Complete Guide to Pulmonary Infections: Understanding and Managing Pneumonia
This comprehensive guide explores pneumonia in detail, covering its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention strategies. Learn how to protect yourself and loved ones from this serious respiratory infection through effective management tips and lifestyle changes.

Complete Guide to Pulmonary Infections: Understanding and Managing Pneumonia
In-Depth Overview of Pneumonia: Causes, Risks, and Effective Management Strategies
Pneumonia is a common and potentially serious respiratory illness characterized by inflammation of the lung’s alveoli and surrounding tissues. This inflammation results from infections caused by various pathogens, including viruses, bacteria, and fungi. It affects people of all ages and backgrounds, often presenting with symptoms like cough, fever, and difficulty breathing. If not identified and treated promptly, pneumonia can escalate to severe complications, especially in vulnerable populations.
In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the detailed aspects of pneumonia, including its causes, symptoms, prevention, diagnosis, and treatment options.
What is pneumonia?
Pneumonia is an infectious disease that inflames the air sacs in one or both lungs, leading to fluid or pus filling these alveoli, impairing oxygen exchange.
It usually starts with viral, bacterial, or fungal invasion that penetrates the respiratory system.
Once the pathogens infiltrate the lungs, they trigger an immune response, causing the tissues to become inflamed and swollen.
The alveoli fill with inflammatory fluid or pus, which hampers oxygen transfer to the bloodstream, resulting in breathing difficulties.
While anyone can develop pneumonia, certain groups are at higher risk, including the elderly (over 65), infants and young children under two, immunocompromised individuals, those with chronic illnesses like asthma or COPD, and smokers.
Is pneumonia contagious?
Yes, pneumonia can be contagious and spread from person to person.
The infectious agents—viruses, bacteria, or fungi—are transmitted through respiratory droplets via coughing, sneezing, or close contact.
Healthy individuals exposed to these pathogens may not always become ill, depending on their immunity and the infectious dose.
Fungal pneumonia is usually contracted through environmental exposure rather than direct person-to-person transmission.
Effective management and treatment options for pneumonia
Bacterial pneumonia is typically treated with targeted antibiotics based on the causative bacteria.
Viral pneumonia often improves with supportive care, including rest, hydration, and fever management.
Antifungal medications are necessary for fungal pneumonia cases.
Supportive treatments like oxygen therapy, cough suppressants, and pain relievers help alleviate symptoms.
Preventive measures, including vaccinations like pneumococcal and influenza vaccines, significantly reduce the risk of certain types of pneumonia.
Diagnosing pneumonia
If symptoms such as persistent cough, high fever, chest pain, and shortness of breath occur, seek prompt medical evaluation.
Doctors will review medical history and conduct a physical examination, focusing on respiratory assessment.
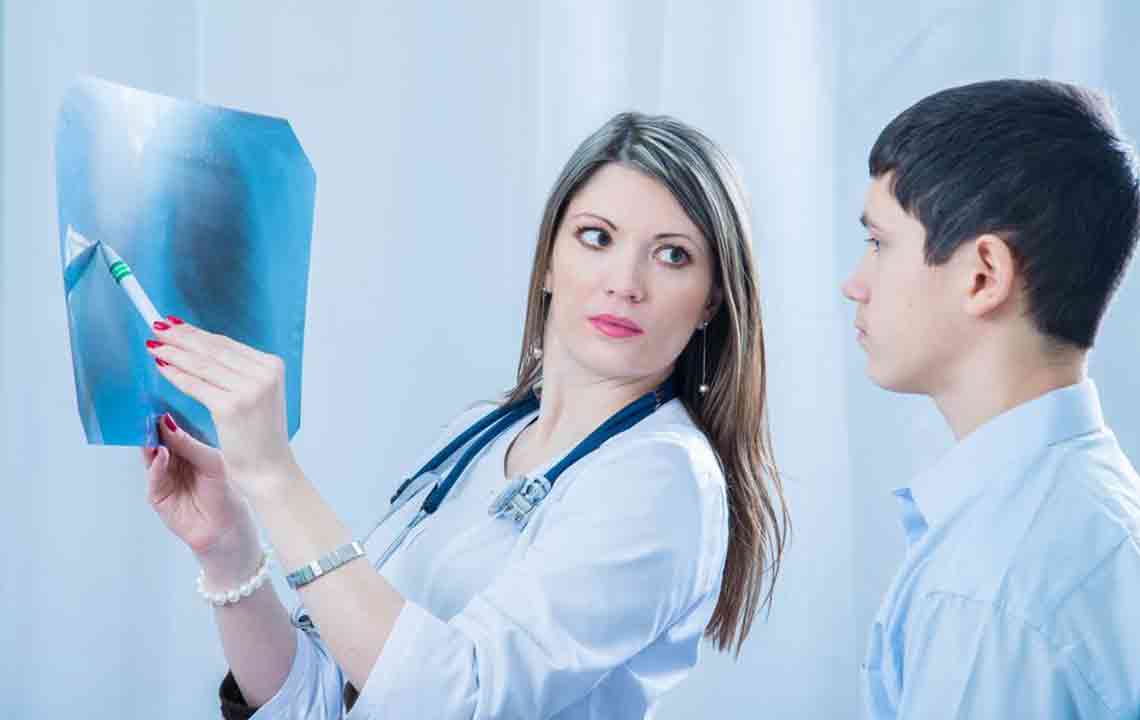
Chest X-rays are essential for confirming lung inflammation and identifying affected areas.
Additional diagnostic tests may include CT scans, blood tests, and sputum analysis to determine the infectious agent and severity.
Early diagnosis and treatment are vital to prevent complications like lung abscesses or systemic infections.
Lifestyle and dietary recommendations for pneumonia prevention and recovery
Avoid smoking and exposure to secondhand smoke, which impair lung function.
Limit alcohol consumption, as excessive drinking weakens the immune system.
Maintain a balanced diet rich in vitamins A, C, E, zinc, and antioxidants to bolster immunity.
Hydrate adequately by drinking plenty of water, herbal teas, and natural fruit juices.
Practice good hygiene, such as regular handwashing and using masks when necessary, to prevent infection spread.
Adhere to prescribed medications and complete antibiotic courses to ensure full recovery.
Get sufficient rest and avoid strenuous activity during illness to help your body heal effectively.