilization or inactivity. Factors such as shoulder injuries, surgeries, or illnesses that restrict movement can trigger inflammatory processes, leading to scar tissue formation around the joint capsule. These adhesions cause thickening and tightening of the shoulder tissues, making normal movement difficult. Common risk factors include diabetes, thyroid disorders, cardiovascular disease, and previous shoulder trauma.
Severe cases see extensive scar tissue buildup, severely restricting arm mobility and causing persistent pain. The condition's progression can span from 2 to 9 months, with some individuals experiencing prolonged recovery periods depending on severity. Understanding the trajectory of frozen shoulder helps in timely diagnosis and treatment, preventing long-term disability.
Signs and Symptoms of Frozen Shoulder
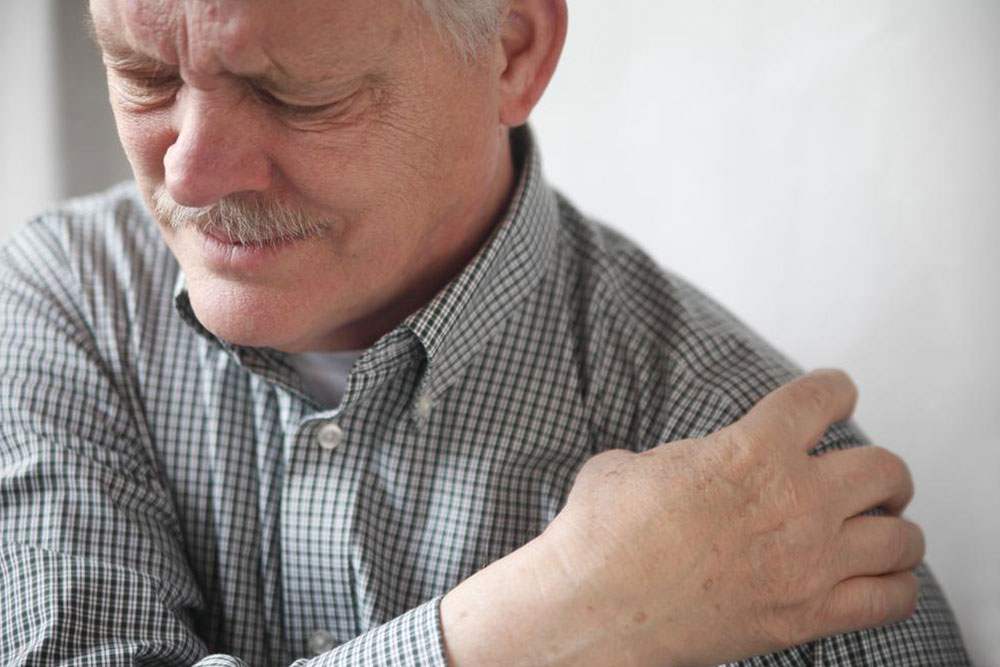
Recognizing early symptoms is vital for prompt intervention. Common signs include persistent shoulder pain that may be dull or aching, stiffness, and decreased range of motion. People often report that pain intensifies during activities such as reaching overhead, lifting objects, dressing, or other daily tasks requiring shoulder mobility. As the condition advances, even simple actions become challenging, affecting work, recreational activities, and overall quality of life.
For many, the initial pain may be mild but gradually worsens, accompanied by a physical stiffening that reduces the ability to rotate or elevate the arm. In advanced stages, atrophic changes and muscle weakness may also occur, complicating recovery efforts.
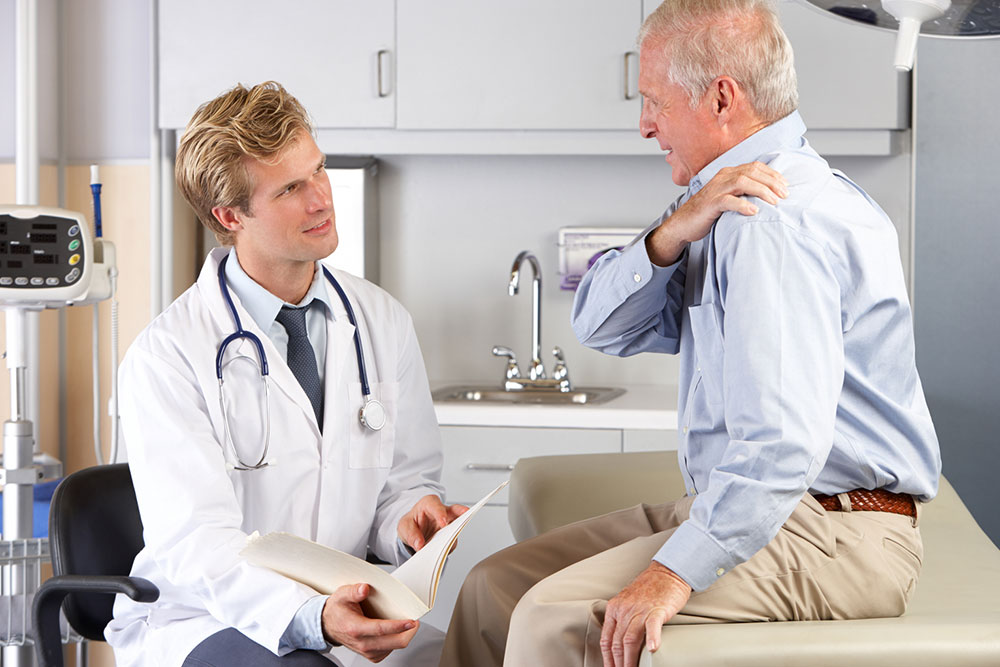
Diagnosing Frozen ShoulderWhen a patient presents with shoulder pain and restricted movement, consulting a healthcare professional is essential. Diagnosis typically begins with a thorough physical examination to assess the range of motion, strength, and pain levels. The clinician might perform specific tests to pinpoint the exact issue. To rule out other potential causes such as arthritis, rotator cuff injuries, or labral tears, imaging techniques like X-rays and MRI scans are employed. These imaging tools help visualize joint structures, confirm the presence of adhesions, and exclude other pathologies.
Early diagnosis significantly improves the success of treatment, emphasizing the importance of seeking medical advice promptly when experiencing symptoms.
Effective Treatment Options for Frozen ShoulderManaging frozen shoulder involves a combination of therapies aimed at reducing pain, restoring mobility, and shortening the recovery timeline. Common treatment strategies include physical therapy, medication, home remedies, and in some cases, surgical intervention.
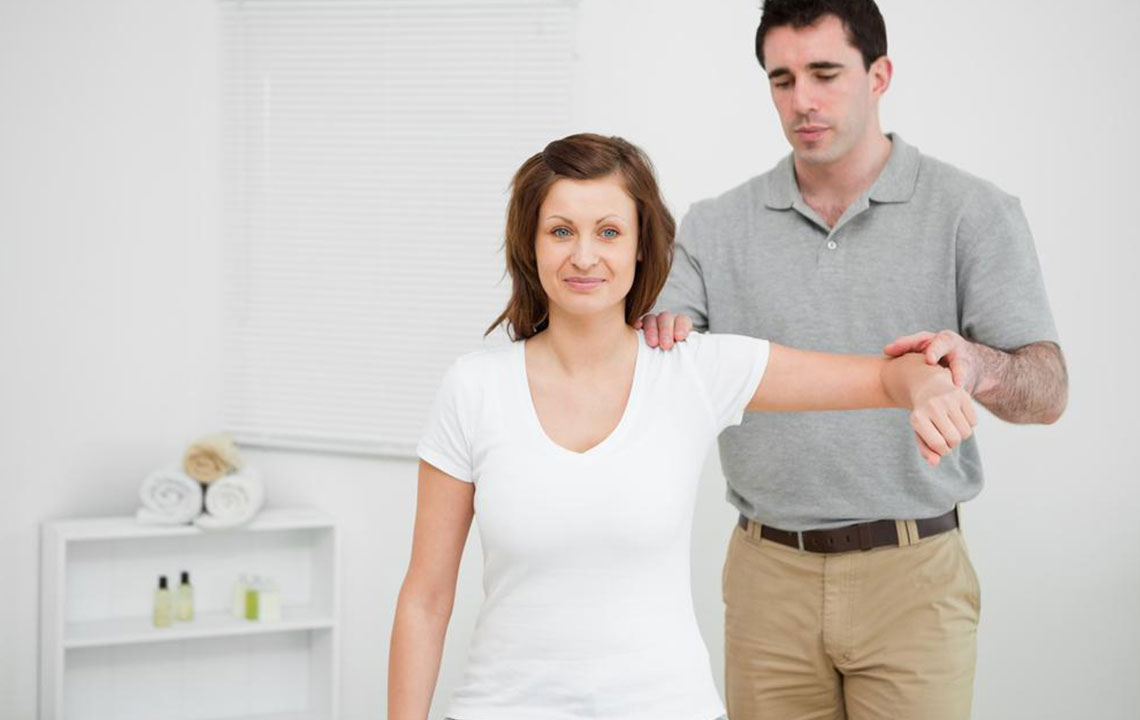
Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation
The cornerstone of frozen shoulder treatment is physiotherapy. Physical therapists design specific stretching and mobilization exercises tailored to the patient's severity. These exercises aim to gradually increase the shoulder's range of motion by breaking down scar adhesions and preventing further stiffness. Sessions may last several weeks to months, depending on individual progress.
A typical physical therapy regimen may include passive stretching, joint mobilization techniques, and strengthening exercises. Consistency and patience are crucial, as diligent adherence can accelerate recovery and restore full function.
Medication and Injections
Anti-inflammatory medications like NSAIDs help manage pain and inflammation. Corticosteroid injections directly into the shoulder joint can provide more targeted relief, especially during severe pain episodes or the initial stages of treatment. However, these should be administered under medical supervision to prevent potential side effects.
Home Care Remedies to Complement Therapy
Applying ice packs for 15-20 minutes can help reduce initial swelling and pain. Gentle, prescribed exercises performed at home can promote joint mobility, but activities should be completed with guidance from a healthcare provider. Maintaining shoulder movement without overexertion helps prevent further stiffness and encourages healing.
Surgical Options and Advanced Treatments
Surgery is rarely necessary but may be considered if conservative treatments fail. Procedures like shoulder arthroscopy allow surgeons to release adhesions or remove scar tissue, restoring mobility. Such interventions are typically followed by intensive physiotherapy to maximize benefits and prevent recurrence.
In summary, early recognition and comprehensive management of frozen shoulder are key to a swift recovery. Patients are encouraged to seek medical advice at the first sign of symptoms and commit to prescribed therapies for optimal results.