Comprehensive Dietary Strategies for Effective Management of Type 2 Diabetes
This comprehensive guide offers effective dietary strategies for managing type 2 diabetes, emphasizing nutrient-rich foods, healthy fats, fiber, and lifestyle changes. Proper nutrition plays a critical role in controlling blood sugar levels and preventing complications. Consulting healthcare professionals for personalized advice is also crucial for optimal diabetes management. These insights can help individuals adopt sustainable dietary habits to improve their overall health and well-being.

Holistic Nutritional Approaches to Control and Manage Type 2 Diabetes
Managing type 2 diabetes effectively is a multifaceted process that involves not only medication but also significant lifestyle changes, particularly focusing on diet and physical activity. Since the condition impacts the body's ability to regulate blood sugar levels properly, adopting specific nutritional strategies can significantly improve symptom management and overall health outcomes. Although the pancreas continues to produce insulin, its efficiency diminishes in individuals with type 2 diabetes, leading to higher blood glucose levels. Therefore, closely monitoring blood glucose levels under medical supervision and using insulin therapy if prescribed become critical components of management.
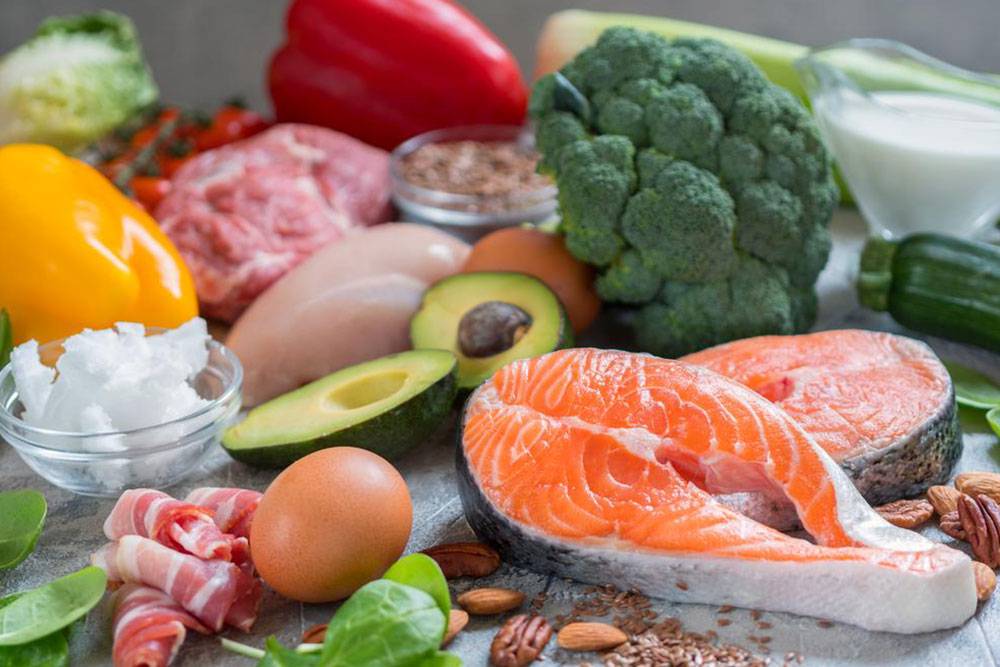
Diet plays a pivotal role in maintaining blood sugar within a healthy range. Implementing balanced eating habits that emphasize nutrient-dense foods can make a substantial difference. Consuming foods high in dietary fiber, such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, helps slow down glucose absorption, preventing sudden spikes in blood sugar post-meals. Incorporating healthy fats, like those found in avocados, nuts, seeds, and oily fish, supports cardiovascular health—a common concern for diabetics. For example, fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which help reduce inflammation and improve lipid profiles.
Incorporate a variety of nutrient-rich foods like whole grains—including oats, barley, and quinoa—known for their low glycemic index and high fiber content. Leafy greens, such as spinach, kale, and Swiss chard, are packed with essential nutrients and antioxidants beneficial for managing blood sugars. Cruciferous vegetables like broccoli, cauliflower, and Brussels sprouts not only add bulk to the diet but also contain compounds that may improve insulin sensitivity. Nuts, especially almonds and walnuts, provide healthy fats and proteins that stabilize blood sugar levels. Additionally, spices like garlic and turmeric have been studied for their potential to enhance insulin sensitivity and reduce inflammation.
Superfoods like flaxseeds and chia seeds are excellent sources of soluble fiber and omega-3s, aiding in blood sugar management and heart health. To personalize your dietary plan, it is highly recommended to consult healthcare professionals or registered dietitians who can tailor advice based on individual health profiles. Combining dietary strategies with regular physical activity, weight management, and medication adherence forms the cornerstone of effective type 2 diabetes control. Remember, early intervention and sustained lifestyle changes can significantly improve quality of life and reduce the risk of complications associated with diabetes.