Comprehensive Guide to Diverticulitis: Recognizing Symptoms and Understanding Causes of Digestive Disorders
This comprehensive article provides in-depth knowledge about diverticulitis, including its causes, symptoms, and preventive measures. It emphasizes early recognition of symptoms like abdominal pain, fever, and bleeding, highlighting the importance of lifestyle choices such as a high-fiber diet and hydration. Understand how aging increases risk and learn how to manage or prevent this common digestive disorder effectively. Ideal for anyone seeking detailed insights into digestive health issues and their management strategies.

Comprehensive Guide to Diverticulitis: Recognizing Symptoms and Understanding Causes of Digestive Disorders
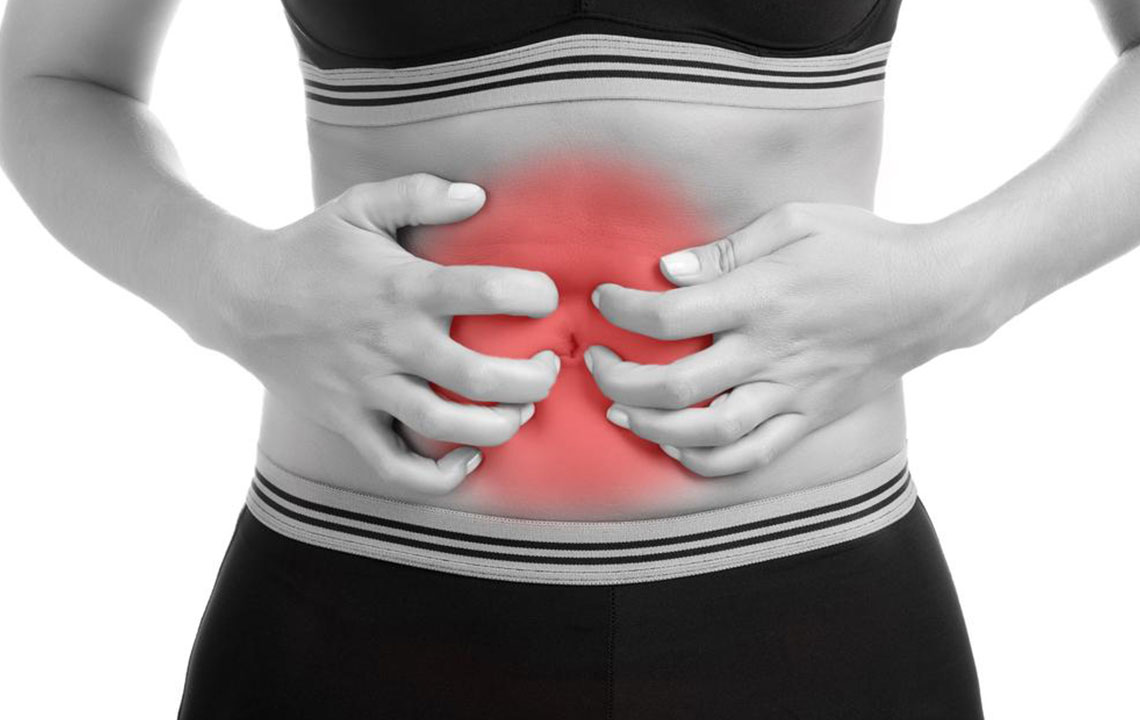
Diverticulitis is a common gastrointestinal condition that can significantly impact quality of life if not diagnosed and managed promptly. To understand diverticulitis better, it's essential to examine its origins, how it progresses, and the key signs and symptoms that indicate its presence. This condition develops when small pouches, known as diverticula, form along the walls of the colon—most frequently in the sigmoid colon—due to increased pressure and weakening of the intestinal walls. These pouches are generally asymptomatic initially, but their inflammation or infection can cause notable health issues. Recognizing the early symptoms such as abdominal pain, changes in bowel habits, fever, rectal bleeding, and bloating allows for early intervention, which can prevent complications like perforation, abscesses, or severe infection.
To fully grasp diverticulitis, it’s important to distinguish between diverticulosis and diverticulitis. Diverticulosis refers to the presence of diverticula—those small, pouch-like protrusions in the colon wall—and many individuals are unaware they have it because it often remains asymptomatic. However, when these pouches become inflamed or infected, the condition is termed diverticulitis, which can cause an array of symptoms that significantly disrupt daily life. The formation of diverticula is primarily linked to a combination of lifestyle factors, especially a diet low in fiber, which results in increased colonic pressure. As the colon works harder to move stool, the walls weaken over time, leading to pouch formation. Additionally, aging plays a considerable role; studies show that nearly 50% of those over 80 years old develop diverticulosis, highlighting the strong association with age-related changes in the colon.
Infection and inflammation of diverticula often arise due to bacterial invasion, as food particles and bacteria become trapped within these pouches. This bacterial growth can lead to complications such as abscess formation, bleeding, or even perforation of the colon wall—conditions that may require urgent medical intervention. Many individuals with diverticulosis do not experience symptoms initially, but once inflammation occurs, symptoms become more apparent. Typical symptoms include sudden on-set abdominal pain—usually on the lower left side—along with fever, nausea, vomiting, constipation or diarrhea, and sometimes rectal bleeding. Bloating and a general sense of malaise are also common indicators of progressing inflammation. Recognizing these signs early is vital, as untreated diverticulitis can lead to severe complications including peritonitis and the need for surgical removal of affected parts of the colon.
Preventive strategies play a crucial role in reducing the risk of developing diverticulitis. A high-fiber diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and nuts promotes healthy bowel movements and decreases colonic pressure, thereby reducing the development of diverticula and their subsequent inflammation. Hydration is similarly important, ensuring stool consistency that minimizes strain during defecation. Lifestyle modifications such as regular exercise and avoiding smoking further contribute to gut health. For those diagnosed with diverticulosis, routine medical check-ups and monitoring can help identify any progression toward diverticulitis early. When symptoms such as severe abdominal pain, rectal bleeding, or fever arise, immediate medical attention is essential to determine the severity and initiate appropriate treatment, which may include antibiotics, dietary modifications, or even surgical interventions.