Comprehensive Nutrition Plans to Manage Diverticulosis Effectively
Discover effective nutritional strategies to manage diverticulosis, including high-fiber diets, lifestyle tips, and avoiding aggravating foods. Learn how proper diet and habits can prevent complications like diverticulitis and promote overall colon health with this comprehensive guide.

Comprehensive Nutrition Plans to Manage Diverticulosis Effectively
Diverticulosis is a medical condition characterized by the formation of small pouch-like protrusions called diverticula on the inner wall of the large intestine. This condition tends to become more common as individuals age, often remaining asymptomatic but posing potential health risks if not properly managed. These pouches can sometimes cause discomfort, mild cramps, bloating, or irregular bowel movements. Although many people remain unaware of their presence, diverticulosis can develop into diverticulitis, which involves inflammation and infection of the diverticula, leading to more severe health issues. Proper dietary management plays a critical role in preventing the progression of this condition, and understanding the right nutritional strategies is essential for effective control and overall gut health.
Understanding Diverticulosis and Its Risks
Diverticulosis occurs when weak spots in the intestinal wall give way under pressure, creating small sacs or pouches. These diverticula are often discovered incidentally during colonoscopies or imaging tests for unrelated health concerns. Despite its prevalence, diverticulosis remains largely asymptomatic in most cases. However, certain lifestyle factors, such as a low-fiber diet, obesity, and a sedentary lifestyle, can increase the risk of developing diverticula. If not addressed through proper nutrition and lifestyle adjustments, diverticulosis may lead to diverticulitis, which involves inflammation, pain, fever, and sometimes complications like abscesses or perforation.
To prevent disease progression, it is essential to adopt dietary habits that promote a healthy, high-fiber gut environment.
Key Dietary Strategies to Manage Diverticulosis
Effective management of diverticulosis hinges upon nutritional choices that support intestinal health, reduce pressure on the colon, and prevent inflammation. Incorporating high-fiber foods into daily meals is paramount. Fiber's ability to add bulk, soften stools, and promote regular bowel movements helps to minimize pressure on diverticula, thereby preventing complications. Conversely, a diet high in processed foods, refined grains, and red meats can worsen symptoms and increase the risk of inflammation.
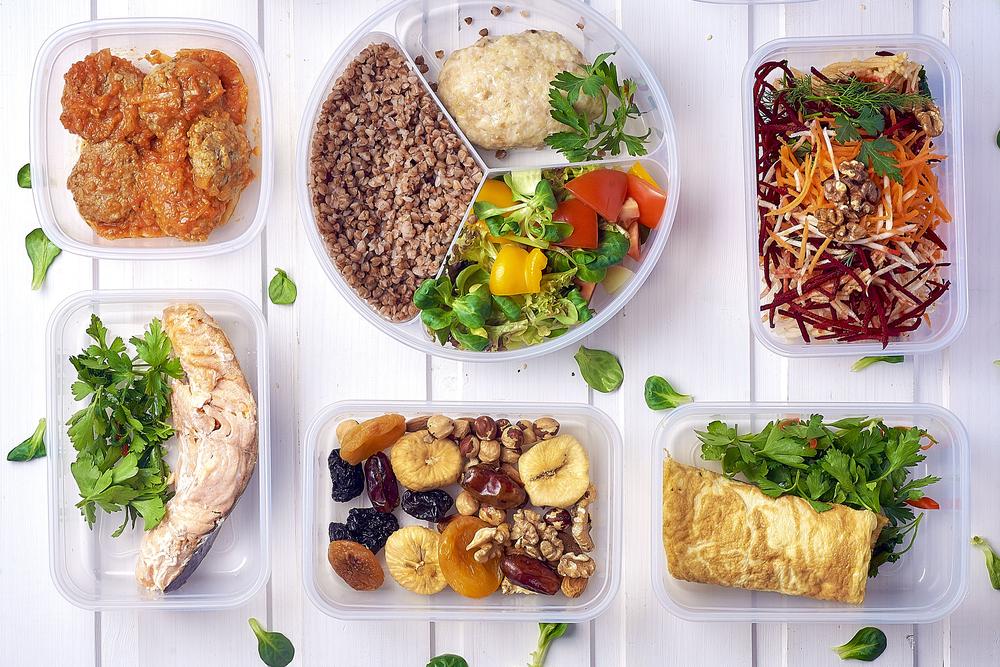
Recommended Foods for Managing Diverticulosis
Choose Whole Grains: Replacing refined grains with whole wheat, oats, barley, and brown rice ensures higher fiber content. Whole grain bread, pasta, and cereals are excellent staples.
Legumes: Incorporate beans, lentils, chickpeas, and peas regularly into meals. These foods are rich in both soluble and insoluble fibers, vital for healthy digestion.
Fruits with Skin: Opt for apples, pears, berries, and grapes with their skins intact. The skins are high in fiber and add extra bulk to stool, aiding in regularity.
Vegetables: Aim for a colorful variety of vegetables daily. Raw, steamed, or in broth-based soups and salads, they provide essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber.
Hydration: Consuming adequate fluids, especially between meals, helps fiber do its job by softening stool and facilitating smoother passage through the colon.
Foods to Limit or Avoid
While increasing fiber intake, it is equally important to avoid foods that could irritate the digestive system or exacerbate symptoms:
Limit Processed and Refined Foods: White bread, white rice, pastries, and snack foods are low in fiber and may contribute to constipation.
Reduce Red and Processed Meat: Excessive intake has been linked to increased colon inflammation risks.
Avoid Seeds and Nuts (Cautiously): Although recent research suggests seeds and nuts are generally safe, some individuals prefer to limit them if they experience discomfort.
Additional Lifestyle Considerations
Diet alone isn't enough; lifestyle modifications are equally crucial for controlling diverticulosis. Regular exercise promotes healthy bowel movements and reduces colon pressure. Maintaining a healthy weight alleviates strain on the colon and reduces inflammation risk. Stress management and avoiding smoking can further improve digestive health. Patients should also ensure adequate hydration daily, often aiming for at least 8-10 glasses of water, especially when increasing fiber intake.
Monitoring and Medical Advice
Regular medical check-ups and colonoscopies are essential for individuals with diverticulosis to monitor disease progression and catch any early signs of diverticulitis. If symptoms such as persistent abdominal pain, fever, or changes in bowel habits occur, prompt medical evaluation is necessary. Specialists might recommend additional interventions if complications arise, but the cornerstone of management remains a high-fiber diet and healthy lifestyle choices.
Conclusion: The Power of Dietary Management in Diverticulosis
Managing diverticulosis effectively requires a comprehensive understanding of dietary and lifestyle principles. Prioritizing high-fiber foods, staying well-hydrated, and avoiding inflammatory triggers are fundamental steps toward preventing complications like diverticulitis. Adopting these nutritional strategies not only alleviates symptoms but also promotes long-term colon health, enhancing quality of life. Empowered with knowledge and proactive habits, individuals can take control of their condition and minimize health risks associated with diverticulosis. Remember, personalized advice from healthcare professionals is vital to tailor a diet plan suited to individual needs and health status.