Comprehensive Guide to Managing and Preventing Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
Learn comprehensive strategies for managing and preventing urinary tract infections (UTIs). This guide covers symptoms, diagnostic steps, effective treatments, and lifestyle tips to reduce recurrence. Staying informed can help you take proactive steps toward urinary health, minimizing discomfort and complications associated with UTIs. Discover the importance of proper hygiene, hydration, and early intervention to maintain urinary tract health and prevent future infections.
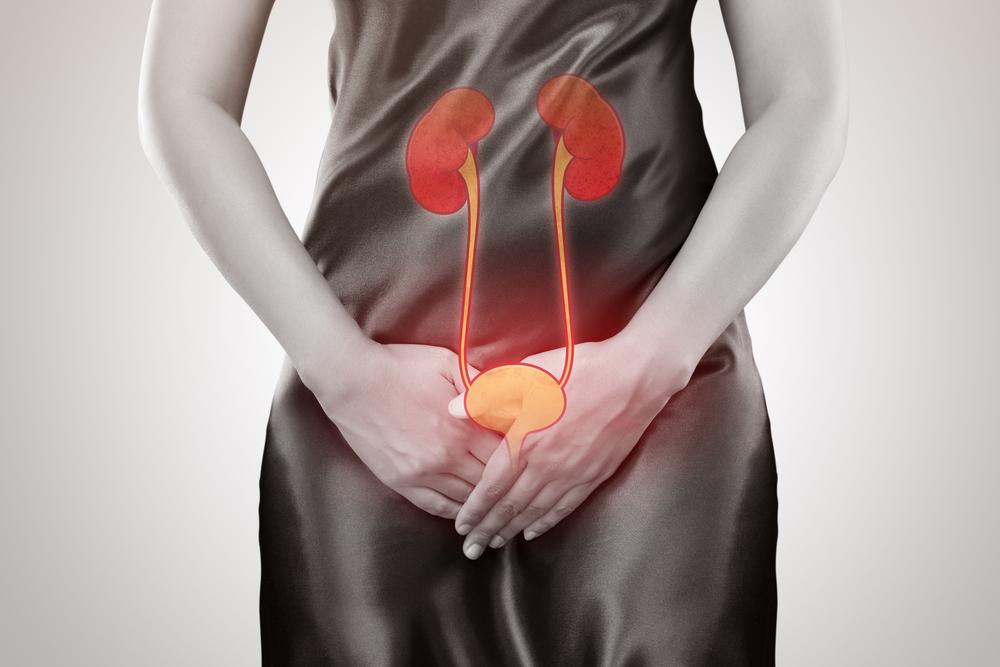
Comprehensive Strategies for Effectively Managing and Preventing Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are among the most common bacterial infections affecting millions worldwide, particularly women. Often referred to as cystitis, UTIs can cause significant discomfort and health complications if not diagnosed and treated promptly. According to medical studies, nearly half of all women will experience at least one episode of a UTI during their lifetime, making awareness and prevention strategies essential for overall health and well-being.
UTIs develop when bacteria from the gastrointestinal tract or pelvic area migrate into the urinary system, leading to inflammation of the bladder and other parts of the urinary tract. While bacteria are primarily responsible for these infections, other factors such as chemical irritants, fungi, kidney stones, and physical injuries can also contribute to the onset of UTIs. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and effective management techniques can help individuals reduce the risk and effectively treat UTIs when they occur.
Identifying UTI Symptoms
Recognizing the early signs of a urinary tract infection is crucial for prompt treatment. Common symptoms include:
Lower abdominal pain and pressure
Burning sensation or pain during urination
Persistent urge to urinate, even if little urine is produced
Cloudy urine, sometimes with a foul odor
Blood in urine (hematuria), which may appear pink or reddish
Symptoms can vary depending on age and overall health. Infants and young children might present with fever, irritability, or feeding difficulties. Older adults may experience unexplained fatigue, urinary incontinence, or mental status changes like confusion, which can complicate diagnosis.
Effective UTI Treatment Strategies
Step 1: Confirm the Diagnosis
Accurate diagnosis is vital before initiating treatment. Healthcare providers typically utilize several diagnostic tests:
Urinalysis: Analyzes urine samples to detect white blood cells, red blood cells, bacteria, and other markers of infection. A count of more than 5 white blood cells per high power field usually indicates infection.
Dipstick Test: Rapid testing method that detects leukocyte esterase and nitrites, both of which suggest bacterial presence.
Urine Culture: The most definitive test for bacterial infection, which identifies specific bacteria and determines their sensitivity to antibiotics. A bacterial count exceeding 100,000 colony-forming units per milliliter (CFU/ml) confirms infection.
In some cases, such as when pus is observed without bacteria, sterile pyuria may be diagnosed, which can indicate urethritis or other non-bacterial causes.
Step 2: Managing and Treating UTI
Antibiotic Therapy: The cornerstone of UTI treatment involves antibiotics tailored to the bacteria identified. Mild cases may be diagnosed based on symptoms and treated empirically, sometimes via telephone consultation. For severe or complicated cases, in-person evaluation is necessary to determine the appropriate course.
Pain Relief: Analgesics such as acetaminophen or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help alleviate pain and discomfort associated with UTIs.
Hydration: Consuming plenty of water is critical to flushing bacteria out of the urinary system. Drinking at least 8-10 glasses daily can accelerate recovery and reduce recurrence chances.
Vitamin C Intake: Increasing vitamin C intake raises urine acidity, creating an environment less conducive to bacterial growth. Incorporate citrus fruits, supplements, or vitamin C-rich foods into your diet under healthcare guidance.
Avoid Bladder Irritants: Reduce consumption of substances that can irritate or inflame the bladder, including caffeine, alcohol, spicy foods, nicotine, and artificial sweeteners. These can exacerbate symptoms or hinder healing.
Frequent Urination and Personal Hygiene: Urinate regularly, especially after sexual activity, to prevent bacterial buildup. Proper hygiene practices are essential—wipe from front to back, and keep the genital area clean and dry to prevent bacteria transfer.
Always consult healthcare professionals before starting or changing treatments. They can recommend the best approach based on individual health profiles and infection severity.
**Expanding on UTI Prevention and Lifestyle Tips**
Preventing UTIs involves a combination of behaviors and lifestyle choices. Maintaining good hydration, practicing safe sexual habits, and staying vigilant about personal hygiene are foundational steps. Wearing loose-fitting, breathable clothing and cotton underwear can help reduce moisture buildup and bacterial growth. For women, voiding after sexual intercourse can significantly lower infection risk. Additionally, some research indicates that cranberry products may help prevent recurrent UTIs, although evidence remains mixed, and consulting a healthcare provider is advised before supplementation. Regular health check-ups and prompt treatment of urinary symptoms can help minimize complications and improve quality of life. Educating oneself about early signs and when to seek medical attention is crucial, especially for individuals with recurrent infections or underlying health conditions such as diabetes or immune disorders.