Effective Nutritional Approaches to Reduce Arthritis Symptoms and Improve Joint Health
This comprehensive guide explores dietary strategies to combat arthritis symptoms, highlighting the benefits of omega-3 rich fish, garlic, ginger, cruciferous vegetables, nuts, and berries. It emphasizes the importance of integrating these foods into daily routines and supplemental medical treatments like ACTEMRA® to effectively manage inflammation and joint pain, aiming to improve quality of life for arthritis sufferers.

Effective Nutritional Approaches to Reduce Arthritis Symptoms and Improve Joint Health
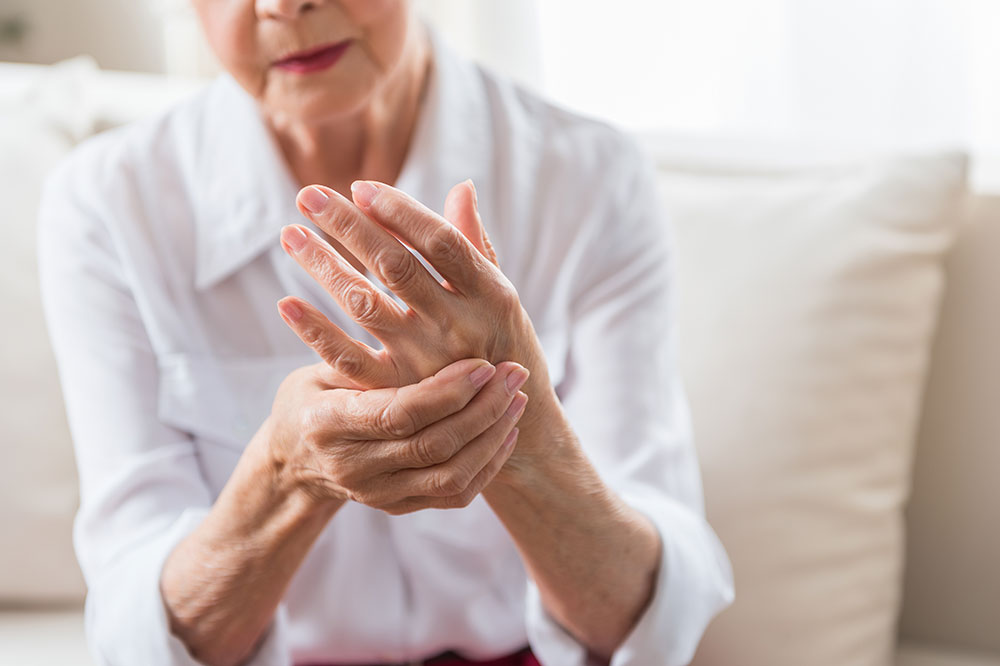
Arthritis is a prevalent condition characterized by inflammation, pain, stiffness, and swelling in the joints, affecting millions of people globally across different age groups, genders, and ethnic backgrounds. The most common forms include rheumatoid arthritis, an autoimmune disease where the body's immune system attacks joint tissues, leading to chronic inflammation and joint destruction, and osteoarthritis, which results from cumulative joint wear and tear over time. While medical treatments are essential, diet and nutrition play a crucial role in managing arthritis symptoms and enhancing joint health.
Adopting anti-inflammatory food choices can significantly help reduce joint pain and stiffness associated with arthritis. Incorporating specific nutrients and foods into daily meals can support the body's natural ability to fight inflammation, thereby improving mobility and quality of life. This comprehensive guide explores scientifically backed nutritional strategies and dietary patterns known to alleviate arthritis symptoms and promote joint health.
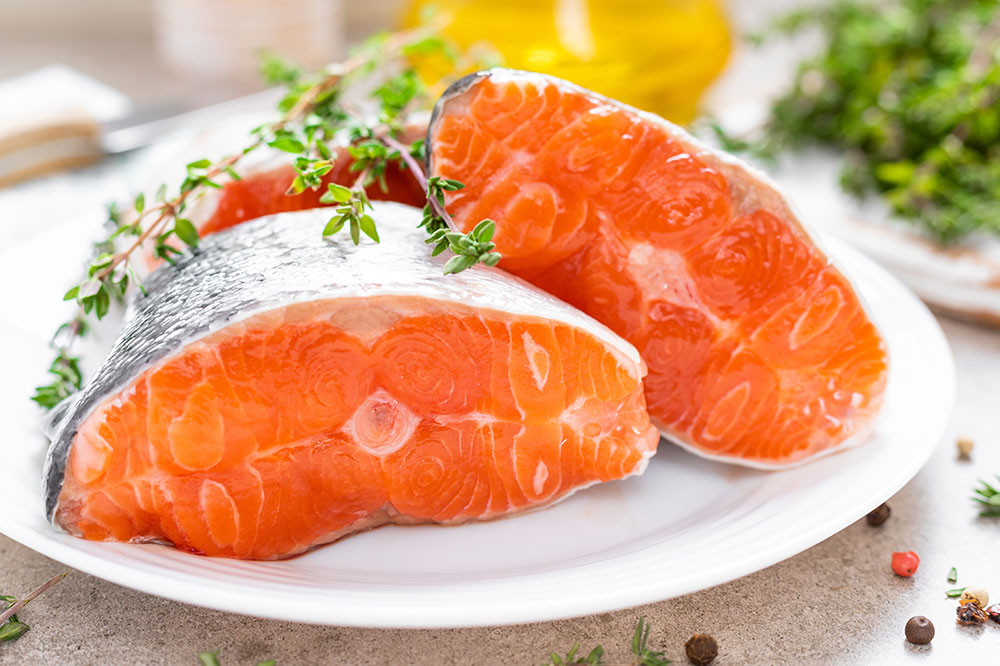
1. Incorporate Omega-3 Rich Fish for Powerful Anti-Inflammatory Effects
Fatty fish such as salmon, sardines, mackerel, and trout are among the best sources of omega-3 fatty acids, essential fats renowned for their potent anti-inflammatory properties. Regular consumption of these fish has been extensively linked to decreased joint stiffness, reduced morning pain, and lower levels of inflammatory markers like cytokines and prostaglandins. In addition to omega-3s, these fish are excellent sources of vitamin D, which is critical for calcium absorption and bone health, potentially providing further protective benefits against rheumatoid arthritis symptoms. Health authorities like the American Heart Association recommend consuming at least two servings of fatty fish weekly to harness these anti-inflammatory benefits effectively, aiming to optimize joint health and reduce systemic inflammation.
2. Use Garlic for Its Natural Disease-Fighting and Anti-Inflammatory Properties
Garlic is a staple in many cuisines and is celebrated for its impressive health benefits, including boosting the immune system and supporting cardiovascular health. Its bioactive compounds, particularly allicin, demonstrate anti-inflammatory effects that may mitigate arthritis symptoms. Incorporating garlic into meals regularly can help enhance immune function and reduce joint inflammation, making it an invaluable component of an anti-inflammatory diet. Studies suggest that garlic's compounds help inhibit the production of inflammatory substances, thereby alleviating joint swelling and pain associated with arthritis.
3. Ginger as a Natural Pain Reliever and Inflammation Reducer
Besides its culinary uses, ginger is well-known medicinally for its anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties. Numerous clinical studies have shown that ginger supplementation can help alleviate osteoarthritis-related knee pain and general joint discomfort. Ginger inhibits the production of inflammatory mediators such as prostaglandins and leukotrienes, thereby contributing to reduced joint swelling and pain. Consuming fresh ginger, ginger powder, or ginger tea on a daily basis can serve as a natural adjunct therapy for arthritis sufferers seeking pain relief and improved mobility.
4. Embrace Cruciferous Vegetables Like Broccoli for Their Anti-Inflammatory Compounds
Broccoli and other cruciferous vegetables like Brussels sprouts, cauliflower, and kale contain phytochemicals such as sulforaphane, which exhibit strong anti-inflammatory properties. These compounds help lower levels of inflammatory markers in the body, potentially easing arthritis symptoms. Regular intake of broccoli has been linked with reductions in joint pain and stiffness, thanks to its ability to modulate inflammatory pathways. Including these vegetables in meals several times a week can boost overall antioxidant defenses and support long-term joint health.
5. Incorporate Nutrient-Rich Nuts Like Walnuts for Joint Support
Walnuts are a rich source of plant-based omega-3 fatty acids, polyphenols, and other bioactive compounds that help suppress inflammation in joints. Scientific research indicates that consuming walnuts as part of a balanced diet can significantly decrease inflammatory markers associated with rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis, thereby reducing pain and improving joint function. As a versatile snack or addition to salads, walnuts provide both nutritional benefits and culinary versatility, making them an ideal choice for those seeking natural inflammation relief.
6. Consume Berries for Their Antioxidant Power to Fight Inflammation
Fresh berries such as strawberries, blueberries, raspberries, and blackberries are packed with vitamins, minerals, and potent antioxidants like rutin and quercetin. These compounds are scientifically proven to inhibit oxidative stress and lower systemic inflammation. Regular consumption of berries—at least two servings per week—has been associated with a 14% reduction in inflammatory markers, aiding in the management of arthritis symptoms. Berries can be enjoyed fresh, added to smoothies, or used as toppings for yogurt and cereals, making them an easy and delicious addition to an anti-inflammatory diet.
While dietary modifications can provide significant relief, they often complement medical treatments prescribed by healthcare professionals. Medications such as ACTEMRA® (tocilizumab), an FDA-approved biologic treatment for rheumatoid arthritis, are designed to target specific pathways involved in joint inflammation. ACTEMRA® works by blocking the activity of interleukin-6 (IL-6), a key protein responsible for promoting inflammation and joint damage. Administered via injection or infusion, ACTEMRA® can be self-injected weekly or biweekly, depending on the treatment plan established by your healthcare provider. Combining medication with a targeted anti-inflammatory diet can lead to more effective management of arthritis symptoms and enhance overall joint health.