Comprehensive Guide to Shoulder Discomfort: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Treatments
This detailed guide explores the leading causes of shoulder discomfort, including rotator cuff tendinitis, tears, frozen shoulder, and bursitis. It explains symptoms and offers effective treatment options like physiotherapy, medication, and surgery. Understanding these common issues helps in early prevention and proper management to restore shoulder health and mobility. Whether you're experiencing mild soreness or severe pain, knowing the root causes can guide timely intervention and long-term recovery.
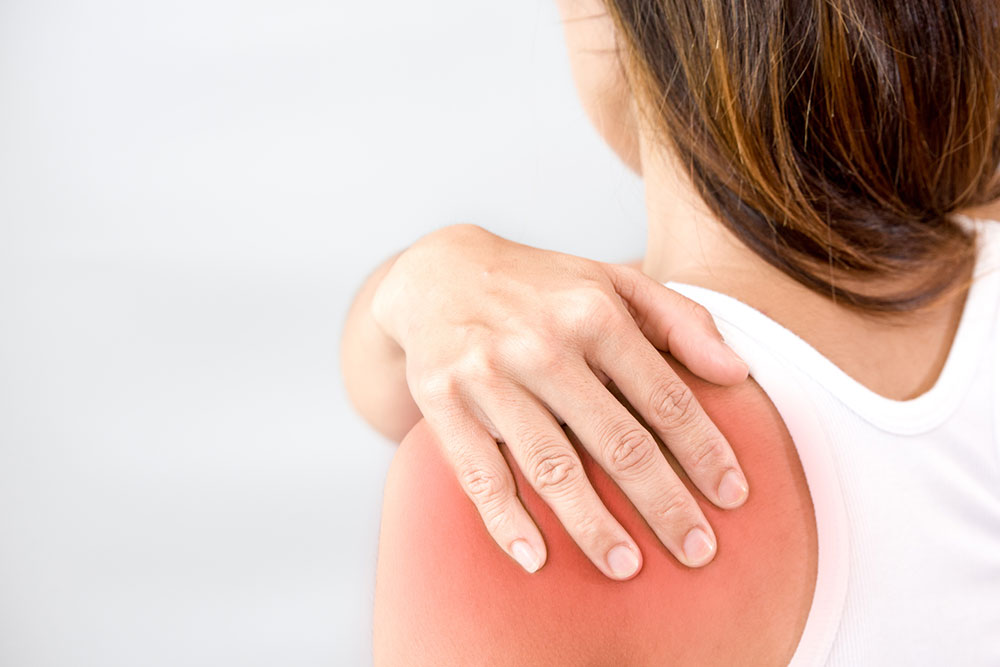

Understanding Common Causes of Shoulder Discomfort and How to Manage Them
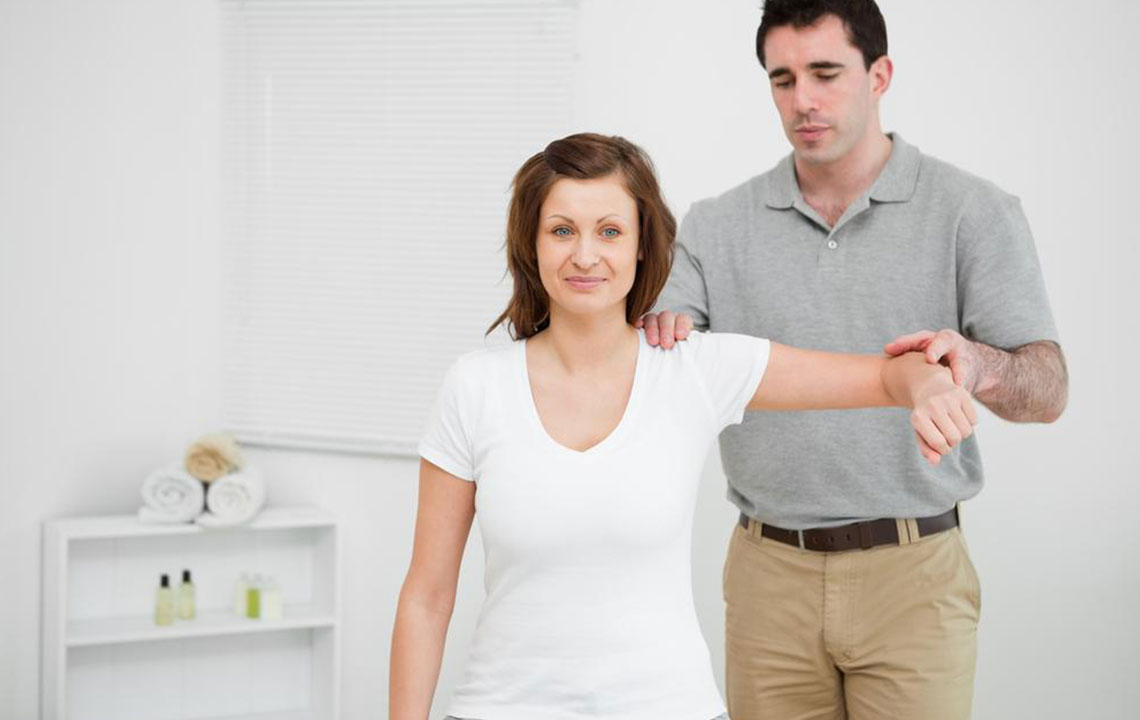
Are you experiencing difficulty lifting your arm or persistent shoulder pain that hampers daily activities? Shoulder discomfort is a widespread issue that affects a significant portion of the population at some point in their lives. From minor discomfort to severe pain, the causes are numerous, and understanding the underlying issues is crucial for effective management and recovery. This comprehensive guide explores the primary reasons behind shoulder pain, their symptoms, and the most effective treatment options available today.
The shoulder joint stands out as one of the most mobile joints in the human body. It comprises a complex network of bones, muscles, tendons, and ligaments that work together seamlessly to allow a wide range ofmotion. This incredible flexibility enables activities such as lifting overhead, swinging a racket, throwing a ball, or reaching behind your back. However, this very complexity makes the shoulder susceptible to various injuries and degenerative conditions.
Maintaining joint health is vital for daily life, as wear and tear can accumulate over time, leading to discomfort, stiffness, and pain. Here, we delve into the most common causes of shoulder pain and how they can be addressed effectively:
Rotator cuff tendinitis
Rotator cuff tears
Frozen shoulder
Shoulder bursitis
Rotator cuff tendinitis
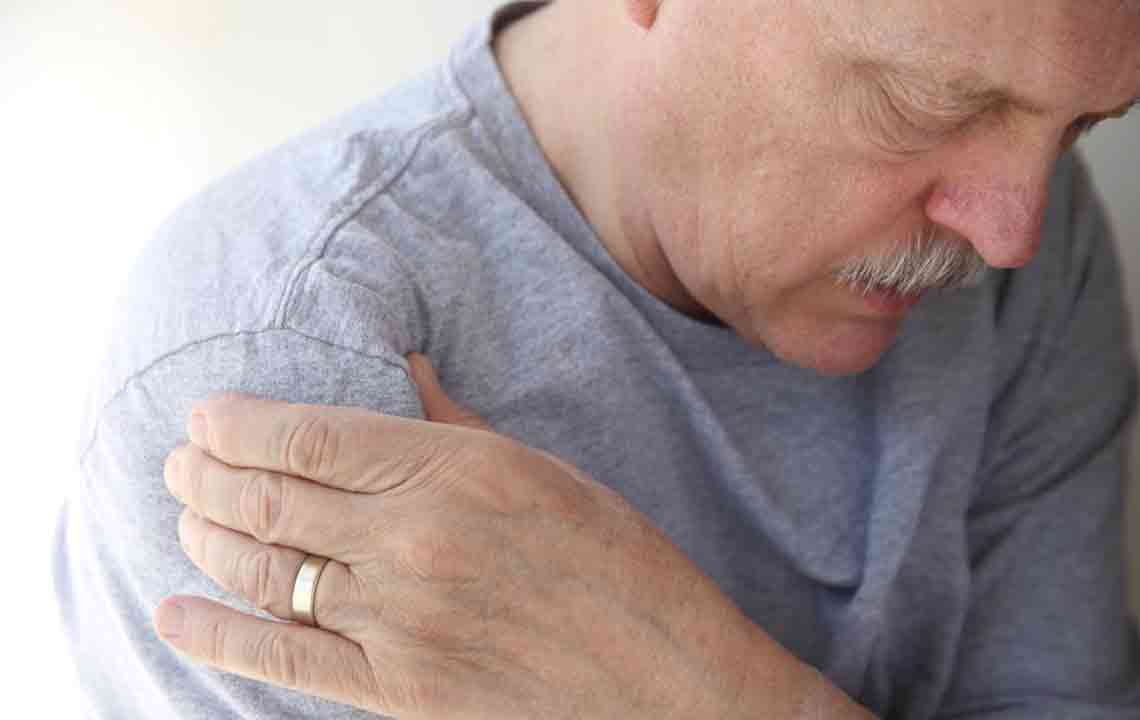
One of the leading causes of shoulder pain is rotator cuff tendinitis, an inflammation of the tendons that support and stabilize the shoulder joint. Repetitive overhead activities, such as swimming, painting, or lifting heavy objects, can cause tiny tears or inflammation in these tendons. Patients often experience mild discomfort initially, which can escalate to persistent pain, especially when raising the arm or sleeping on the affected side.
Managing tendinitis typically involves a combination of rest, application of ice or heat packs, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and targeted physiotherapy exercises aimed at strengthening shoulder muscles. Early intervention is vital to prevent progression and chronicity.
Rotator cuff tears
Rotator cuff tears can be partial or complete and often result from acute trauma or degenerative changes associated with aging. Activities that involve repetitive shoulder movements or heavy lifting increase susceptibility. Patients report sudden pain, weakness in lifting or rotating the arm, clicking sounds, and stiffness. Severe cases may impair movement significantly.
Depending on the severity, treatment may include conservative methods such as rest, ice application, NSAIDs, and physical therapy. In cases of complete tears or persistent symptoms, surgical repair might be necessary to restore shoulder function.
Frozen shoulder (Adhesive capsulitis)
This disabling condition is characterized by severe stiffness and limited range of motion. It develops due to thickening and inflammation of the shoulder capsule, which progressively restricts movement. Frozen shoulder is particularly common in middle-aged individuals, especially women, and is often linked to underlying health conditions like diabetes, thyroid disorders, or Parkinson’s disease.
The condition progresses through three phases: freezing (pain and increasing stiffness), frozen (stiffness with less pain), and thawing (slow recovery of motion). The entire process can last approximately 18 months. Treatment focuses on physical therapy, pain management, and sometimes corticosteroid injections, with many patients achieving full recovery over time.
Shoulder bursitis
Inflammation of the bursae—small fluid-filled sacs that cushion the shoulder's moving parts—causes bursitis. Overuse, repetitive overhead movements, or trauma can irritate or inflame these sacs, leading to deep, aching pain and swelling. Patients may notice increased discomfort when pressing on the shoulder or during shoulder movements.
Management includes rest, physiotherapy, anti-inflammatory medications, and sometimes aspiration of the bursa if swelling is significant. Proper treatment usually results in symptom relief, but persistent bursitis may require more advanced interventions.
Additional causes contributing to shoulder pain encompass labral tears, impingement syndrome, osteoarthritis, and shoulder dislocations. While initial home remedies like rest, ice, and over-the-counter medications can provide temporary relief, it is essential to seek professional medical evaluation for persistent or severe symptoms. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are crucial in preventing long-term damage and restoring shoulder function.