Comprehensive Strategies for Effectively Managing Gout and Rheumatoid Arthritis: Diet, Lifestyle, and Alternative Therapies
This comprehensive guide offers detailed strategies for managing gout and rheumatoid arthritis. It covers tailored diets, lifestyle changes, and alternative therapies aimed at reducing foot pain and inflammation. The article emphasizes the importance of accurate diagnosis, proper nutrition, regular exercise, hydration, and integrating complementary treatments to improve quality of life for those suffering from these chronic joint conditions.

Effective Approaches to Managing Gout and Rheumatoid Arthritis
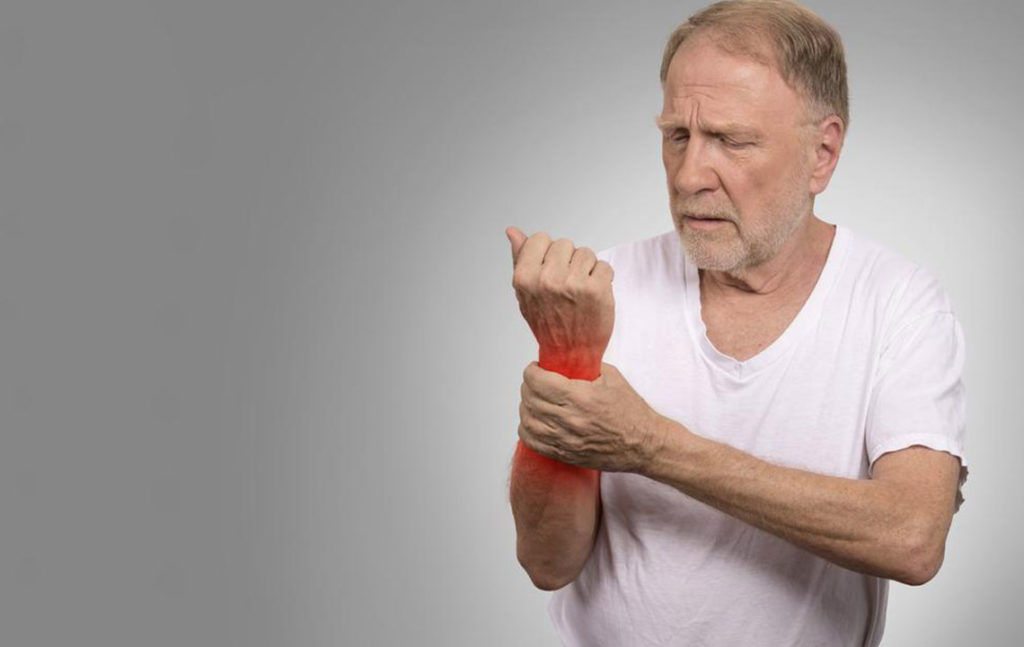
Managing chronic joint conditions like gout and rheumatoid arthritis (RA) requires a detailed understanding of their unique characteristics, symptom management strategies, and lifestyle modifications. Although these two conditions share common symptoms such as joint swelling, tenderness, and discomfort, their underlying causes and treatment methods are fundamentally different. Proper diagnosis is essential to determine the appropriate treatment pathway and to prevent potential complications. This comprehensive guide explores effective dietary recommendations, lifestyle adjustments, and complementary therapies designed to alleviate foot pain caused by both gout and RA, enabling patients to improve their quality of life and reduce disease flare-ups.
Understanding the differences between gout and RA is critical because the treatment strategies for foot pain are distinct. Gout often develops suddenly with acute episodes of intense pain, typically affecting the big toe, while RA is a chronic autoimmune disorder that progressively affects multiple joints and can also impact other organs. Ignoring symptoms and delaying treatment can lead to severe joint damage, persistent disability, and diminished quality of life. Therefore, implementing tailored dietary, lifestyle, and therapeutic strategies is vital for effective management. Continue reading to explore these essential approaches for controlling foot pain linked to gout and rheumatoid arthritis.
Dietary Guidelines for Gout and Rheumatoid Arthritis Management
Diet plays a crucial role in managing both gout and RA, as specific foods can either exacerbate symptoms or help reduce inflammation and uric acid levels. Patients must adopt tailored nutritional habits for each condition, focusing on anti-inflammatory diets for RA and low-purine foods for gout. Proper dietary management can help control disease progression, decrease flare-ups, and improve overall joint health.
Dietary Recommendations for Rheumatoid Arthritis
For individuals battling RA, incorporating anti-inflammatory foods into their daily meals is essential. These foods can help reduce joint inflammation, minimize pain, and support immune health. Here are some key dietary suggestions:
Legumes such as lentils, chickpeas, and beans, which are rich in fiber and anti-inflammatory compounds.
Cherries, which contain antioxidants and compounds that may decrease inflammation and pain.
Cruciferous vegetables like broccoli, Brussels sprouts, and kale, known for their immune-boosting properties.
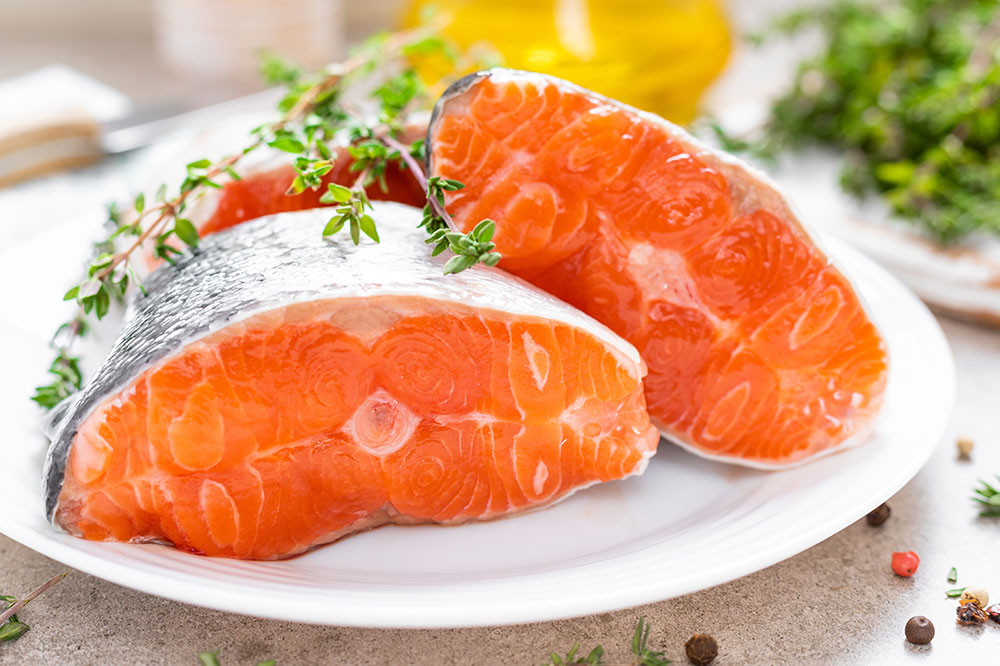
Fatty fish including salmon, mackerel, and sardines rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which are potent anti-inflammatory agents.
Green tea, full of antioxidants that help combat oxidative stress and inflammation.
Pumpkin, rich in antioxidants and low in purines, making it suitable for RA diets.
Citrus fruits like oranges, grapefruits, and lemons, providing vitamin C to support immune function.
Nuts such as walnuts and almonds, which contain healthy fats and anti-inflammatory phytochemicals.
Pomegranates, loaded with antioxidants that may help slow joint damage.
Soy products like tofu and tempeh, which can reduce inflammation and serve as plant-based protein sources.
Ginger and turmeric, natural spices with compounds that have proven anti-inflammatory effects.
Extra virgin olive oil, a staple in Mediterranean diets, known for its beneficial monounsaturated fats and anti-inflammatory properties.
On the other hand, certain foods should be limited or avoided to prevent worsening of symptoms:
Refined sugars, which can promote systemic inflammation.
Red meats, high in saturated fats that may exacerbate inflammation.
Gluten-containing foods, especially for those with gluten sensitivity or celiac disease associated with autoimmune responses.
Fried, processed, and salty foods, which can contribute to inflammation and poor overall health.
Full-fat dairy products, which may increase inflammation in some individuals.
Alcoholic beverages, particularly beer and spirits, which can trigger RA flare-ups and worsen joint discomfort.
Corn oil and other omega-6 rich vegetable oils that may promote inflammatory pathways when consumed excessively.
Dietary Strategies for Gout Management
For gout, controlling uric acid levels through diet is paramount. Patients should focus on foods that lower uric acid and avoid those that increase it. Here are the nutritional guidelines for gout management:
Consuming fresh fruits, especially cherries, which are rich in anthocyanins and may help decrease uric acid levels and reduce attack frequency.
Including low-purine vegetables such as spinach, mushrooms, broccoli, peas, and cauliflower, which are generally safe for gout sufferers.
Eating low-fat dairy products like yogurt and milk that may help reduce uric acid levels.
Integrating moderate amounts of coffee, which has been associated with lower gout risk.
Opting for whole grains including oats, brown rice, and barley, that provide essential nutrients and fiber.
Incorporating legumes like beans, lentils, soy, and tofu, which generally have lower purine content.
Eggs, which are low in purines and a good source of protein.
Using herbs and spices to flavor foods instead of salt or processed seasonings.
Including plant-based oils such as olive, avocado, and canola oils to support healthy fats.
Snacking on nuts and seeds for added nutrition without increasing uric acid levels.
Conversely, foods high in purines should be avoided or minimized, including:
Organ meats like liver and kidneys, which are extremely high in purines.
Shellfish and red seafood such as shrimp, scallops, and mussels, which can elevate uric acid levels.
Alcoholic beverages, especially beer and spirits, known to increase uric acid and trigger attacks.
Sugary sodas and drinks containing high-fructose corn syrup, which can cause uric acid accumulation.
Foods containing high purines and additives that aggravate gout symptoms.
Adopting Lifestyle Changes to Alleviate RA and Gout Symptoms
Beyond dietary adjustments, lifestyle modifications are vital in managing and reducing foot pain caused by rheumatoid arthritis and gout. Implementing healthy habits can significantly contribute to symptom control and improve overall well-being.
For Rheumatoid Arthritis:
Exercise: Engaging in gentle activities such as walking, swimming, or cycling helps improve joint flexibility, reduce stiffness, and strengthen supporting muscles. Regular movement also helps control weight, which lessens joint stress.
Rest: Ensuring adequate sleep and rest periods allows the body to recover and reduce inflammation. Techniques like relaxing baths, deep breathing, or meditation can help improve sleep quality, especially for patients experiencing sleep disturbances.
Support Systems: Managing a chronic autoimmune disorder can be emotionally taxing. Support groups, counseling, and connecting with friends and family boost mental health, reduce feelings of isolation, and enhance emotional resilience.
For Gout:
Health Monitoring: Regular checkups and uric acid testing enable early detection of rising levels, allowing timely interventions to prevent flare-ups.
Hydration: Maintaining excellent hydration by drinking 8-10 glasses of water daily facilitates kidney function and promotes uric acid excretion.
Exercise: Moderate physical activity like walking can help manage stress, improve circulation, and support weight management. During gout attacks, avoiding strenuous exercise prevents exacerbation of symptoms.
Complementary and Alternative Therapies for Foot Pain Relief in RA and Gout
Many patients find relief through complementary therapies that support conventional treatments, improve circulation, and reduce inflammation. These therapies include:
Reflexology, which stimulates pressure points in the feet and hands to improve energy flow and reduce pain.
Massage therapy, promoting relaxation, reducing muscle tension, and increasing blood flow.
Hydrotherapy, using warm water baths or pools to ease joint stiffness and promote circulation.
Acupuncture and acupressure, traditional Chinese medicine techniques that target specific points to relieve pain and inflammation.
These complementary therapies can be integrated into a comprehensive treatment plan to enhance overall foot health, improve mobility, and reduce discomfort.Keywords – gout management, rheumatoid arthritis foot treatment, gouty foot pain relief, alternative arthritis therapies, uric acid control