Comprehensive Guide to Effectively Managing Psoriatic Arthritis
This comprehensive guide provides detailed insights into managing psoriatic arthritis effectively. It covers recognizing early symptoms, understanding causes, exploring treatment options, and adopting lifestyle changes that help alleviate symptoms and prevent joint damage. Whether you are newly diagnosed or seeking ways to improve symptom control, this article offers valuable strategies and expert advice for a holistic approach to psoriatic arthritis management.
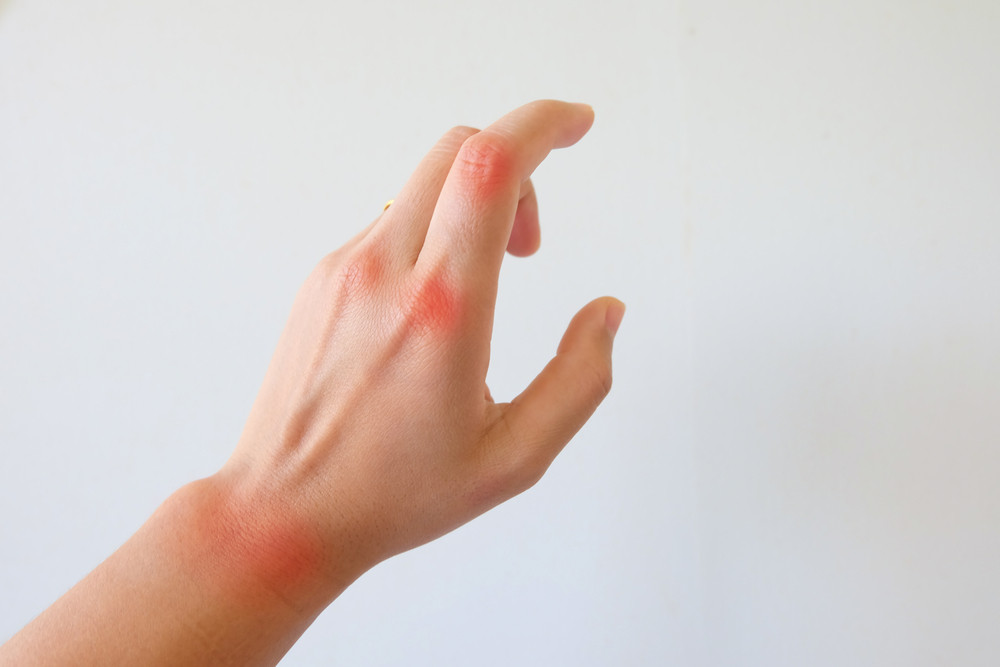

Comprehensive Strategies for Managing Psoriatic Arthritis
Expert Guidelines for Managing Psoriatic Arthritis
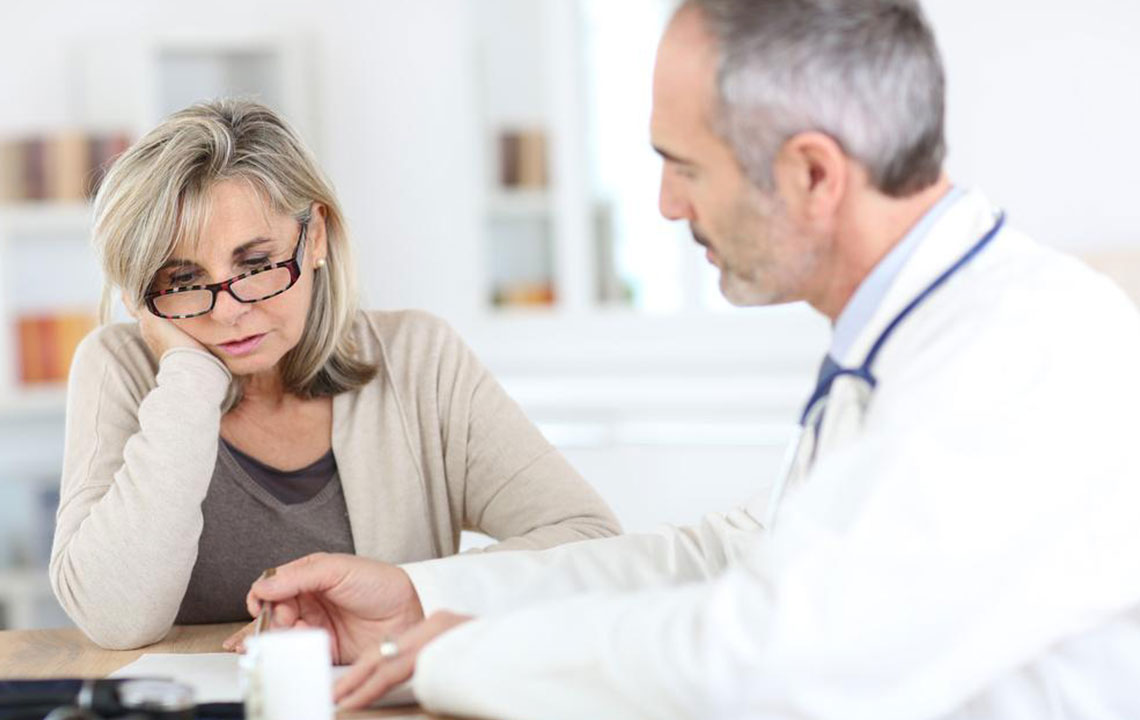
Psoriatic arthritis is a complex, inflammatory autoimmune condition that commonly coexists with psoriasis, a chronic skin disorder characterized by the appearance of itchy, red, and often scaly patches on the skin. It affects approximately 30% of individuals suffering from psoriasis, making it a significant health concern that requires attentive management. This form of arthritis can cause joint pain, swelling, and stiffness, and can sometimes lead to joint deformity if left untreated. The disease often impacts joints in fingers, toes, elbows, knees, and sometimes the spine, diminishing quality of life and functional ability. Although there is currently no cure for psoriatic arthritis, a variety of medical treatments combined with lifestyle modifications can substantially reduce symptoms and slow disease progression.
This comprehensive guide aims to provide you with detailed information on how to manage psoriatic arthritis effectively, including recognizing symptoms early, understanding its causes, exploring the available treatment options, and adopting lifestyle changes that can support symptom control and improve overall well-being.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Psoriatic Arthritis
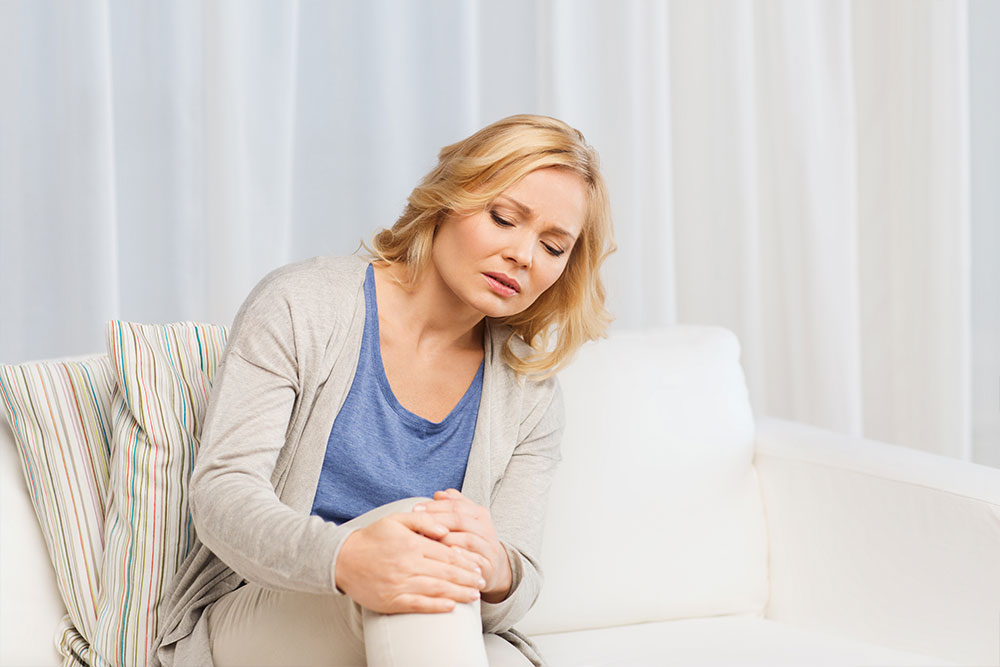
Symptoms of psoriatic arthritis vary widely among individuals but tend to follow a common set of signs that can help with early diagnosis and prompt management. The initial symptoms may be subtle or easily mistaken for other conditions, so awareness is vital. As the disease progresses, more distinct signs become evident. Key symptoms to watch out for include:
Swelling in fingers and toes, often described as sausage-like deformities
Grooved, pitted, or misshapen nails
Exacerbation of psoriasis, with thickened, erythematous, and scaly skin patches
Persistent joint stiffness, especially after periods of inactivity
Joint pain and tenderness, impacting daily activities
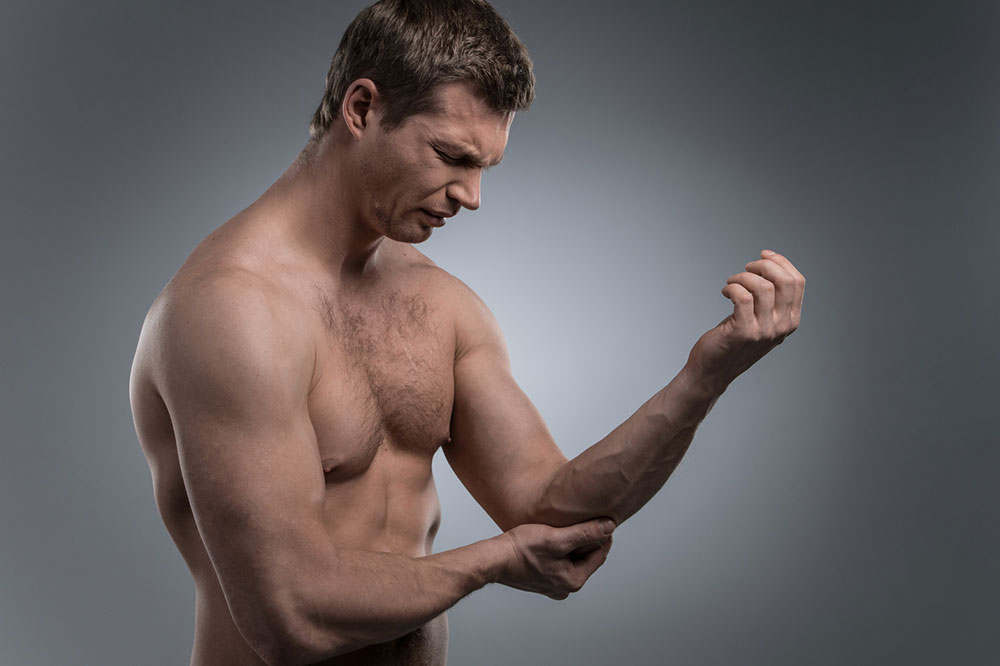
Enthesitis — inflammation where tendons or ligaments attach to bones, causing localized pain and tenderness
Fatigue, which can be severe and affect overall energy levels
Eye problems such as redness, soreness, dryness, irritation, or blurred vision
Early detection of these symptoms can significantly improve management outcomes, and individuals experiencing these signs should consult a healthcare professional promptly for accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment plans.
Understanding the Causes of Psoriatic Arthritis
The root cause of psoriatic arthritis remains partially understood, but it is firmly linked to psoriasis, an autoimmune disorder where the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin and joint tissues. The immune dysfunction leads to inflammation, which causes both skin and joint symptoms. Genetic predisposition also plays a role, with a family history increasing the risk. Environmental factors such as infections or trauma may act as triggers in susceptible individuals. Most patients affected are adults between their 30s and 50s, highlighting the importance of early recognition and intervention in this age group.
Available Treatments for Psoriatic Arthritis
Managing psoriatic arthritis involves a range of medical strategies designed to reduce inflammation, control symptoms, and prevent joint damage. The choice of treatment depends on the severity of disease activity, the extent of joint and skin involvement, and individual patient factors. Medical professionals often prescribe a combination of therapies tailored to each patient’s needs:
NSAIDs (Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs): These are the first line of defense for mild to moderate symptoms, helping to alleviate pain, stiffness, and swelling. They are available over the counter or by prescription, and should be used under medical supervision to minimize side effects.
Topical Treatments: Corticosteroid creams, ointments, and medicated shampoos applied directly to affected skin can reduce inflammation, itching, and scaling. They are often used in conjunction with systemic therapies for comprehensive management.
Corticosteroids: Administered orally or through targeted injections, corticosteroids provide potent anti-inflammatory effects, particularly useful during flare-ups or for severe joint pain.
DMARDs (Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs): These drugs, such as methotrexate, sulfasalazine, and leflunomide, work by suppressing immune activity to prevent joint destruction and reduce inflammation. They require careful monitoring due to potential side effects.
Biologic Therapies: Modern biologics target specific components of the immune system, such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors, interleukin blockers, and other monoclonal antibodies. They have revolutionized psoriatic arthritis treatment for patients with moderate to severe disease that doesn't respond to traditional therapies.
Phototherapy: Controlled ultraviolet (UV) light treatments can be effective in managing skin symptoms, particularly for stubborn psoriasis patches. These therapies should be carried out under specialized medical supervision.
It is crucial to consult healthcare professionals before initiating any treatment, including over-the-counter options. Regular follow-up allows for adjustments based on treatment response and potential side effects, ensuring safe and effective disease management.
Supporting Management with Natural and Lifestyle Approaches
In addition to prescribed medications, lifestyle choices significantly influence disease outcomes and overall quality of life. Here are some natural and practical strategies to complement medical treatment for psoriatic arthritis:
Balanced Anti-Inflammatory Diet: Emphasize foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and vitamins such as fruits, vegetables, fatty fish, nuts, and seeds. Reduce intake of processed foods, refined sugars, saturated fats, and alcohol, all of which can exacerbate inflammation.
Stress Management Techniques: Chronic stress can trigger flare-ups. Incorporate relaxation practices such as yoga, meditation, tai chi, or deep-breathing exercises. Adequate sleep and mindfulness can help manage stress levels more effectively.
Regular Exercise: Engage in low-impact activities like swimming, walking, or stretching exercises. Physical activity can improve joint flexibility, strengthen muscles, and boost mental health, aiding in symptom control and overall well-being.
Skin Care Practices: Opt for loose, breathable clothing that minimizes irritation. Use gentle, fragrance-free moisturizers to keep skin hydrated and reduce dryness or cracking. Avoid harsh chemical skincare products that can worsen irritation.
Avoid Smoking and Excessive Alcohol: Both habits are linked to increased inflammation and worsen disease symptoms. Quitting smoking and moderating alcohol intake can lead to better health outcomes.
By integrating these approaches into daily routines, individuals with psoriatic arthritis can experience improved symptom management, enhanced quality of life, and potentially a reduction in medication reliance over time.