Comprehensive Guide to Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): Causes, Symptoms, Prevention, and Treatment
This comprehensive guide provides detailed insights into urinary tract infections, including their causes, symptoms, risk factors, prevention strategies, and treatment options. Understanding UTIs enables early recognition and effective management, reducing complications and recurrences. The article emphasizes lifestyle habits, hygiene practices, and medical therapies that promote urinary health and prevent infection. Whether you're prone to UTIs or seeking preventive advice, this extensive overview aims to empower individuals with knowledge to maintain a healthy urinary system and improve overall well-being.

Comprehensive Guide to Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): Causes, Symptoms, Prevention, and Treatment
An In-Depth Look at UTIs: Causes, Risk Factors, and Effective Management
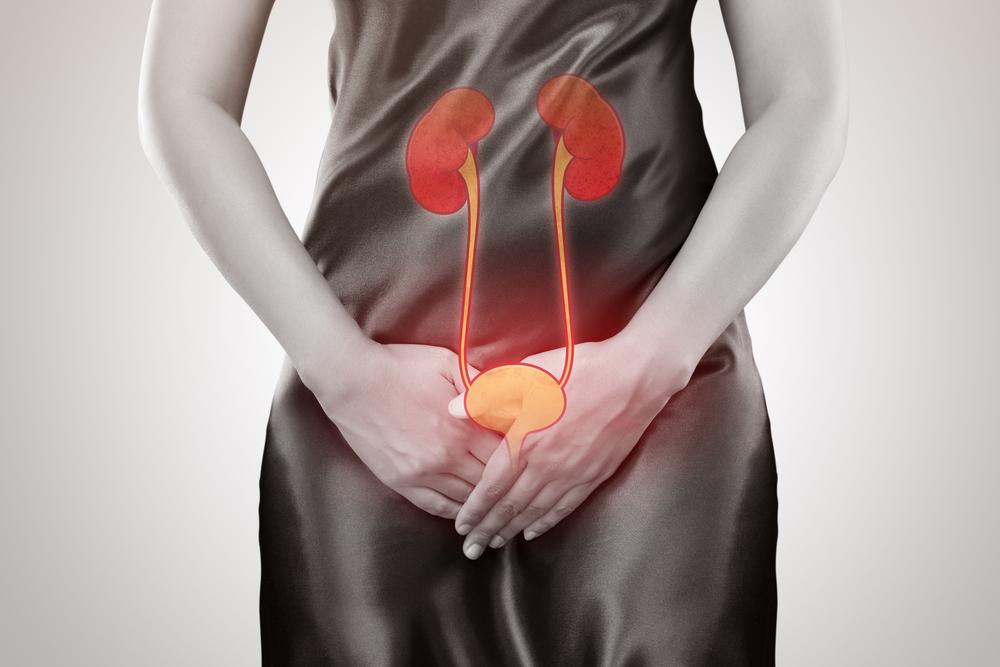
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are among the most common infections affecting people worldwide, especially women. These infections result from microbial invasion of the urinary system, which includes the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. While bacteria are the primary culprits, fungi and viruses can occasionally cause UTIs, complicating diagnosis and treatment. Understanding the intricate causes, recognizing the symptoms early, and adopting effective prevention and treatment strategies are crucial for managing this common health issue.
Most urinary tract infections involve the lower urinary system, including the urethra and bladder. This comprehensive overview covers their causes, symptoms, treatment options, and prevention tips to help individuals effectively combat UTIs and maintain urinary health.
Understanding UTI Causes and Risk Factors
UTIs develop when harmful microorganisms, predominantly bacteria, invade parts of the urinary tract. Several factors can predispose individuals to these infections, and understanding these risk factors can help in prevention and early detection:
Gender Differences: Women are significantly more prone to UTIs compared to men. The primary reason is anatomical; women have a shorter urethra, making it easier for bacteria to ascend into the bladder. The proximity of the urethra to the anus also facilitates bacterial transfer. Additionally, certain contraceptive methods like diaphragms or spermicidal jellies can increase susceptibility.
Menopause and Hormonal Changes: Postmenopausal women experience decreased estrogen levels, which causes thinning of the vaginal and urethral tissues, reducing their ability to defend against bacterial invasion. This hormonal change significantly raises the risk of UTIs in older women.
Age-Related Factors: Elderly populations face higher UTI rates due to factors like weakened immune function, chronic health conditions, and increased use of urinary catheters or other invasive devices.
Urinary Tract Abnormalities: Congenital malformations or acquired anomalies such as urinary reflux or obstructions can hinder normal urine flow, creating an environment conducive to bacterial growth.
Use of Urinary Catheters: Long-term catheterization is a major risk factor, as the device can introduce bacteria directly into the urinary tract, leading to infections.
Other Contributing Factors: Poor hygiene, dehydration, and certain medical conditions like diabetes also contribute to increased risk by impairing immune defenses or providing a nutrient-rich environment for bacteria.
Recognizing the Symptoms of UTIs
Early detection of UTIs is vital for prompt treatment. Common symptoms include:
Urgent and frequent need to urinate, often in small amounts
Burning sensation during urination, which indicates inflammation
Cloudy, foul-smelling urine suggesting infection
Blood in the urine, visible or microscopic
Lower abdominal or pelvic pain, sometimes radiating to the back or sides
Persistent discomfort or pressure in the bladder area
Fever or chills, especially in upper urinary tract infections affecting the kidneys
Feeling generally fatigued or malaise, which can accompany systemic infection
Effective Treatment Strategies for UTIs
Management of UTIs typically involves several approaches to eliminate the infection and prevent recurrence:
Antibiotics and Antimicrobials: Doctors usually prescribe antibiotics based on the type and severity of infection. It is critical to complete the full course to prevent antibiotic resistance and ensure complete eradication.
Hydration: Increasing fluid intake, particularly water, helps flush out bacteria from the urinary system and reduces irritation.
Pain Management: OTC pain relievers or heat application can relieve discomfort. analgesics like acetaminophen or NSAIDs are commonly recommended.
Monitoring and Follow-up: For recurrent or complicated UTIs, regular medical follow-up is essential. Imaging studies or urine cultures may be necessary to identify underlying issues.
Addressing Underlying Causes: Postmenopausal women may benefit from vaginal estrogen therapy to restore healthy flora. In cases of urinary retention or anatomical abnormalities, surgical or medical interventions may be required.
Preventive Measures to Reduce UTI Risk
Prevention is better than cure, and adopting healthy habits can significantly lower the chances of developing UTIs:
Frequent and Complete Urination: Don't delay urination when the urge arises, and ensure complete bladder emptying to prevent stagnation of urine.
Proper Hygiene: Wipe from front to back after using the toilet to prevent bacterial transfer. Keep the genital area clean and dry.
Hydration: Drink plenty of water daily to dilute urine and facilitate bacterial elimination.
Avoid Irritants: Steer clear of scented soaps, douches, and feminine hygiene sprays that can disrupt natural flora.
Pre- and Post-Sex Hygiene: Urinate before and after sexual activity, and clean genital areas to reduce bacteria transfer.
Appropriate Clothing: Wear loose-fitting, cotton underwear and avoid synthetic fabrics that trap moisture and create a breeding ground for bacteria.
Limit Use of Spermicide and Diaphragms: These contraceptives can increase UTI risk; consider alternatives if prone to infection.
Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Maintain a balanced diet, manage blood sugar levels if diabetic, and avoid smoking, which can impair immune function.
By understanding the causes and adopting effective prevention techniques, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of UTIs, improving overall urinary health and quality of life. Prompt treatment combined with good hygiene and lifestyle habits is essential in managing and preventing these common infections.