Comprehensive Guide to Hepatitis C: Causes, Symptoms, and Modern Treatment Strategies
Hepatitis C is a prevalent viral liver infection with often silent progression. This detailed guide covers causes, symptoms, and the latest treatment options, emphasizing the importance of early diagnosis and effective antiviral therapies. Learn about transmission risks, prevention techniques, and lifestyle modifications that aid in managing and curing Hepatitis C, reducing long-term liver complications and improving quality of life.
Comprehensive Guide to Hepatitis C: Causes, Symptoms, and Modern Treatment Strategies
Hepatitis C is a significant viral infection affecting the liver, caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV). It is a leading cause of chronic liver disease worldwide. The disease primarily results in liver inflammation that can progress to fibrosis, cirrhosis, or even liver cancer if left untreated. Unlike some other hepatitis infections, Hepatitis C often remains asymptomatic for years, which makes early detection challenging but essential for successful management. This comprehensive guide explores the causes, symptoms, diagnostic methods, and the latest treatment options for Hepatitis C, providing valuable insights for those at risk or diagnosed with the condition.
Hepatitis C spreads mainly through exposure to infected blood. Common transmission routes include sharing contaminated needles or syringes, receiving unscreened blood transfusions, or organ transplants from infected donors. Less frequently, the virus can be transmitted through skin piercings or tattooing if sterile procedures are not followed. Sexual transmission is considered possible but is relatively rare, and casual contact such as hugging or sharing utensils does not spread the virus. Understanding these transmission routes helps in implementing proper preventive measures. Early diagnosis is crucial, especially since many individuals remain asymptomatic for years. Recognizing the symptoms—ranging from mild fatigue to severe jaundice—is vital for prompt treatment and preventing long-term complications.
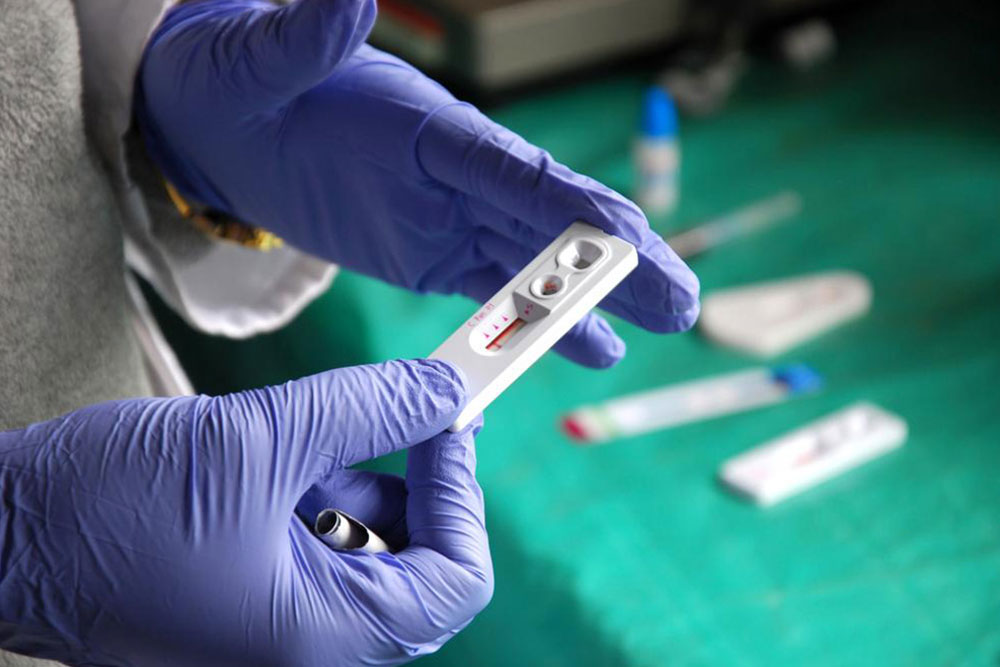
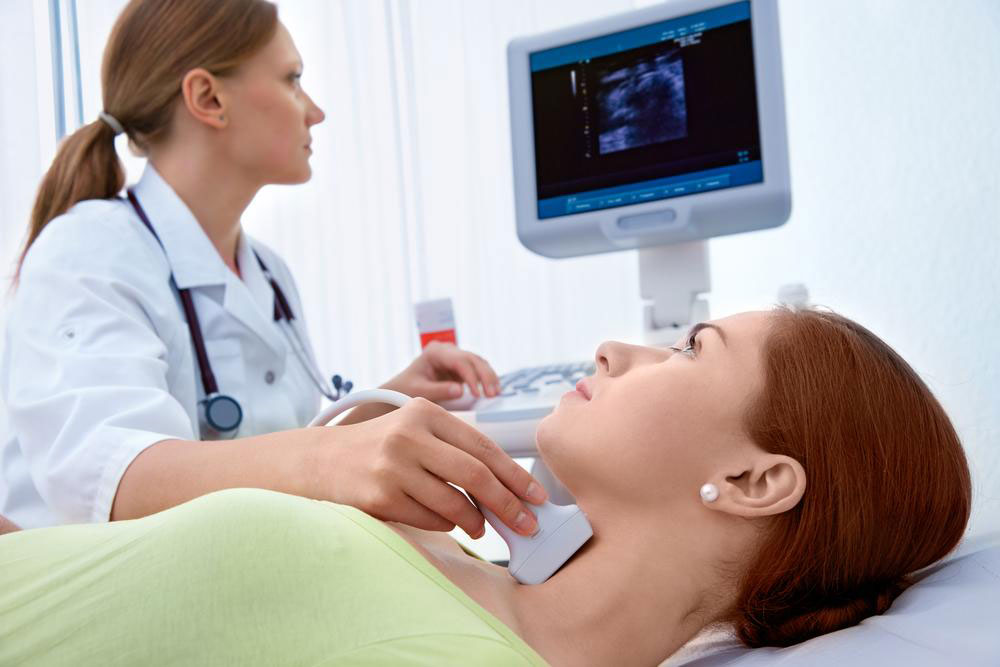
Knowing the symptoms and undergoing timely testing are critical steps in managing Hepatitis C. In the early stages, individuals might experience subtle signs such as fatigue, loss of appetite, nausea, and mild jaundice—yellowing of the skin and eyes. As the infection advances, more severe symptoms like abdominal pain, dark urine, and bleeding problems may manifest. Some patients might develop depressive symptoms or experience weight loss. Since these signs can mimic other illnesses, blood tests are essential for accurate diagnosis. Initial screening involves detecting anti-HCV antibodies, while confirmatory RNA tests identify active infection. Recent advances in antiviral medications have revolutionized Hepatitis C treatment, with cure rates now exceeding 95%.
Effective management of Hepatitis C relies heavily on antiviral medications like Daclatasvir, Sofosbuvir, and other direct-acting antivirals (DAAs). These drugs work by targeting specific stages of the viral lifecycle, effectively eliminating the virus from the body. Treatment regimens typically last from 8 to 12 weeks and are highly effective, even in patients with advanced liver disease. Adherence to the prescribed treatment is essential for success. Additionally, lifestyle modifications such as avoiding alcohol, maintaining a balanced diet, and quitting smoking can help improve liver health during and after treatment.
Prevention measures are a cornerstone of controlling Hepatitis C spread. These include using sterile needles for injections, testing blood donations thoroughly, and avoiding sharing personal items like razors or toothbrushes that might have blood residues. Healthcare providers emphasize the importance of regular screening, especially for at-risk populations, including intravenous drug users, healthcare workers, and individuals with a history of blood transfusions before the early 1990s. Public health initiatives aim to educate about transmission routes and promote safe practices to minimize new infections. For those diagnosed, regular follow-up is essential to monitor liver health and evaluate treatment efficacy.
Additional factors that exacerbate liver damage include lifestyle choices such as alcohol consumption and smoking. These habits can accelerate liver scarring and increase the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma. Therefore, comprehensive care involves not only antiviral therapy but also lifestyle counseling and management of co-existing conditions like obesity or diabetes. Emerging therapies continue to improve outcomes for Hepatitis C patients worldwide. Staying informed and proactive about testing and treatment options remains vital in reducing the global burden of this silent yet potentially devastating disease.