Complete Overview of Rotator Cuff Injury Treatment and Recovery
This comprehensive guide details the causes, symptoms, non-surgical treatments, and surgical options for rotator cuff injuries. It emphasizes the importance of early intervention, proper rehabilitation, and choosing experienced surgeons to ensure successful recovery and shoulder health. Suitable for athletes and active individuals, the article provides insights into preventing and managing rotator cuff damage effectively.
Effective Strategies for Managing Rotator Cuff Injuries
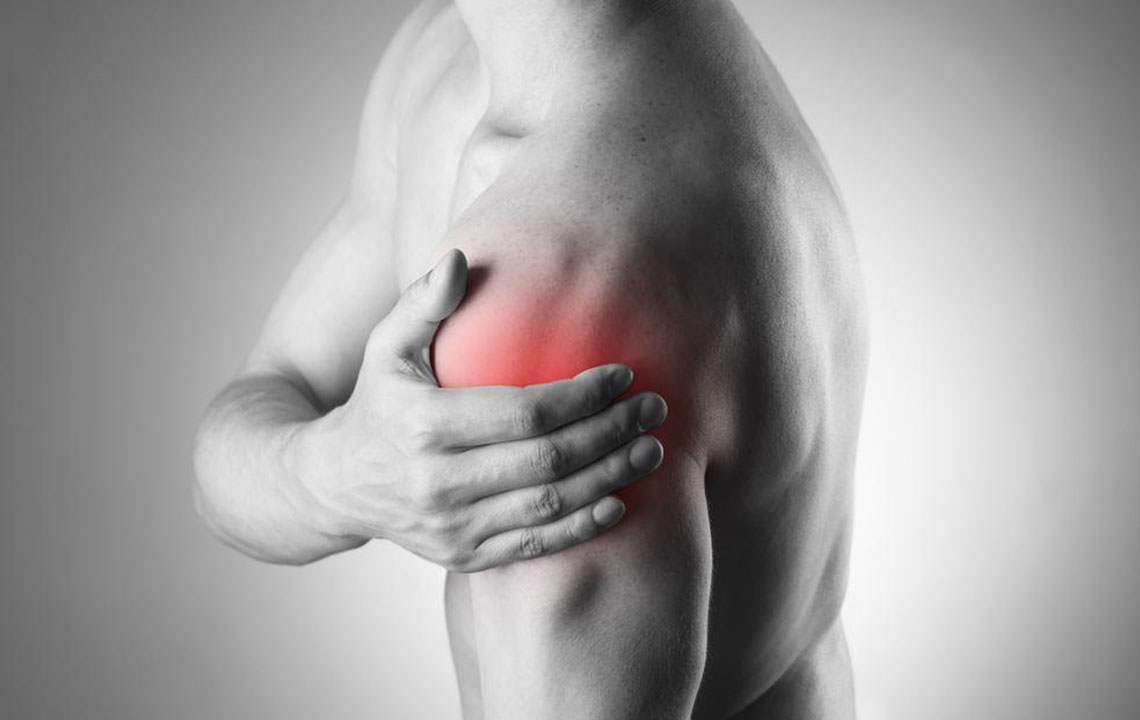
Rotator cuff injuries are common among individuals involved in repetitive overhead movements or high-impact sports. These injuries affect a group of muscles and tendons that secure the shoulder joint, enabling a full range of motion and stability. The rotator cuff consists of four primary muscles: supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, and subscapularis. Damage to any of these components can lead to significant functional impairment and may require a combination of treatments to heal properly.
Injuries to the rotator cuff can occur suddenly due to trauma, such as falls or heavy lifting, or develop gradually from overuse or degeneration. Tendonitis, characterized by inflammation of the tendons, significantly increases the risk of subsequent rotator cuff injuries. Athletes like baseball players, tennis players, weightlifters, and painters are particularly vulnerable to repetitive strain injuries, while accidental falls or lifting heavy objects can cause acute tears. Early prevention measures such as proper training, strengthening exercises, and ergonomic practices are vital. However, if injury occurs, timely medical intervention is essential to prevent chronic dysfunction and degenerative changes in the shoulder joint.
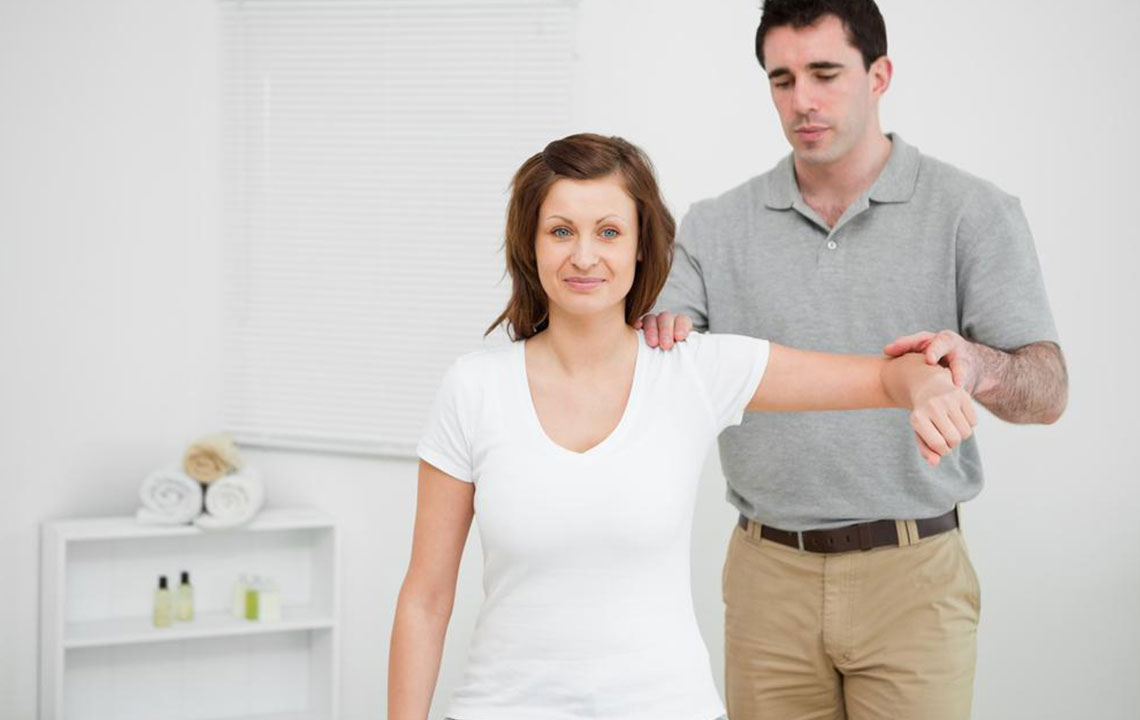
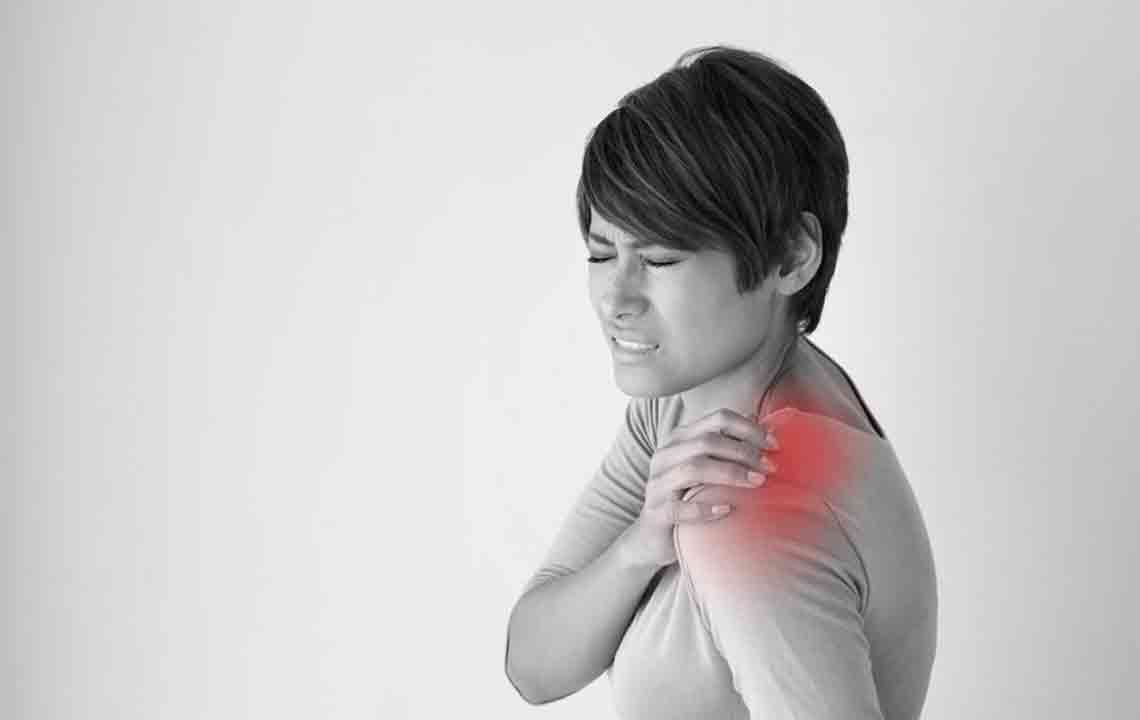
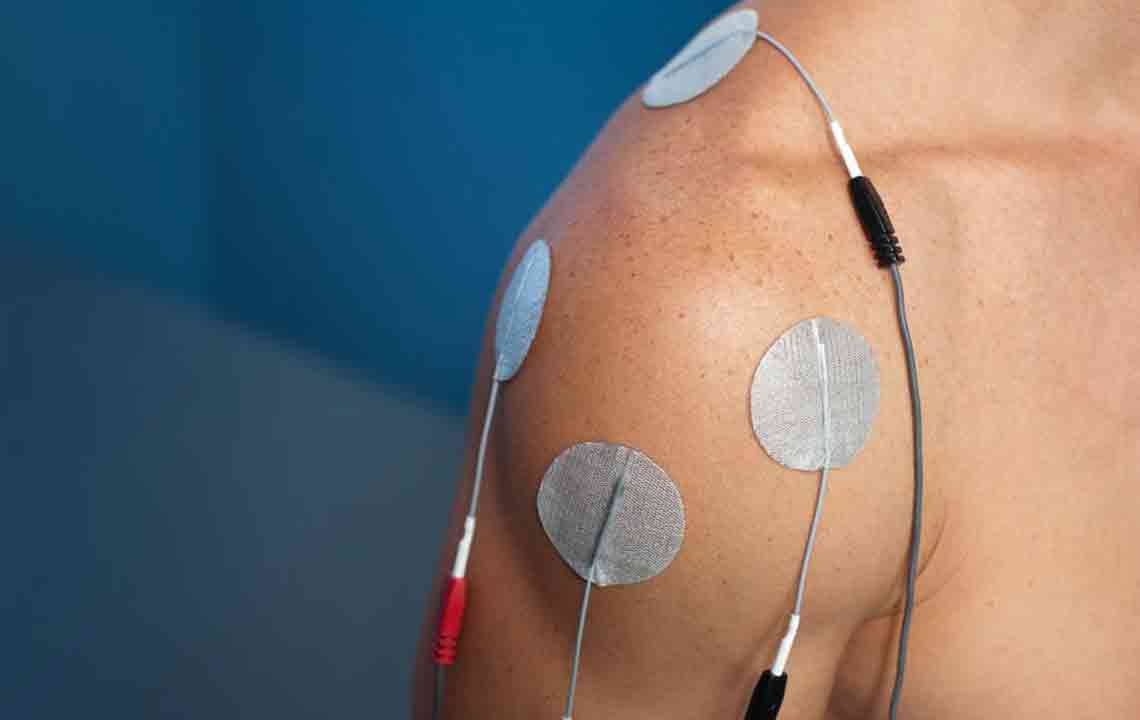
The symptoms of rotator cuff injuries often include intense, localized shoulder pain, especially when lifting or lowering the arm, along with stiffness, swelling, and a noticeable decrease in mobility. These symptoms can severely impact daily activities, from dressing to basic household chores. Fortunately, advancements in medical technology have expanded treatment options. Most mild to moderate cases respond well to conservative therapies, while severe injuries may require surgical repair. Non-invasive treatments such as rest, ice or heat therapy, and physiotherapy can significantly help restore shoulder function and alleviate pain. Implementing home exercises and proper rehabilitation strategies accelerates recovery, reduces the risk of future injuries, and improves overall shoulder health.
Surgical intervention typically involves reattaching torn tendons directly to the bone using specialized suture anchors, which are often designed from dissolvable materials. The minimally invasive nature of arthroscopic surgery allows for smaller incisions, less pain, faster recovery, and less scarring. During these procedures, surgeons use a small camera—an arthroscope—to visualize the shoulder joint precisely. Post-operative care includes immobilization, pain management, physical therapy, and gradually increasing activity levels to facilitate optimal healing. Adhering to the surgeon’s guidelines and engaging in prescribed physiotherapy is crucial for restoring maximum shoulder strength and mobility.
When is surgery recommended? Typically, surgical repair becomes necessary when conservative treatments fail to alleviate persistent pain, especially in active individuals or athletes, or when imaging reveals a large tear or significant shoulder instability. Minor tears or inflammation often heal well with rest, corticosteroid injections, and physiotherapy, but larger or complete tears frequently require surgical correction. Factors influencing the decision include age, activity level, and overall health. In some cases, early surgical intervention can prevent further joint deterioration and offer better long-term outcomes.
All surgical procedures carry inherent risks, including anesthesia reactions, excessive bleeding, infections, nerve damage, or stiffness. Therefore, choosing a highly experienced orthopedic surgeon with specialized training in shoulder repairs is critical. Patients are advised to discuss potential risks and benefits thoroughly before proceeding. Post-surgery, adherence to physical therapy and follow-up appointments is vital for optimal recovery. For many, surgical repair results in substantial pain relief, restored shoulder function, and an improved quality of life, especially when performed promptly and with proper post-operative care. If shoulder pain or dysfunction persists despite non-surgical treatments, surgical options can offer a reliable solution for restoring shoulder health and preventing future issues.