Comprehensive Guide to Causes and Effective Treatments for Frequent Bruising
Frequent bruising can be a sign of underlying health issues or lifestyle factors. This comprehensive guide explains the causes, including aging, nutritional deficiencies, and medical conditions, and offers practical remedies such as topical gels, nutritional support, and preventive measures. Understanding these aspects helps individuals manage and reduce bruising effectively, improving skin health and overall well-being. Consulting healthcare professionals is advised for persistent or severe cases to rule out serious underlying conditions, ensuring comprehensive care and peace of mind.
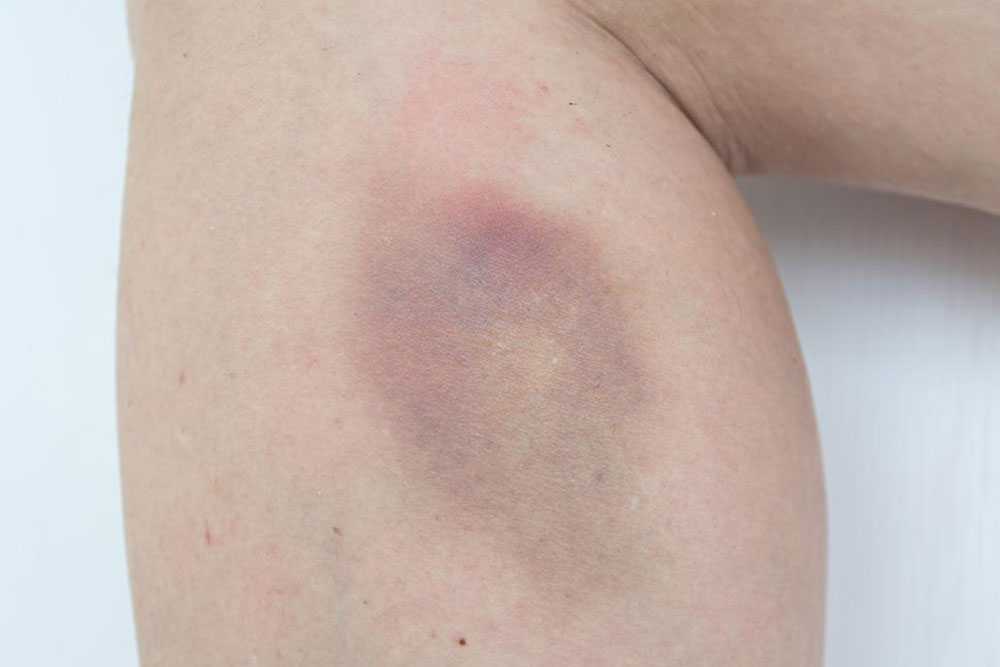
Comprehensive Guide to Causes and Effective Treatments for Frequent Bruising
Bruising is a common skin concern that occurs when small blood vessels beneath the skin rupture, leading to discoloration and swelling. While occasional bruising is normal after minor injuries, frequent or unexplained bruising may signal underlying health issues or other factors. Understanding the causes of frequent bruising is crucial for proper management and seeking appropriate medical attention when necessary. This extensive guide explores the main reasons behind frequent bruising and provides practical remedies to alleviate its appearance and discomfort.
What Causes Frequent Bruising?
Bruising happens when soft tissues sustain an impact, causing blood vessels to break and blood to leak into surrounding tissues. The leaked blood pools beneath the skin, resulting in the familiar blue, purple, or black marks. Several factors can contribute to why some individuals bruise more easily or experience frequent bruising.
Many people are naturally predisposed to easier bruising as they age. As skin becomes thinner and blood vessels weaken over time, even minor bumps can cause visible marks. Additionally, genetic factors can influence vein strength and skin resilience, making some more prone to bruising.
Frequent bruising may also be symptomatic of underlying health conditions. For example, blood disorders such as thrombocytopenia, which involves low platelet counts, impair the blood’s ability to clot, leading to easy bruising. Bleeding disorders like hemophilia or liver diseases can similarly affect clotting mechanisms, increasing bruising risk.
Other systemic conditions, including certain infections and autoimmune diseases, may impact blood vessel health and collagen production, resulting in fragile vessel walls. Medications such as blood thinners, aspirin, or corticosteroids can also lower clotting ability, making bruising more common after minor impacts.
Moreover, nutritional deficiencies play a significant role. Lack of essential nutrients like Vitamin K, crucial for blood clotting, or Vitamin C, which supports blood vessel strength, can weaken vascular integrity. Leafy greens, citrus fruits, and certain supplements help maintain optimal levels of these nutrients, reducing the likelihood of excessive bruising.
Medical and Lifestyle Factors That Contribute to Frequent Bruising
**Aging:** Thinning skin and weakened blood vessels
**Genetic predispositions:** Family history of easy bruising
**Blood disorders:** Thrombocytopenia, hemophilia
**Liver and autoimmune diseases:** Affecting clotting factors
**Medications:** Blood thinners, corticosteroids
**Nutritional deficiencies:** Vitamin K, Vitamin C
**Lifestyle factors:** Alcohol consumption, smoking, poor nutrition
Understanding these factors can help in distinguishing between benign causes and those requiring medical attention. If you experience frequent or unexplained bruising, especially accompanied by other symptoms such as bleeding gums, nosebleeds, or fatigue, consult a healthcare professional promptly for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
Effective Remedies and Preventive Measures for Bruising
Addressing frequent bruising involves a combination of lifestyle adjustments, nutritional support, and topical treatments. Here are some effective strategies:
Aloe Vera: Applying pure aloe vera gel to bruised areas can soothe irritated skin, reduce inflammation, and promote faster healing. Aloe vera’s natural anti-inflammatory properties help minimize discoloration and swelling.
Vitamin C Supplements: Consuming vitamin C through dietary sources or supplements enhances capillary strength and collagen formation, making blood vessels less prone to rupture. Regular intake can help reduce the frequency and severity of bruises.
Arnica Gel or Cream: Derived from the Arnica Montana plant, topical arnica is widely used to treat bruises. Its anti-inflammatory properties can diminish discoloration, swelling, and pain associated with bruises when applied promptly after injury.
Diet and Nutrition: Incorporating foods rich in vitamins K and C, such as leafy greens, citrus fruits, berries, and bell peppers, supports vascular health and blood clotting. Maintaining a balanced diet bolsters overall skin and vessel resilience.
Protective Measures: Using protective gear, cushioning sharp edges, and being cautious in daily activities can help prevent injuries that lead to bruising.
Medical Treatments: In cases where bruising indicates an underlying health problem, medical intervention may involve blood tests, medication adjustments, or managing chronic conditions affecting blood health.
Ensuring proper management of health and lifestyle factors plays a vital role in minimizing the occurrence of frequent bruising. Always seek medical attention if bruising is severe, persistent, or accompanied by other concerning symptoms.
In conclusion, understanding the underlying causes of frequent bruising empowers individuals to adopt effective preventive and treatment strategies. Whether due to natural aging, nutritional deficiencies, or underlying medical conditions, targeted remedies can significantly improve skin resilience and overall health. Regular medical check-ups and personalized care plans are essential for those prone to frequent bruising to maintain optimal vascular health and prevent complications.





