Comprehensive Guide to Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms of Crohn’s Disease
This comprehensive article provides an in-depth overview of Crohn’s disease, emphasizing early signs, causes, symptoms, complications, and management strategies. It helps readers understand the importance of early diagnosis and treatment to improve quality of life and prevent severe health issues related to this chronic gastrointestinal condition.
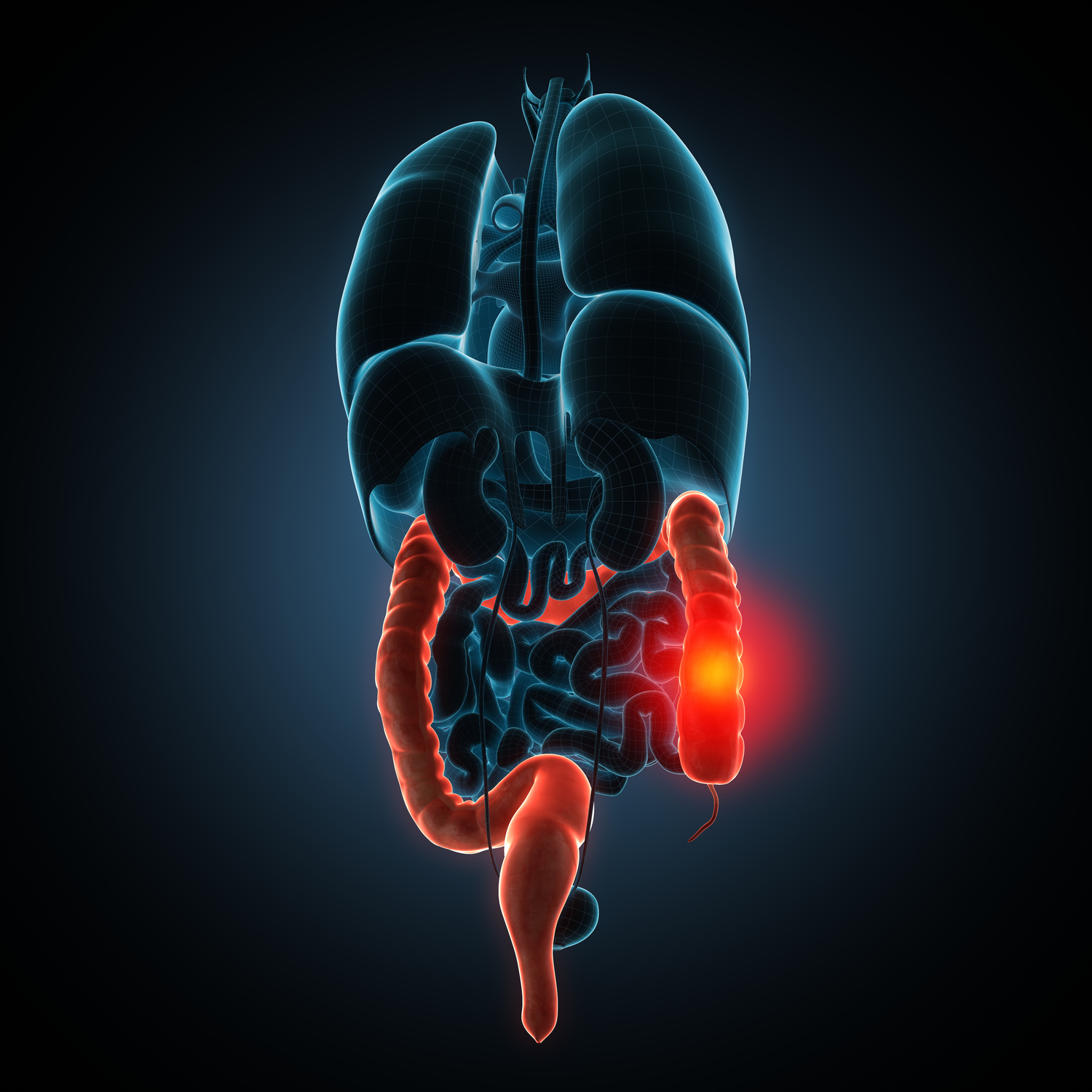
Crohn’s disease is a persistent and often debilitating inflammatory condition that can affect any part of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, from the mouth all the way to the anus. This chronic disorder typically targets areas such as the small intestine and colon, leading to a range of uncomfortable and, at times, severe symptoms. Understanding the key indicators of Crohn’s disease is crucial for early diagnosis and effective management, which can significantly improve patients’ quality of life. This detailed guide aims to shed light on the primary signs, underlying causes, potential complications, and treatment considerations associated with this complex condition.
Crohn’s disease arises due to a multifaceted interplay of genetic predispositions, immune system irregularities, and environmental influences. These factors contribute to the abnormal immune response that causes inflammation in the gastrointestinal lining, ultimately leading to tissue damage. Early stages of the disease often manifest as inflammation localized to the ileum — the last part of the small intestine — and the proximal colon. Such inflammation results in symptoms like persistent diarrhea, abdominal pain, and unintended weight loss, which can sometimes be mistaken for less severe digestive issues. Recognizing these symptoms early is vital for timely intervention and preventing potential complications.
Understanding the Underlying Causes of Crohn’s Disease
Genetics: A family history of Crohn’s disease increases the likelihood of developing the condition, suggesting a hereditary component that influences immune regulation and gut integrity.
Immune System Dysregulation: An abnormal immune response mistakenly targets healthy tissues within the GI tract, leading to chronic inflammation and tissue damage.
Environmental Triggers: Factors such as bacterial infections, smoking, dietary patterns, and stress can precipitate or exacerbate symptoms, acting as external triggers for flare-ups.
Common Symptoms That Signal Crohn’s Disease
Persistent Diarrhea: Characterized by frequent, watery stools, often accompanied by cramping and abdominal discomfort, persistent diarrhea is a hallmark of Crohn’s and warrants prompt medical evaluation. This symptom can vary in severity but generally indicates ongoing inflammation in the gastrointestinal lining.
Rectal Bleeding: The presence of blood in stools suggests bleeding within the intestinal tract. This can result from ulcerations or fissures caused by inflamed tissues and should be investigated thoroughly.
Unexplained Weight Loss: A significant reduction in weight despite adequate dietary intake often reflects systemic inflammation and malabsorption associated with Crohn’s, indicating disease progression and the need for medical management.
Fatigue and Weakness: Chronic inflammation and nutritional deficiencies can lead to persistent tiredness, low energy levels, and general malaise, heavily impacting daily functioning.
Reduced Appetite: A decreased desire to eat may result from abdominal discomfort or nausea, further contributing to weight loss and nutritional deficiencies.
Potential Complications if Not Managed Properly
Left untreated, Crohn’s disease can lead to serious health complications. These include bowel obstructions caused by scar tissue formation, fistulas—abnormal connections between different parts of the intestine or other organs—and fissures, which are deep ulcers prone to infection. Moreover, ongoing inflammation increases the risk of colon cancer over time. Recognizing symptoms early and seeking appropriate medical care are critical steps in preventing these severe outcomes. With proper treatment, many patients can manage symptoms effectively and prevent or delay the development of complications.
Managing Crohn’s Disease: Treatment and Lifestyle Strategies
Effective management of Crohn’s involves a combination of medication, dietary adjustments, and lifestyle modifications. Medications such as anti-inflammatory drugs, immune suppressants, and biologic agents aim to control inflammation and maintain remission. Dietary strategies include personalized nutrition plans to reduce symptoms and address nutritional deficiencies. Lifestyle factors like quitting smoking, managing stress, and regular medical checkups are vital components of comprehensive disease management. For individuals experiencing flare-ups or complications, surgical intervention may sometimes be necessary to remove damaged sections of the GI tract. Collaboration with a healthcare team ensures a tailored approach that optimizes outcomes and enhances quality of life for those living with Crohn’s disease.
In summary, understanding the key indicators of Crohn’s disease allows for early detection and proactive management. Awareness of symptoms like chronic diarrhea, rectal bleeding, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, and reduced appetite can prompt timely medical intervention. Recognizing the potential severity of the condition underscores the importance of ongoing medical oversight, lifestyle modifications, and adherence to treatment plans to reduce the risk of complications and improve long-term health outcomes.