Comprehensive Guide to Eye Twitching: Causes, Types, and Practical Remedies
This comprehensive guide explores the causes, types, and effective remedies for eye twitching. Understanding the physiological basis and common triggers helps individuals manage symptoms better. Practical tips such as proper sleep, stress management, and eye care routines can significantly reduce the frequency of eyelid spasms. The article also discusses when to seek medical attention for persistent or severe cases. With detailed insights and actionable strategies, readers can gain a better understanding of this common condition and take proactive steps to maintain healthy and comfortable eyes.

Comprehensive Guide to Eye Twitching: Causes, Types, and Practical Remedies
Eye twitching, also known as eyelid spasms, is a common involuntary muscle movement that affects many individuals at some point in their lives. These twitches usually involve a sudden, repetitive contraction of the eyelid muscles, primarily affecting the upper or lower eyelids. While most cases are benign and temporary, understanding the underlying causes, different types, and effective remedies can help manage and reduce their occurrence. This detailed guide aims to provide in-depth insights into eye twitching, including its causes, variations, symptoms, and practical strategies to alleviate discomfort.
What is Eye Twitching?
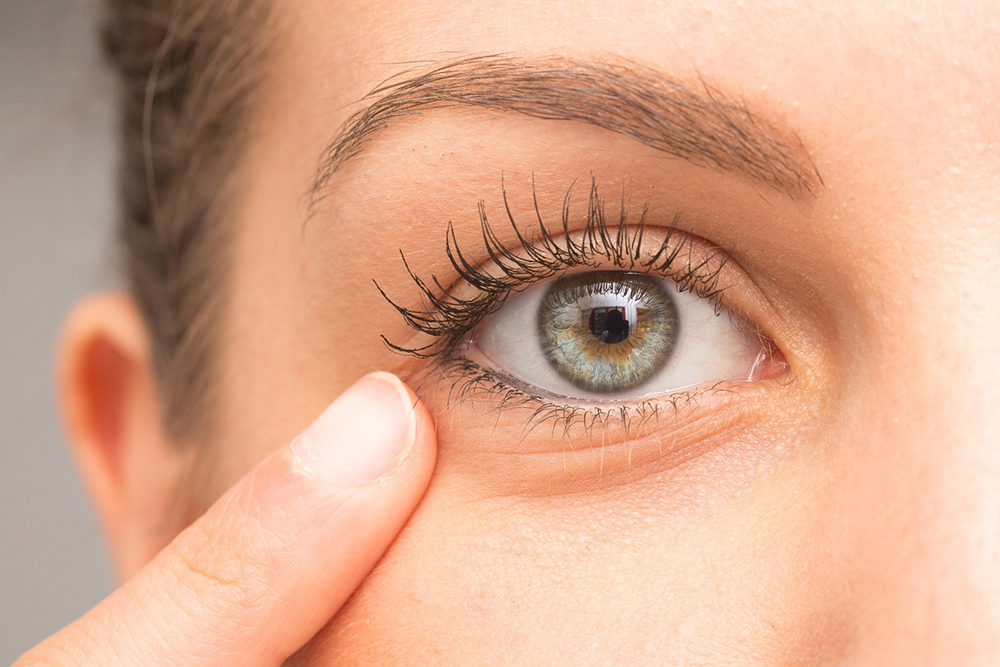
Eye twitching refers to involuntary spasms or contractions of the eyelid muscles, primarily the orbicularis oculi muscle responsible for blinking and eyelid movement. These spasms can range from mild flickering to persistent twitching that lasts for days or weeks. Although generally harmless, persistent eye twitching might indicate underlying health issues requiring medical consultation.
Understanding the physiology behind eye twitching helps in appreciating its causes and potential treatments. These spasms involve rapid, involuntary contractions of the eyelid muscles that can be triggered by various external or internal factors. In most cases, you might notice the eyelid fluttering perhaps after long screen exposure, fatigue, or heightened stress levels. Recognizing the signs early allows for intervention, preventing possible discomfort or complications.
Types of Eye Twitching
Benign Myokymia - The most common form of eyelid twitching is benign myokymia. It usually involves irregular, trembling movements affecting the lower eyelid but can sometimes affect the upper eyelid. The twitch is typically mild, short-lived, and often triggered by fatigue, stress, or caffeine intake. These spasms are harmless and tend to resolve with proper rest and stress management.
Chronic Blepharospasm - Unlike benign myokymia, blepharospasm is a more persistent and involuntary contraction of both eyelids, potentially interfering with vision. Usually affecting middle-aged and older adults, this condition can be progressive, causing discomfort, eye irritation, and sensitivity to light. It may occur sporadically but can become a frequent frequency, significantly impacting daily life.
Hemifacial Spasm - This condition involves involuntary spasms affecting one side of the face, often linked to nerve compression, such as the facial nerve (cranial nerve VII). Hemifacial spasm can start as episodic twitches and may progress, involving multiple facial muscles, sometimes leading to eyelid closure or grimacing. It often requires medical diagnosis and treatment, especially if it affects quality of life.
Common Causes of Eye Twitching
Various internal and external factors contribute to eye twitching. Recognizing these causes is essential for effective management and prevention:
Lack of Sleep or Fatigue - Sleep deprivation significantly affects the nervous system, leading to muscle fatigue and increased likelihood of eyelid spasms. Ensuring adequate rest is crucial for preventing twitching episodes.
Stress and Anxiety - Psychological stress triggers muscle tension and nerve hyperactivity, often manifesting as eye twitching. Incorporating relaxation techniques can help reduce the incidence.
Eye Strain - Extended exposure to digital screens, poor lighting conditions, or reading without breaks causes eye strain, often leading to spasms. Adopting proper eye ergonomics reduces this risk.
Excessive Caffeine or Stimulants - High caffeine intake can overstimulate the nervous system, resulting in muscle spasms, including eyelid twitching.
Additional factors include allergies, dryness of the eyes, exposure to bright lights or irritants, neurological conditions like multiple sclerosis, eyelid infections, and migraines. Understanding the full spectrum of causes helps in adopting targeted remedy strategies.
Effective Remedies for Eye Twitching
Prioritize Rest and Sleep - Achieving 7-8 hours of quality sleep every night is vital. Maintaining a consistent sleep schedule and avoiding stimulants like caffeine before bedtime can significantly reduce twitching episodes. Creating a calming bedtime routine enhances sleep quality and promotes eye health.
Limit Screen Time and Practice the 20-20-20 Rule - During prolonged use of computers, smartphones, or tablets, take regular breaks. Every 20 minutes, look at something 20 feet away for 20 seconds. This practice helps alleviate eye strain, relaxes the eye muscles, and diminishes twitching.
Apply Warm Compresses - Using a clean, warm cloth over closed eyelids for 5-10 minutes can soothe muscle spasms and promote relaxation. This natural remedy enhances blood circulation and reduces tension in the eyelid muscles.
Manage Stress Effectively - Engage in mindfulness practices such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or yoga to control stress levels. Reducing psychological stress can prevent associated muscle spasms.
Stay Hydrated and Maintain Electrolyte Balance - Drinking plenty of water and consuming electrolyte-rich fluids like coconut water or herbal broths help prevent dehydration, which can trigger muscle spasms.
Additional measures include avoiding eye irritants and allergens, using artificial tears to combat dryness, and visiting an eye specialist if symptoms persist or worsen. Adopting these lifestyle adjustments can substantially decrease the frequency and severity of eye twitching episodes.
Understanding eye twitching in depth enables individuals to adopt effective strategies for prevention and relief. While minor twitches are usually harmless and resolve on their own, persistent or severe cases warrant medical evaluation. By managing stress, ensuring adequate rest, and practicing healthy eye habits, most people can significantly reduce the occurrence of eyelid spasms and maintain optimal eye health.