Comprehensive Guide to Head and Neck Cancers: Symptoms, Types, and Early Detection
Discover a comprehensive overview of head and neck cancers, including their common types, early warning signs, risk factors, and modern treatment approaches. Early detection through awareness of symptoms like persistent mouth sores, neck lumps, and voice changes can dramatically improve patient outcomes. Learn about preventive strategies, diagnostic methods, and the latest advances in treatment that are transforming the prognosis for those affected by these complex malignancies. Stay informed to recognize early signs and seek timely medical care for better health outcomes.
Head and neck cancers encompass a broad spectrum of malignant tumors that develop in various regions within the head and neck area. These cancers can manifest in multiple parts of the head, including the oral cavity, pharynx, larynx, sinuses, salivary glands, and other adjacent tissues. Due to the complex anatomy and vital functions of these areas, early detection is critical for effective treatment and improved prognosis. Recognizing the early signs and understanding the common types of head and neck cancers can significantly enhance patient outcomes through timely medical intervention.
Understanding the Anatomy and Types of Head and Neck Cancers
Head and neck cancers are not a single disease but a collection of different malignancies arising in specific anatomical sites. The most common types include:
Oral Cavity Cancers: Affecting the lips, tongue, gums, floor of the mouth, and palate. These are often associated with tobacco use, alcohol consumption, and human papillomavirus (HPV) infection.
Pharyngeal Cancers: Developing in the throat, including the nasopharynx, oropharynx, and hypopharynx, often linked to HPV and smoking.
Laryngeal Cancers: Involving the voice box, which can impact speech and breathing. Heavy smoking and alcohol are significant risk factors.
Sinus and Nasal Cavity Cancers: Forming in the paranasal sinuses and nasal cavity, presenting with facial pain, nasal obstruction, and sometimes vision problems.
Salivary Gland Tumors: Affecting the glands that produce saliva, leading to facial swelling, pain, and difficulty swallowing.
The Importance of Recognizing Early Signs
Early diagnosis of head and neck cancers relies heavily on recognizing characteristic symptoms. These signs can often be subtle and mistaken for benign conditions, which underscores the importance of awareness. Some of the key early symptoms include:
Persistent mouth sores that do not heal within two weeks.
Unexplained pain or tenderness in the mouth, throat, or neck.
Speech changes or hoarseness lasting more than two weeks.
Difficulty swallowing or a feeling of food sticking in the throat.
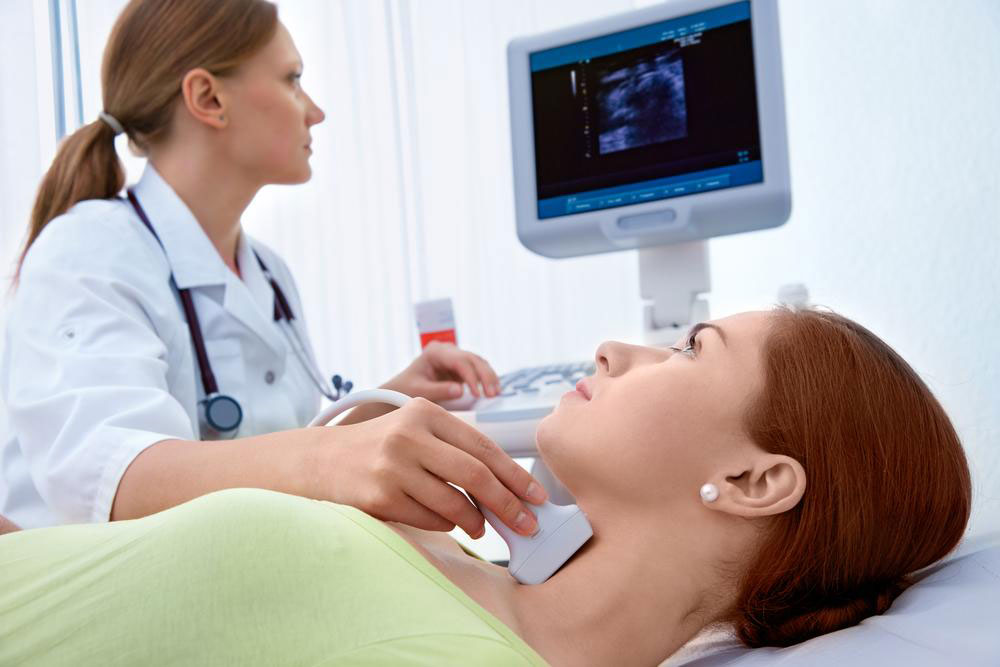
Unexplained neck lumps or swelling.
Facial pain or numbness, particularly around the jaw.
Persistent nasal congestion or bleeding.
Loss of taste or persistent foul breath.
Noticing these symptoms early and consulting a healthcare professional can lead to prompt diagnosis and more effective treatment options, potentially saving lives.
Risk Factors and Prevention Strategies
Several lifestyle factors and environmental exposures increase the risk of developing head and neck cancers. These include:
Tobacco use: Cigarettes, cigars, pipe smoking, and smokeless tobacco are strong contributors.
Alcohol consumption: Heavy drinking significantly elevates risk, especially when combined with tobacco.
Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection: Certain strains of HPV are linked to oropharyngeal cancers.
Prolonged sun exposure: Increases risk for lip cancers.
Poor oral hygiene and chronic irritation: Can predispose to some oral cancers.
Preventative measures include quitting tobacco, limiting alcohol intake, practicing good oral hygiene, using sun protection for lips, and receiving HPV vaccinations where appropriate. Regular dental check-ups and awareness about early signs are crucial components of prevention.
Diagnosis and Treatment Approaches
Early detection is vital and involves a combination of physical examinations, imaging studies such as CT scans, MRIs, and PET scans, and biopsy procedures. Multidisciplinary teams—including oncologists, ENT specialists, radiologists, and speech therapists—collaborate to develop personalized treatment plans.
Treatment options depend on the location and stage of the tumor and can include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy. Advances in minimally invasive surgical techniques and targeted treatments have improved the quality of life and survival rates for many patients.
Living with Head and Neck Cancers
Beyond treatment, patients often face challenges related to speech, swallowing, and appearance. Rehabilitation services, including speech therapy and nutritional support, play essential roles in recovery. Support groups and counseling offer emotional assistance during and after treatment.
Conclusion
Head and neck cancers present a complex array of malignancies requiring heightened awareness for early detection. Recognizing the early signs like mouth sores, neck lumps, persistent pain, and voice changes can lead to earlier diagnosis, significantly improving treatment outcomes. Emphasizing risk factor modification, regular screening, and prompt medical attention are fundamental in combating these cancers. With ongoing advances in medical technology and targeted therapies, the outlook for patients continues to improve, highlighting the importance of awareness and proactive healthcare engagement.