Comprehensive Guide to HIV: Recognizing Symptoms and Effective Treatment Approaches
This comprehensive article explores HIV, detailing symptoms at various stages, emphasizing early detection, and highlighting modern treatment options. It offers valuable insights into prevention, management, and reducing stigma, aiming to educate and empower individuals about living with HIV. Emphasizing the importance of early testing and consistent treatment, the guide underscores advances in medical science that enable those infected to lead healthy lives, playing a vital role in global health efforts against HIV/AIDS.
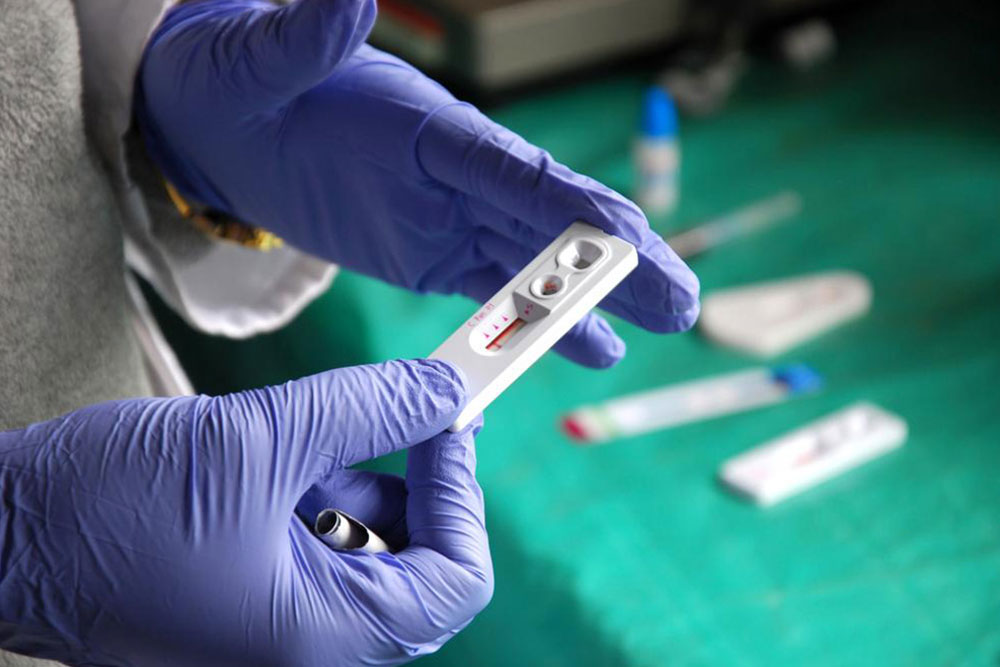
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) remains a significant global health challenge, impacting millions of lives worldwide. Understanding the nature of HIV, its symptoms, and the approaches to management is crucial for early detection and effective treatment. This comprehensive guide aims to provide an in-depth overview of HIV, detailing the symptoms associated with different stages of the infection, the importance of early diagnosis, and the latest strategies for management to prevent progression to AIDS. By increasing awareness and knowledge, individuals can better protect themselves and seek timely medical care to maintain their health and well-being.
What is HIV? An Overview
HIV is a virus that attacks the body’s immune defense system, specifically targeting CD4 cells, also known as T-helper cells. These cells play a vital role in helping the immune system combat infections. When HIV destroys these cells, the body's ability to fight common infections and certain cancers diminishes, leading to a weakened immune system. If untreated, HIV can lead to AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome), the most severe phase of HIV infection, where the immune system becomes so compromised that life-threatening opportunistic infections and cancers can develop.
Stages of HIV Infection
1. Acute HIV Infection
This initial stage occurs within 2 to 4 weeks after exposure to the virus. Many individuals experience flu-like symptoms, which can often be mistaken for other illnesses. Symptoms include fever, rash, sore throat, headache, muscle aches, and swollen lymph nodes. During this period, the viral load in the blood is high, and the individual is highly contagious. Recognizing these early signs is crucial for prompt testing and treatment.
2. Clinical Latency Stage
The second stage, also known as asymptomatic or chronic HIV infection, can last for several years. During this time, the virus continues to multiply at low levels. People may experience mild or no symptoms; therefore, many remain unaware of their infection. Regular testing is vital because individuals can still transmit the virus even when no symptoms present. This stage can be effectively managed with antiretroviral therapy (ART), which can suppress the virus and prevent progression to AIDS.
3. AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome)
The final and most severe stage of HIV infection occurs when the immune system becomes badly damaged. Without treatment, individuals typically develop opportunistic infections or certain cancers that are rare in people with healthy immune systems. Symptoms include persistent fever, rapid weight loss, extreme fatigue, night sweats, swollen lymph nodes, and neurological issues. Without intervention, AIDS can be fatal.
Recognizing Symptoms of HIV
Understanding the symptoms associated with each stage of HIV is essential for early diagnosis and treatment. Common symptoms during the initial infection phase include:
Fever
Rash
Sore throat
Muscle and joint pain
Swollen lymph nodes, especially in the neck and armpits
Headaches
Night sweats
Fatigue
As the infection progresses into the chronic stage, symptoms may subside or be mild, which often leads to underdiagnosis. However, as the disease advances toward AIDS, symptoms become more severe and include:
Unexplained weight loss
Chronic diarrhea
Persistent fevers and night sweats
Rapid or unexplained fatigue
Lesions or skin issues
Neurological complications such as memory loss or confusion
Importance of Early Testing and Diagnosis
Early detection of HIV is vital for effective management. Many individuals remain unaware of their status because symptoms can be mild or nonexistent, especially during the latent stage. Regular testing, especially for those at higher risk, allows for timely initiation of antiretroviral therapy, which can suppress the virus, maintain immune function, and greatly reduce the risk of transmitting the virus to others.
Modern HIV Management and Treatment Strategies
Advancements in medical research have led to the development of highly effective antiretroviral drugs that control the replication of HIV. ART does not cure HIV but suppresses the virus to undetectable levels, enabling individuals to lead healthy lives. Consistent adherence to treatment regimens is essential for maintaining viral suppression and preventing drug resistance.
Besides medication, comprehensive management includes regular health monitoring, lifestyle modifications, and addressing co-infections or other health issues. In some cases, healthcare providers may recommend prophylactic measures to prevent opportunistic infections.
Preventative Measures and Reducing Transmission Risks
Prevention remains a cornerstone in controlling HIV spread. Safe sex practices, including consistent condom use, are highly effective. Other preventive options include Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis (PrEP) for high-risk individuals, Regular testing, and minimizing sharing of needles or syringes. Educating communities about HIV transmission routes ensures broader awareness and encourages testing and safe practices.
Stigma and Support for People Living with HIV
Addressing social stigmas associated with HIV is vital for encouraging more people to seek testing and treatment. Support groups, counseling, and public education campaigns help combat misinformation and stigma. Healthcare providers play a crucial role in providing compassionate care and guidance, ensuring that individuals living with HIV can maintain a good quality of life.
Conclusion: Taking Action Against HIV
Understanding the symptoms, transmission, and management of HIV empowers individuals to protect themselves and their loved ones. Early testing and consistent treatment are key to living healthy lives despite the diagnosis. Advances in treatment have transformed HIV from a fatal condition to a manageable health issue. Public awareness, education, and ongoing research are fundamental pillars in the global effort to reduce new infections and improve quality of life for those affected.