Comprehensive Guide to Accelerating Frozen Shoulder Recovery: Effective Strategies and Treatments
This detailed guide explores effective strategies for rapid frozen shoulder healing, emphasizing physiotherapy, temperature therapies, medications, surgical options, and lifestyle modifications. By understanding these comprehensive approaches, individuals can accelerate recovery, reduce pain, and restore shoulder mobility efficiently, preventing long-term disability. Early intervention, personalized treatment plans, and consistent effort are key components to a successful outcome for those suffering from frozen shoulder.

Comprehensive Guide to Accelerating Frozen Shoulder Recovery: Effective Strategies and Treatments
Frozen shoulder, medically known as adhesive capsulitis, is a condition characterized by stiffness and pain in the shoulder joint, restricting movement and affecting daily activities. This condition often develops gradually, impacting individuals aged between 40 and 70 years, with women being more commonly affected. While it can resolve naturally within 12 to 15 months, many patients seek effective treatment options to expedite recovery and reduce discomfort. This extensive guide explores proven strategies, therapies, and lifestyle adaptations to promote rapid healing of frozen shoulder.
Understanding Frozen Shoulder: Causes and Symptoms
Frozen shoulder typically develops following injury, overuse, or due to underlying health conditions like diabetes, thyroid issues, or neurological disorders such as stroke. It often begins with mild discomfort, progressing to significant pain and stiffness, which severely limits arm mobility. Recognizing early symptoms and initiating treatment promptly can significantly influence the speed and success of recovery.
Effective Management and Treatment Approaches for Frozen Shoulder
Successful treatment involves a combination of therapies aimed at reducing pain, improving joint flexibility, and restoring shoulder function. This section details comprehensive methods tailored to individual needs, emphasizing physical therapy, temperature therapies, medication, minimally invasive procedures, and lifestyle modifications.
1. Physiotherapy: The Cornerstone of Frozen Shoulder Treatment
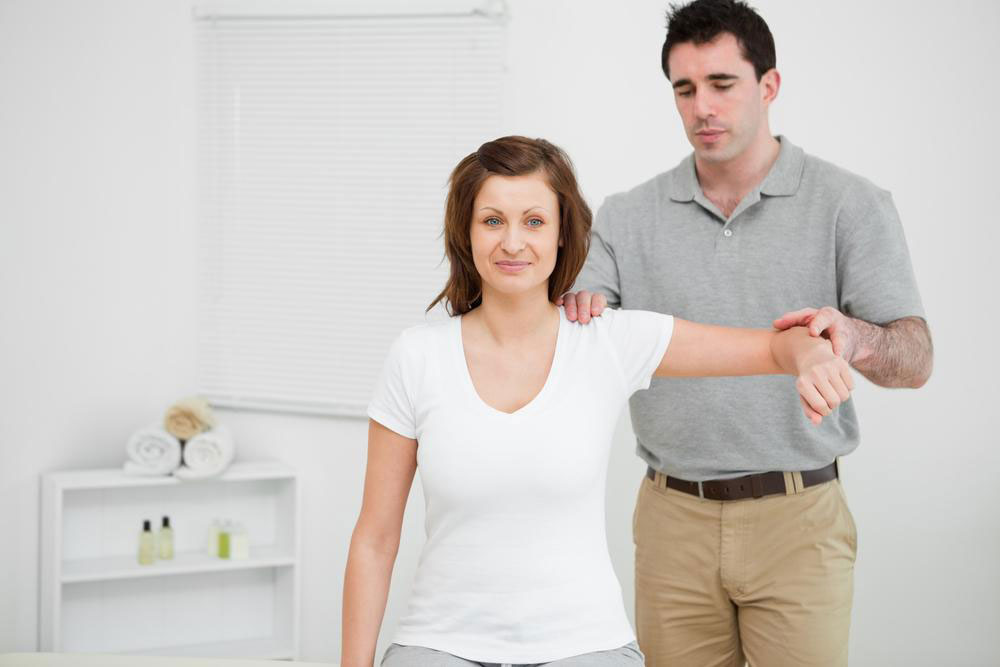
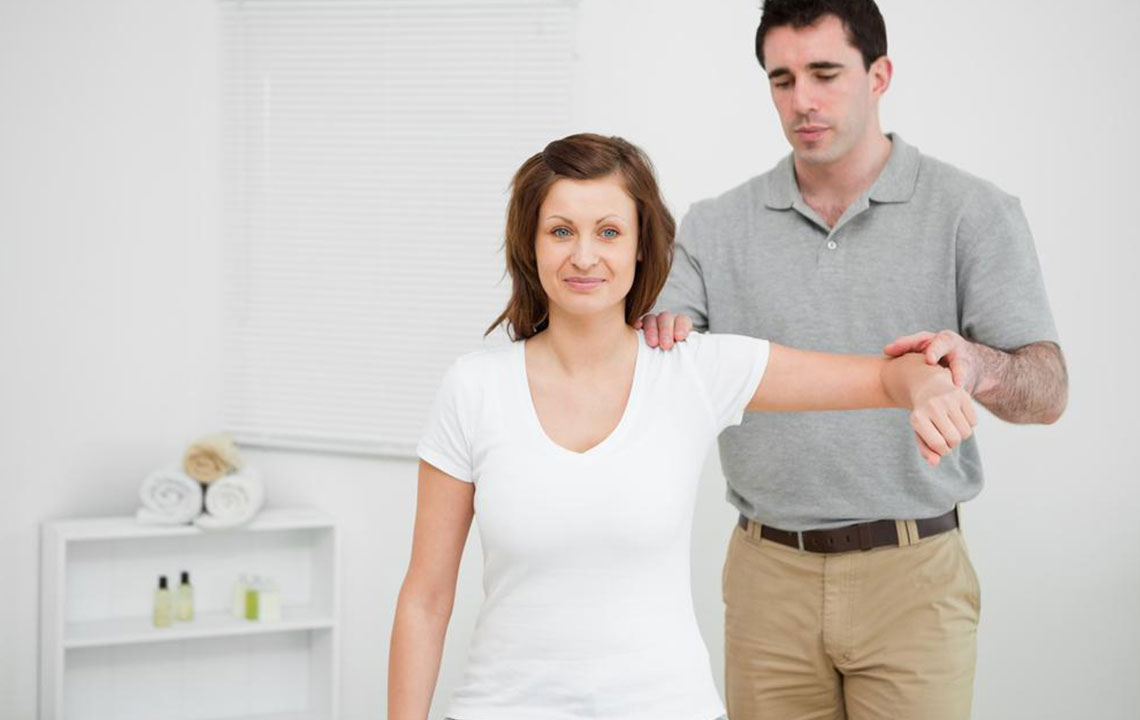
Physiotherapy remains the most effective non-invasive approach for recovering from frozen shoulder. A specialized physiotherapist develops a personalized rehabilitation plan comprising stretching, strengthening exercises, massage therapy, and thermal treatments to target tight tissues and enhance range of motion.
Stretching exercises: These exercises aim to gradually loosen the shoulder capsule and surrounding tissues. Proper warm-up is essential, often involving heat packs before stretching sessions. Key routines include:
Pendulum exercise: Bend over slightly, supporting yourself with the unaffected arm on a table. Let the affected arm hang freely, then swing it gently in small circles clockwise and counterclockwise for about 10 times each. As comfort improves, gradually increase the circle size to enhance flexibility.
Finger walking: Stand facing a wall with the affected arm positioned against it. Walk your fingers upward as high as comfortably possible, then slowly bring them back down to waist level. Repeat 10–20 times daily to improve upward arm movement.
Cross-body stretch: Extend the affected arm across the chest, then use the opposite hand to gently pull the arm closer to the body, holding for 15–30 seconds. Switch arms and repeat. This stretch relieves tension in the shoulder capsule and improves lateral motion.
Strengthening exercises: Once flexibility improves, incorporate resistance training using rubber bands or light weights. These exercises help strengthen shoulder muscles and support joint stability, crucial for sustained recovery.
2. Temperature Therapies for Pain Relief
Applying heat or cold packs can significantly alleviate shoulder pain, especially during the acute phase. Cold packs help reduce inflammation and numb the area, while heat packs relax muscles and promote blood flow, accelerating healing. Always use a cloth barrier between the skin and packs, limiting application to 20-minute sessions, and alternate between heat and cold every few hours as needed.
3. Medication Options for Symptom Management
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen and naproxen, are commonly used to reduce inflammation and relieve pain. Paracetamol (acetaminophen) provides additional analgesic effects. In some cases, over-the-counter or prescribed codeine may be considered for severe discomfort. It's essential to follow medical guidance when using these medications to avoid side effects or dependency.
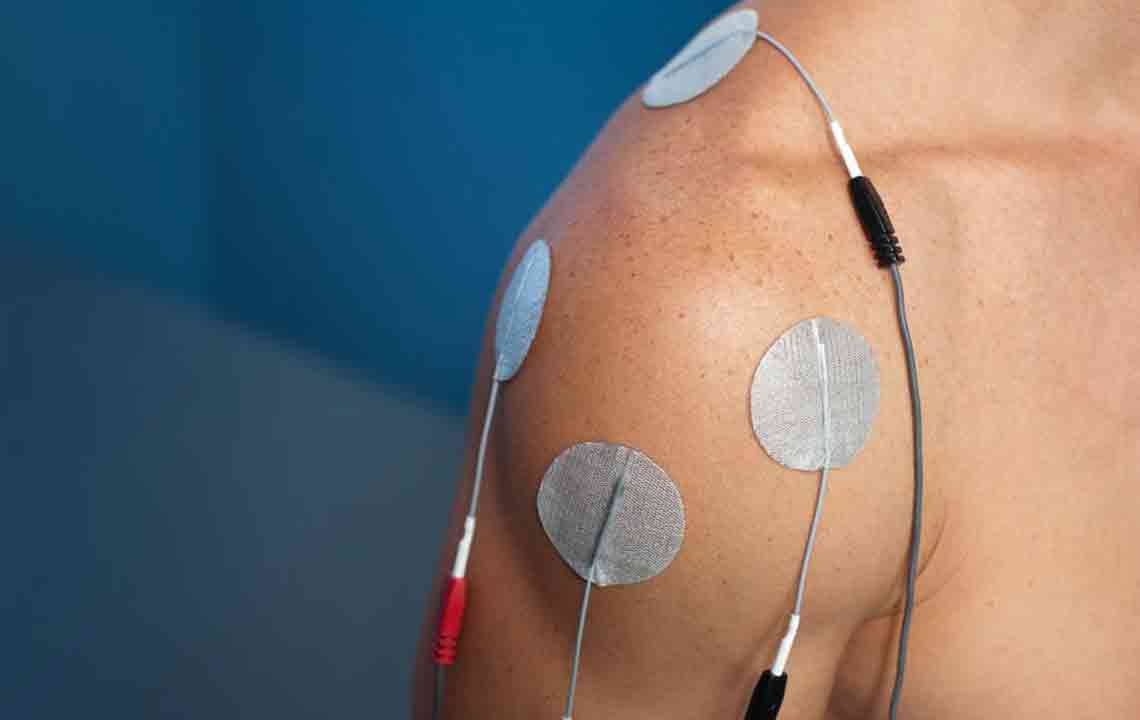
4. Corticosteroid Injections: Targeted Inflammation Control
For persistent symptoms, corticosteroid injections directly into the shoulder joint can provide rapid and significant pain relief by reducing inflammation. These injections are typically administered under imaging guidance, such as X-ray or ultrasound, to ensure precise delivery. While effective, their effects are temporary, lasting a few months, and repeated injections should be avoided to minimize potential side effects like joint damage or osteoporosis.
5. Surgical Interventions for Severe Cases
When conservative treatments do not yield desired results, minimally invasive procedures like arthroscopic capsular release can be considered. This surgery involves small incisions to cut through tight tissues and fascia, providing immediate improvement in shoulder mobility. Such procedures are usually performed under local anesthesia and require post-operative physiotherapy for optimal recovery.
Additionally, hydrodilatation or shoulder distension, which involves injecting a mixture of steroids, saline, and anesthetic into the joint, can help stretch the capsule, reduce scar tissue, and provide lasting relief. This outpatient procedure offers quick benefits and can be repeated if necessary.
6. Lifestyle Modifications to Promote Healing
Managing frozen shoulder effectively also involves adopting lifestyle habits that support joint health. Regularly performing prescribed stretches, maintaining good posture, and avoiding activities that strain the shoulder are crucial. For individuals with underlying conditions like diabetes, managing blood sugar levels diligently can prevent recurrence or worsening of symptoms. An overall healthy diet, weight management, and avoiding smoking enhance tissue healing and reduce inflammation.
7. Prevention and Long-term Maintenance
Preventing frozen shoulder from recurring involves ongoing shoulder care even after recovery. Incorporate daily stretching routines, stay active, and monitor any signs of stiffness or pain. If symptoms reappear, seek early intervention to prevent significant restriction of movement. Additionally, addressing contributory health issues such as hypothyroidism or neurological conditions can markedly reduce risks.
With a comprehensive approach combining physiotherapy, medication, minimally invasive procedures, and lifestyle adjustments, individuals diagnosed with frozen shoulder can achieve faster recovery and regain normal shoulder function. Early diagnosis and consistent adherence to treatment plans are vital for optimal results.
In summary, understanding the multifaceted management strategies for frozen shoulder enables patients to take active roles in their recovery process, leading to improved quality of life and reduced discomfort.