Comprehensive Home and Medical Strategies for Managing Gout Effectively
This article provides an in-depth look into effective strategies and home remedies for managing gout. It covers medical treatments like NSAIDs and corticosteroids, discusses controlling uric acid levels, and offers natural remedies such as cherry juice, hydration, and dietary tips for long-term prevention. Combining professional treatment with lifestyle modifications can significantly reduce gout flare-ups and improve joint health. Ideal for those seeking comprehensive guidance on managing gout effectively, whether through medication or natural approaches, to enhance quality of life.

Comprehensive Home and Medical Strategies for Managing Gout Effectively
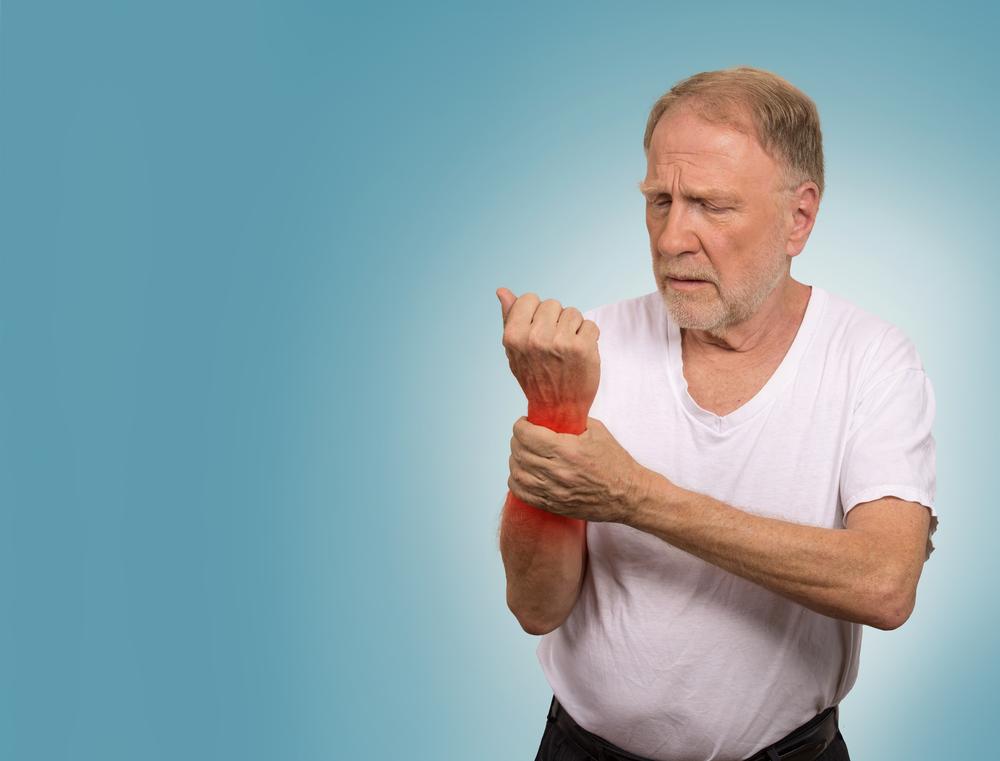
Gout is a painful form of arthritis that results from the buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints. This condition often leads to sudden and severe episodes of joint inflammation, swelling, redness, and intense pain, predominantly affecting men. The primary sites of gout attacks include the knees, feet, ankles, and toes. While gout can be debilitating if untreated, there are numerous effective medical treatments and home remedies that can help control symptoms, reduce flare-ups, and improve quality of life. Understanding both pharmaceutical options and natural approaches enables individuals to manage the condition proactively and prevent recurrent attacks.
Medical Treatments for Gout
Managing gout typically involves prescribed medications aimed at alleviating pain, reducing inflammation, and controlling uric acid levels. Consulting a healthcare professional is essential for developing a personalized treatment plan that fits your specific condition and health profile.
NSAIDs (Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs) - NSAIDs are often the first line of treatment during acute gout attacks. They work by decreasing inflammation and pain effectively. It is crucial to start taking NSAIDs within the first 24 hours of an attack for maximum benefit. Common NSAIDs used for gout include ibuprofen, naproxen, and indomethacin. Proper dosage and duration should be directed by a healthcare provider to prevent side effects.
Corticosteroids - When NSAIDs are contraindicated or ineffective, corticosteroids can be prescribed. These drugs reduce inflammation and swelling rapidly and can be administered orally or via injections. In some cases, doctors may inject adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) to stimulate the body’s natural corticosteroid production, offering targeted relief. Long-term use of corticosteroids should be carefully monitored due to potential side effects.
Colchicine - With a history dating back thousands of years, colchicine remains a reputable treatment for gout flare-ups. It works by disrupting the inflammatory process triggered by uric acid crystals. While effective, colchicine can cause gastrointestinal side effects like nausea and stomach upset, particularly at higher doses. Physicians typically recommend adjusting dosage to minimize adverse effects while maintaining efficacy.
Controlling Uric Acid Levels
Prevention of future gout attacks largely depends on keeping uric acid levels in check. Several medications help achieve this goal:
Probenecid - Facilitates the excretion of uric acid through the kidneys.
Allopurinol - Reduces uric acid production in the body.
Lesinurad - Enhances uric acid elimination when combined with other medications.
Febuxostat - Similar to allopurinol, it decreases uric acid synthesis.
Pegloticase - Used in severe cases, converting uric acid into a more soluble form for easy elimination.
Initiating uric acid-lowering medication should typically occur after an acute attack is resolved, as starting during a flare-up can exacerbate symptoms. Always seek professional medical advice before beginning any medication regimen to ensure safety and effectiveness.
Home and Natural Remedies for Gout Relief and Prevention
Supplementing medical treatments with supportive home remedies can enhance comfort during attacks and help prevent future episodes. These natural strategies are generally safe when used appropriately but should not replace professional medical care.
Apply an ice pack wrapped in a thin cloth directly to the affected joint to reduce swelling and numb pain. Do this for 15-20 minutes multiple times a day during flare-ups.
Elevate the affected limb to minimize blood flow and decrease swelling, especially during acute attacks.
Maintain good hydration by drinking plenty of plain water throughout the day. Adequate hydration helps prevent uric acid crystal formation.
Seek emergency medical attention if the pain worsens or if there are signs of infection or other complications.
Additionally, incorporating certain foods and natural remedies into your lifestyle can support long-term management and reduce the risk of recurrent gout attacks:
Consume tart cherry juice or fresh cherries, which have been shown to lower uric acid levels and reduce inflammation.
Include magnesium-rich foods such as nuts, seeds, and leafy greens, as magnesium may inhibit uric acid formation.
Drink warm water infused with turmeric, apple cider vinegar, and lemon, as these ingredients possess anti-inflammatory and detoxifying properties.
Add celery and celery seed extracts to your diet due to their natural anti-inflammatory benefits.
Lifestyle modifications also play a crucial role in managing gout effectively. Regular exercise, weight management, and avoiding foods high in purines (like red meats, organ meats, and certain seafood) can significantly reduce flare-up frequency and severity.
In summary, managing gout requires a comprehensive approach that combines medical treatments with natural home remedies and lifestyle changes. Early intervention, consistent medication adherence, and dietary adjustments can make a substantial difference in controlling symptoms, preventing attacks, and improving overall joint health. By staying informed and working closely with healthcare professionals, individuals affected by gout can lead healthier, more comfortable lives.