Comprehensive Guide to Recognizing the Early Signs of Rheumatoid Arthritis
This comprehensive article explores the early signs of rheumatoid arthritis, emphasizing the importance of early detection for effective treatment. It covers symptoms such as joint swelling, stiffness, systemic signs, and skin changes, offering valuable insights into managing and recognizing this autoimmune disorder. Understanding these symptoms can lead to prompt medical intervention, preventing irreversible joint damage and improving patient outcomes.

Comprehensive Guide to Recognizing the Early Signs of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis and Its Impact
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic, systemic autoimmune disease that primarily targets the joints but can also affect other organs and tissues within the body. It occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks the synovial membranes lining the joints, leading to inflammation, pain, swelling, and potential long-term damage to bone and cartilage. If left untreated, RA can significantly impair mobility and reduce quality of life.
Beyond the joints, rheumatoid arthritis may also manifest in various organs, including the skin, eyes, blood vessels, heart, and lungs. The disease’s progression can be unpredictable, with periods of flare-ups and remission. Early detection and management are crucial, as starting treatment early can help prevent irreversible joint damage, preserve function, and improve overall prognosis.
Recognizing the Common Symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis
1. Persistent Joint Swelling
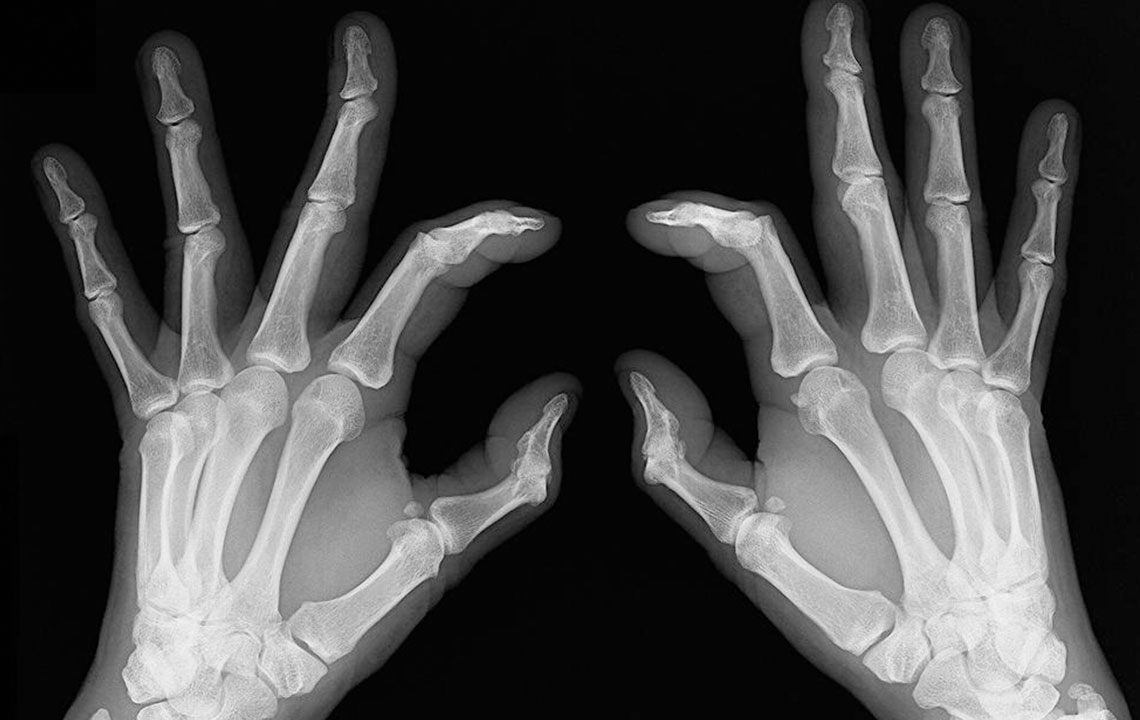
One of the hallmark symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis is swelling in multiple joints. These are often symmetric, affecting paired joints on both sides of the body — for example, both wrists or both knees. Swelling tends to be prominent in the small joints of the hands and feet, but larger joints such as the shoulders, hips, elbows, and knees can also be involved.
Patients might notice that the affected joints look enlarged, feel tender to touch, and may be warm due to inflammation. The swelling is usually persistent and does not subside easily, which distinguishes RA from other joint conditions. Additionally, swelling in the jaw area can occur, often resulting in pain and discomfort while moving or even at rest. Over time, ongoing joint swelling can lead to damage to tendons and soft tissues surrounding the joints.
Chronic inflammation can also affect non-joint tissues, including bones, blood vessels, skin, salivary glands, and vital organs such as the heart and kidneys. Recognizing swelling in the early stages provides critical clues for diagnosis and management.
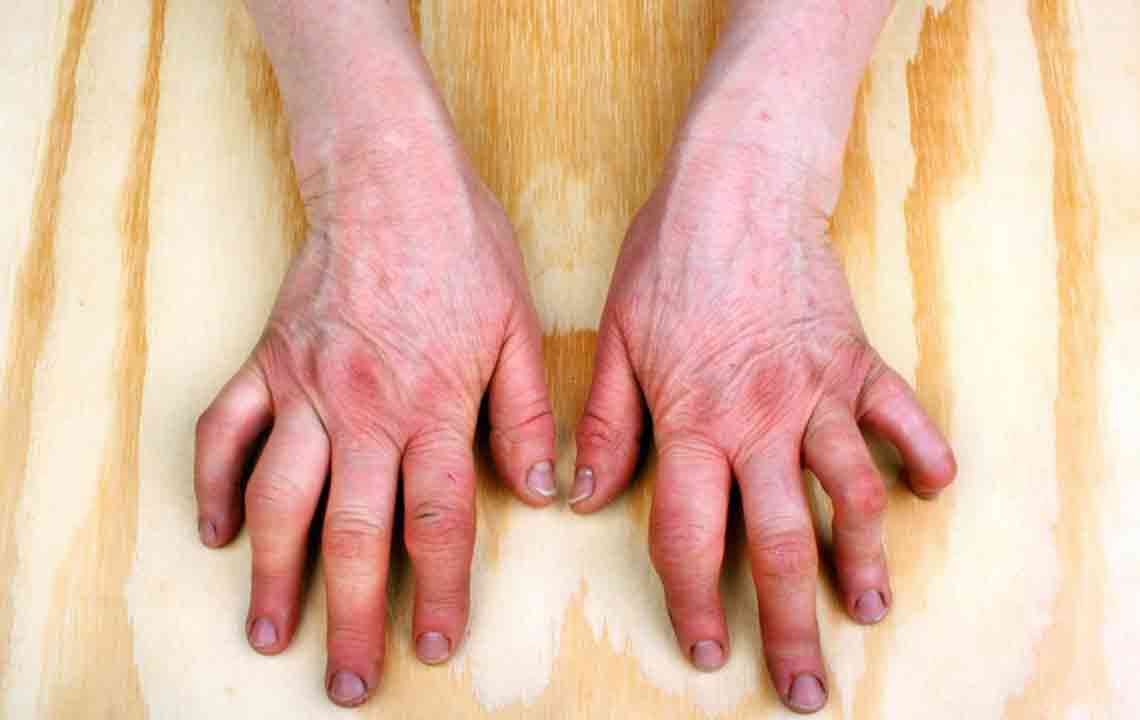
2. Rheumatoid Nodules and Skin Changes
Rheumatoid nodules are firm, lump-like lesions that can develop beneath the skin, typically near affected joints such as the elbows or fingers. These nodules are often visible when joints are flexed or extended and are a distinctive feature of RA.
In addition to nodules, some individuals may exhibit purple patches known as purpura on their skin, which results from inflammation of small blood vessels. These skin changes often indicate systemic involvement of the disease and warrant thorough evaluation by healthcare professionals.
3. Prolonged Joint Stiffness and Reduced Mobility
One of the early, characteristic symptoms of RA is stiffness, especially noticeable in the mornings. Unlike some forms of arthritis which may improve with movement, RA-related stiffness tends to last over an hour, gradually diminishing as the day progresses. This stiffness is due to inflammation within the joint capsules, leading to reduced flexibility and function.
If untreated, persistent stiffness can cause joint dislocation and deformity, significantly impairing mobility and daily functioning. Recognizing early morning stiffness as a symptom can prompt timely medical consultation, helping to initiate treatment before irreversible damage occurs.
4. Systemic Symptoms: Fever and Fatigue
Rheumatoid arthritis is associated with systemic symptoms that extend beyond joint issues. Many patients experience general malaise, persistent fatigue, and low-grade fever, especially during flare-ups. These symptoms often arise from anemia caused by inflammation-related red blood cell reduction, leading to constant tiredness.
Fever accompanying joint swelling signals active inflammation and the body's immune response. Monitoring these systemic signs alongside joint symptoms can provide critical clues for diagnosis and disease activity assessment.
5. Eye Inflammation and Other Extra-Articular Manifestations
Some individuals with RA develop inflammation or irritation in the eyes, such as dryness, redness, or soreness. Conditions like scleritis, episcleritis, or keratoconjunctivitis can occur, requiring specialized eye care and treatment.
Other extra-articular manifestations include inflammation of blood vessels (vasculitis), which might present as skin rashes or numbness, and involvement of internal organs such as the heart and lungs. Recognizing these symptoms early is vital for comprehensive management of the disease.
6. Redness and Warmth in Joints
Involved joints often appear reddish and feel warm to the touch due to active inflammation. These signs are indicative of increased blood flow and immune activity within the joint tissues. Persistent redness and warmth, especially when accompanied by swelling and pain, are key indicators of active rheumatoid arthritis.
The Importance of Early Diagnosis and Management
Detecting rheumatoid arthritis in its initial stages is crucial for effective treatment. Early intervention with disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) and biologic therapies can significantly reduce joint damage, improve function, and enhance quality of life. Delayed diagnosis often leads to irreversible joint deformities, chronic pain, and loss of mobility.
If you experience symptoms such as joint swelling lasting more than a few weeks, prolonged morning stiffness, persistent fatigue, skin nodules, or systemic signs like fever, consult a healthcare provider promptly. Rheumatologists utilize a combination of clinical examination, blood tests, imaging studies, and sometimes biopsy to confirm the diagnosis.
Preventive Measures and Lifestyle Tips
While medical treatment is essential, patients can adopt lifestyle changes to manage symptoms better and possibly slow disease progression. These include maintaining a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, engaging in gentle exercise to preserve joint flexibility, avoiding smoking, and managing stress effectively.
Regular follow-up with healthcare professionals ensures optimal disease control and early detection of any complications or flare-ups.
Conclusion
Understanding the key signs of rheumatoid arthritis is vital for early diagnosis and effective management. Persistent joint swelling, prolonged stiffness, skin nodules, systemic symptoms like fever and fatigue, and signs of inflammation in other tissues are critical indicators. Recognizing these early can help individuals seek timely medical care, preventing severe joint damage and maintaining a good quality of life. If you suspect you have these symptoms, consult a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation and appropriate treatment plan.