Comprehensive Guide to Effective Treatment and Prevention of Skin Abscesses
This comprehensive article explores effective treatment methods and preventive strategies for skin abscesses, or boils. It highlights causes, symptoms, self-care tips, and medical treatments. Recognizing early signs and understanding when to seek professional care can prevent complications. The article emphasizes hygiene, proper wound care, and when antibiotics or drainage are necessary for healing. Ideal for those seeking in-depth guidance, this guide aims to educate readers on managing and preventing skin abscesses effectively, ensuring healthier skin and avoiding recurrent infections.

Comprehensive Guide to Effective Treatment and Prevention of Skin Abscesses
Skin abscesses, commonly referred to as boils, are localized collections of pus that develop beneath the surface of the skin. These infections can vary significantly in size and severity, ranging from small, barely noticeable bumps to large, painful masses. Understanding the nature of skin abscesses, their causes, symptoms, and effective treatment strategies is essential for promoting skin health and preventing complications. This comprehensive guide aims to provide detailed information on the causes, appearance, management, and preventive measures of skin abscesses, helping individuals recognize when to seek medical attention and how to care for affected skin at home.
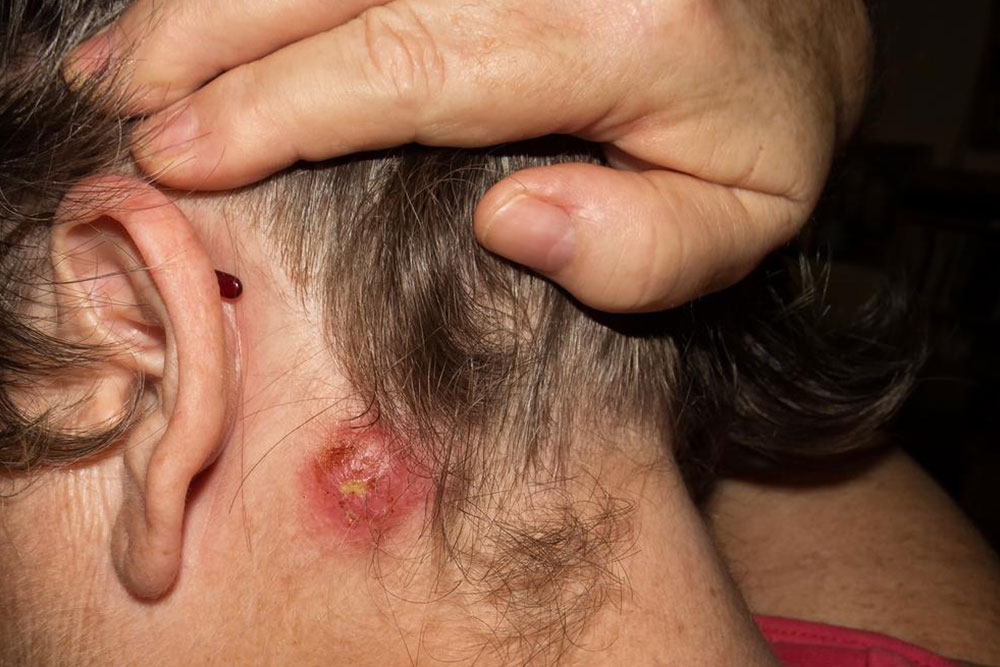
Signs and symptoms of skin abscesses typically include redness, swelling, warmth, tenderness, and the presence of a firm, raised bump. Smaller abscesses might be painless or minimally uncomfortable, but as they grow or fill with pus, they become increasingly tender and painful. Larger boils can cause significant discomfort and may interfere with daily activities. The warmth felt upon touch is a sign of underlying infection and inflammation. Recognizing these early signs is crucial for prompt intervention and preventing the spread of infection to surrounding tissues or other areas of the body.
Most skin abscesses originate around hair follicles or oil glands, especially in areas prone to sweating and friction such as the neck, face, armpits, groin, and buttocks. The primary cause is an infection by bacteria, notably Staphylococcus aureus, which enters the skin through minor cuts, abrasions, or skin injuries. Other factors contributing to abscess formation include insect bites, shaving cuts, skin conditions like folliculitis, and compromised immune systems that reduce the body's ability to fight infections.
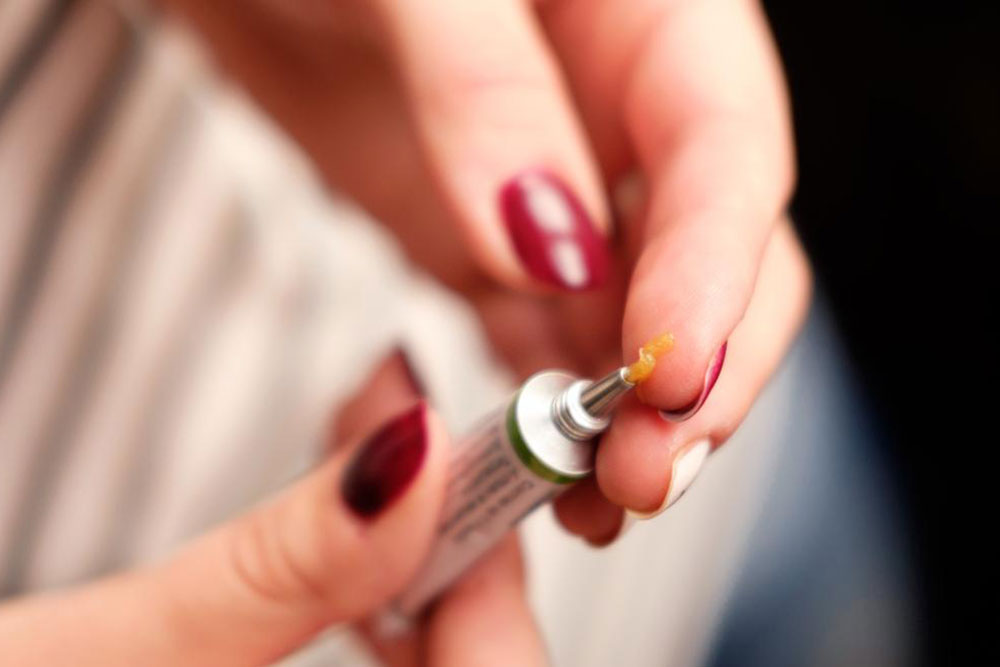
Home remedies and self-care practices play a vital role in managing small skin abscesses. Applying warm compresses multiple times a day encourages blood flow, helps soften the skin, and promotes natural drainage of pus. It’s important to note that individuals should never attempt to puncture or squeeze an abscess themselves, as doing so can worsen the infection or cause it to spread. If the abscess persists, enlarges, or is associated with fever, chills, or other systemic symptoms, seeking medical care is imperative.
Medical treatment for larger or persistent abscesses often involves drainage procedures performed by healthcare professionals. This process involves making a small incision and of course, ensuring proper sterile technique to prevent further infection. In some cases, antibiotics are prescribed to eradicate the bacterial infection, especially if there are signs of spreading infection or multiple abscesses. Proper wound care following drainage, including keeping the area clean and covered, is essential for healing and preventing recurrences.
Preventive strategies are key in reducing the risk of developing skin abscesses. Good personal hygiene, regular handwashing, and keeping the skin clean and dry are fundamental practices. Avoiding skin injuries, using proper shaving techniques, and managing skin conditions like folliculitis can significantly lower risk. Additionally, maintaining a healthy immune system through adequate nutrition, proper rest, and sometimes vaccination can help prevent infections that lead to abscess formation.
Monitoring for signs of infection, such as increased redness, swelling, warmth, pain, or the appearance of pus, allows early intervention. If you notice symptoms worsening or if a boil does not drain or improve within a few days, consult a healthcare professional promptly to prevent complications. Proper diagnosis, timely treatment, and good hygiene practices contribute to effective management and resolution of skin abscesses, ultimately supporting overall skin and systemic health.