Comprehensive Guide to Preventing and Managing Urinary Tract Infections
This comprehensive guide explores effective strategies for preventing and managing urinary tract infections. It covers causes, risk factors, symptoms, prevention techniques, medical treatments, and home remedies. Emphasizing early intervention and healthy lifestyle habits, the article aims to help readers maintain urinary health and avoid serious complications, offering a detailed resource for both prevention and treatment.

Comprehensive Guide to Preventing and Managing Urinary Tract Infections
The human urinary system, also known as the renal system, plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health by removing toxins, waste products, and excess fluids from the body. This complex system is composed of vital organs such as the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. Any infection that occurs within this system is classified under urinary tract infections (UTIs), which can affect various parts including the bladder (a condition known as cystitis), the ureters, or the kidneys (pyelonephritis). UTIs are among the most common bacterial infections, especially affecting women, although men and children can also be susceptible. Understanding the causes, risk factors, symptoms, and effective prevention and treatment strategies is essential for maintaining urinary health and preventing the potential progression of these infections into more severe health issues.
One of the primary culprits behind UTIs is the bacteria Escherichia coli (E. coli), a microorganism naturally present in the digestive tract but capable of causing infection when it enters the urinary tract. Factors that increase susceptibility to UTIs include frequent sexual activity, multiple sexual partners, diabetes, poor personal hygiene, menopause, and the presence of kidney stones. Certain lifestyle choices, such as inadequate hydration or neglecting proper hygiene, also contribute to higher risks. Additionally, environmental factors, like exposure to contaminated water sources or the use of public restrooms without proper hygiene practices, can serve as infection vectors. Recognizing these risk elements can help in adopting preventive measures effectively.
Recognizing UTI Symptoms and the Importance of Early Intervention
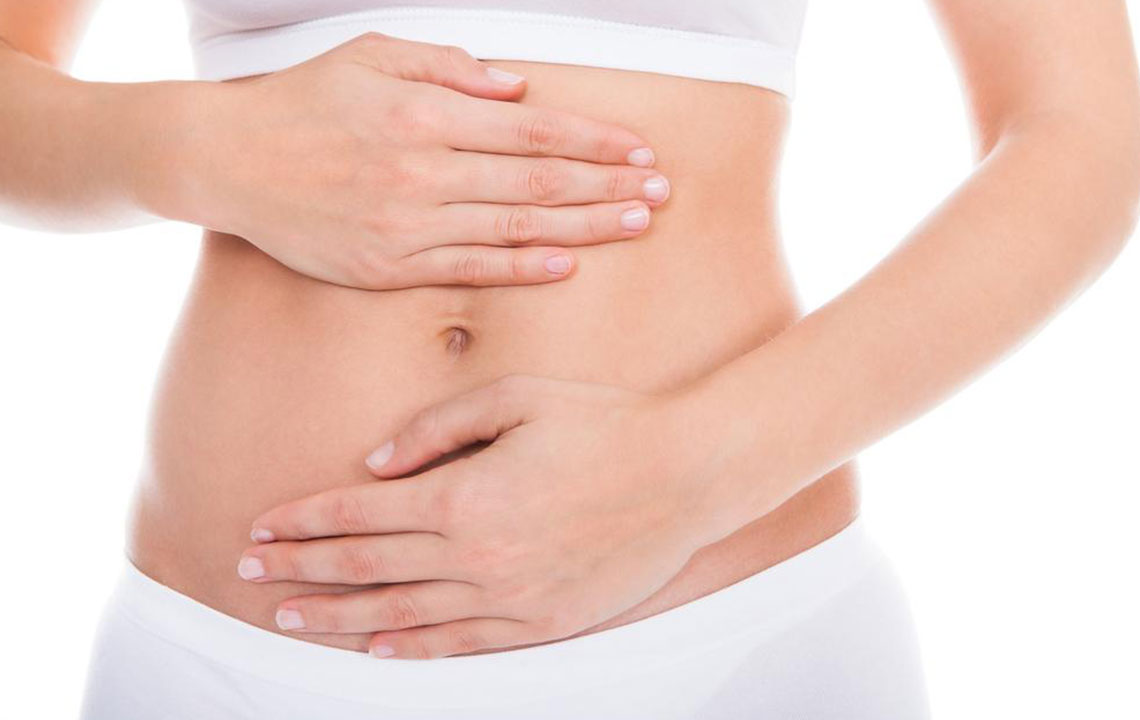
UTIs often present with recognizable symptoms that should prompt immediate medical attention. Typical signs include a persistent and strong urge to urinate, a burning sensation during urination, cloudy or foul-smelling urine, pelvic discomfort, and in some cases, fever and chills if the infection has spread to the kidneys. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial because if left untreated, UTIs can lead to serious complications such as kidney infections, which may cause permanent damage or sepsis in severe cases. Therefore, any persistent symptoms should never be ignored, and visiting a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment is essential.
Effective Prevention Strategies to Reduce UTI Risk
Preventing UTIs involves adopting healthy lifestyle practices and awareness. Hydration is paramount—drinking plenty of water helps to flush bacteria from the urinary tract, reducing bacterial colonization. Regular urination, especially after sexual activity, can also help clear bacteria before they settle into the urinary tissues. Proper personal hygiene practices, such as wiping from front to back, wearing breathable cotton underwear, and avoiding irritating feminine products, can lower infection risks. For women, avoiding prolonged use of irritating hygiene sprays or douches is advisable. Lifestyle modifications like quitting smoking, managing underlying health conditions such as diabetes, and maintaining a balanced diet rich in vitamins can support urinary health.
Medical Treatments and Home Remedies
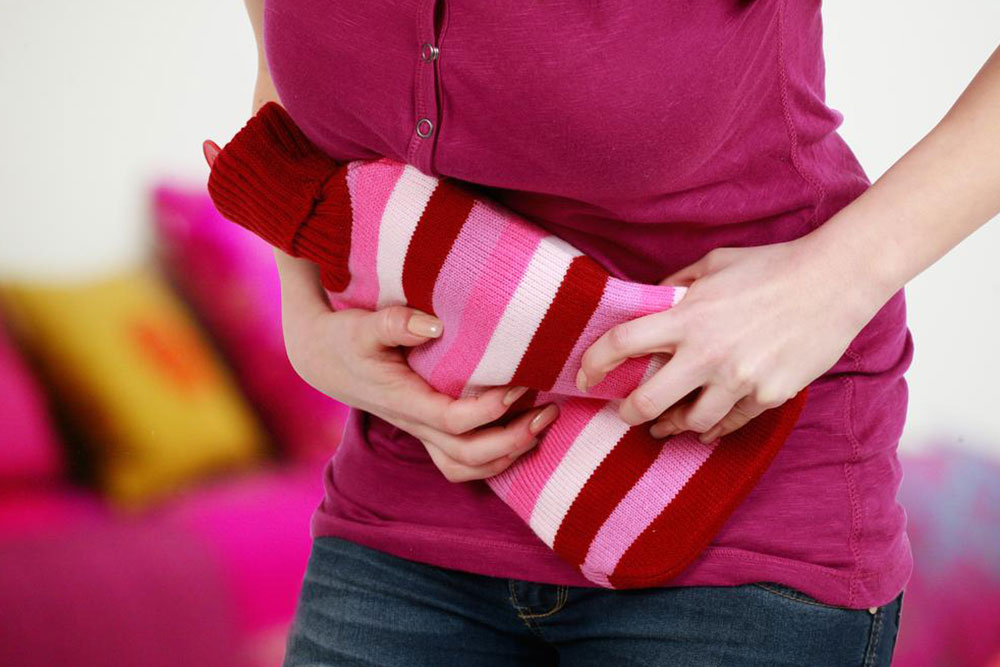
When UTIs occur, medical intervention is often necessary. Healthcare providers typically prescribe a course of antibiotics to eliminate bacterial infection effectively. The choice of antibiotic depends on the severity of the infection and bacterial sensitivity profiles. Over-the-counter pain relief medications, such as ibuprofen, can alleviate discomfort temporarily. Applying heat with a heating pad on the lower abdomen may provide added comfort. For recurrent UTIs, a healthcare professional might suggest continuous low-dose antibiotics, or other strategies such as cranberry extracts or probiotics, although evidence supporting their effectiveness varies.
Additional Home Care Tips and Lifestyle Adjustments
Home remedies and lifestyle adjustments can supplement medical treatment and help prevent recurrence. Increasing vitamin C intake, either through diet or supplements, can acidify the urine and inhibit bacterial growth. Avoiding irritants such as caffeine, alcohol, and spicy foods during infection can help reduce urinary tract inflammation. Ensuring adequate hydration by drinking at least 8-10 glasses of water daily is vital. Good personal hygiene, urinating when needed without delaying, and practicing sexual hygiene—such as urinating before and after intercourse—are simple yet effective ways to prevent future infections.
The Importance of Regular Medical Follow-up
If you experience recurrent UTIs or symptoms that do not resolve after initial treatment, it is essential to seek medical advice. Chronic or recurrent infections may require further investigation to identify underlying causes, such as anatomical abnormalities or chronic health conditions. Regular medical check-ups and urine tests can help monitor urinary tract health, prevent complications, and ensure appropriate management of persistent issues.
Conclusion
Urinary tract infections are common but manageable health issues when proper precautions and timely treatment are applied. Understanding the causes, recognizing symptoms early, maintaining good personal hygiene, and staying well-hydrated are key factors in preventing UTIs. For those affected, medical treatment with antibiotics combined with lifestyle changes can effectively eliminate infection and reduce the risk of recurrence. Healthcare professionals can provide personalized advice tailored to individual risk factors, ensuring optimal urinary health and overall well-being.