Comprehensive Guide to Factors Influencing Psoriasis Development and Management
This comprehensive article explores the many factors influencing psoriasis development, including genetics, environmental triggers, lifestyle choices, and infections. It offers insights into managing the condition through awareness, lifestyle modifications, and medical treatments, helping sufferers improve their quality of life by reducing flare-ups and understanding their disease better.
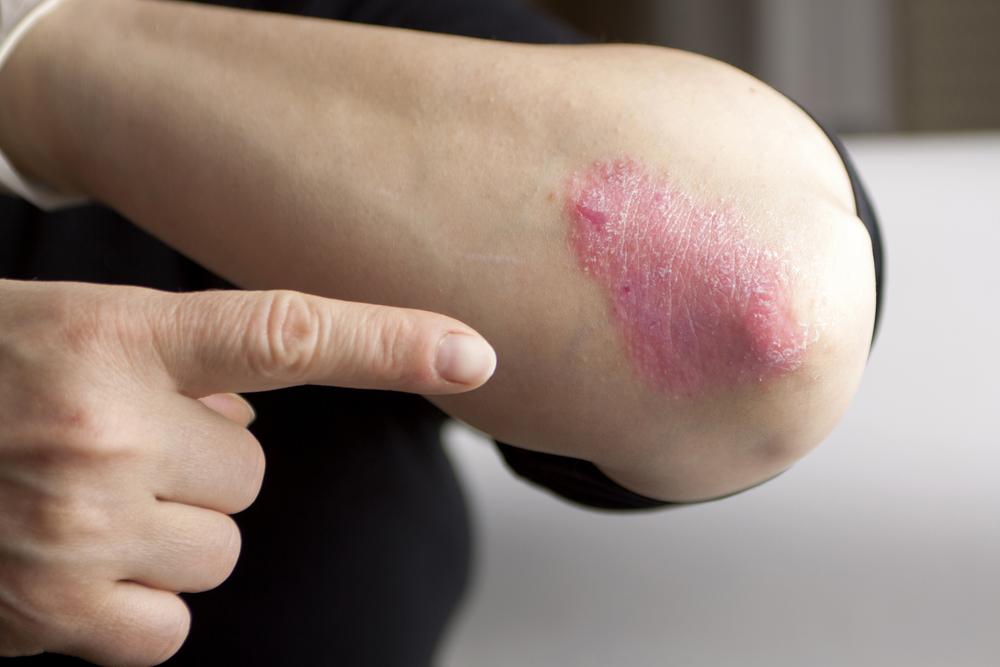
Comprehensive Guide to Factors Influencing Psoriasis Development and Management
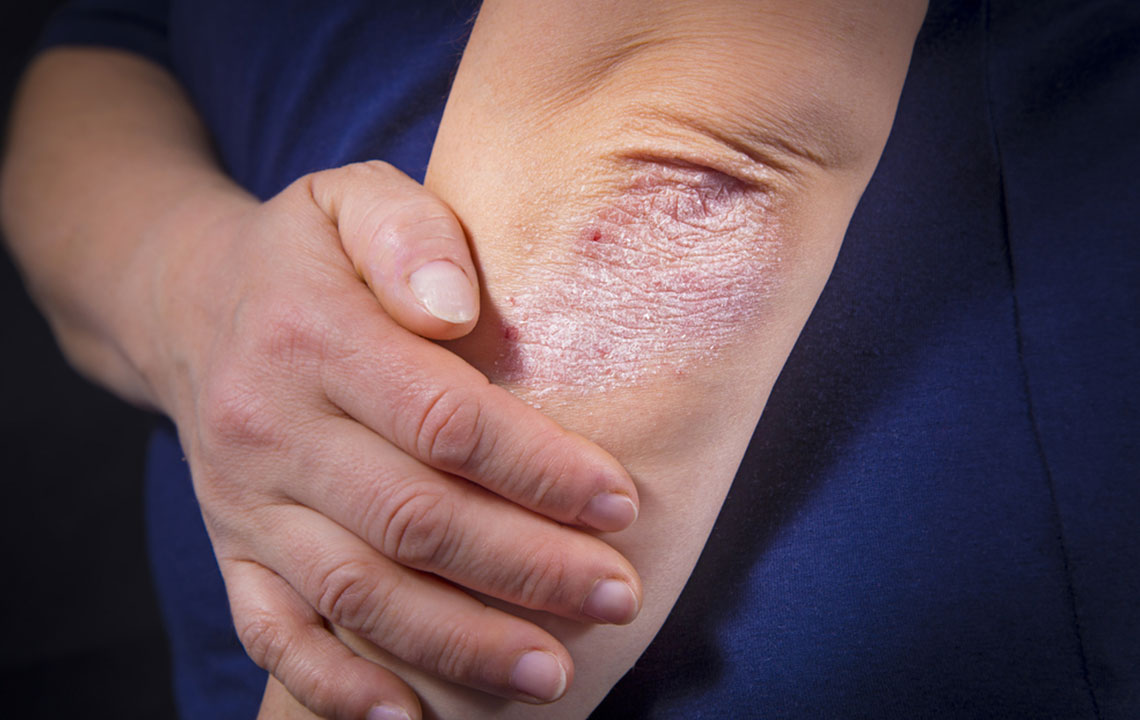
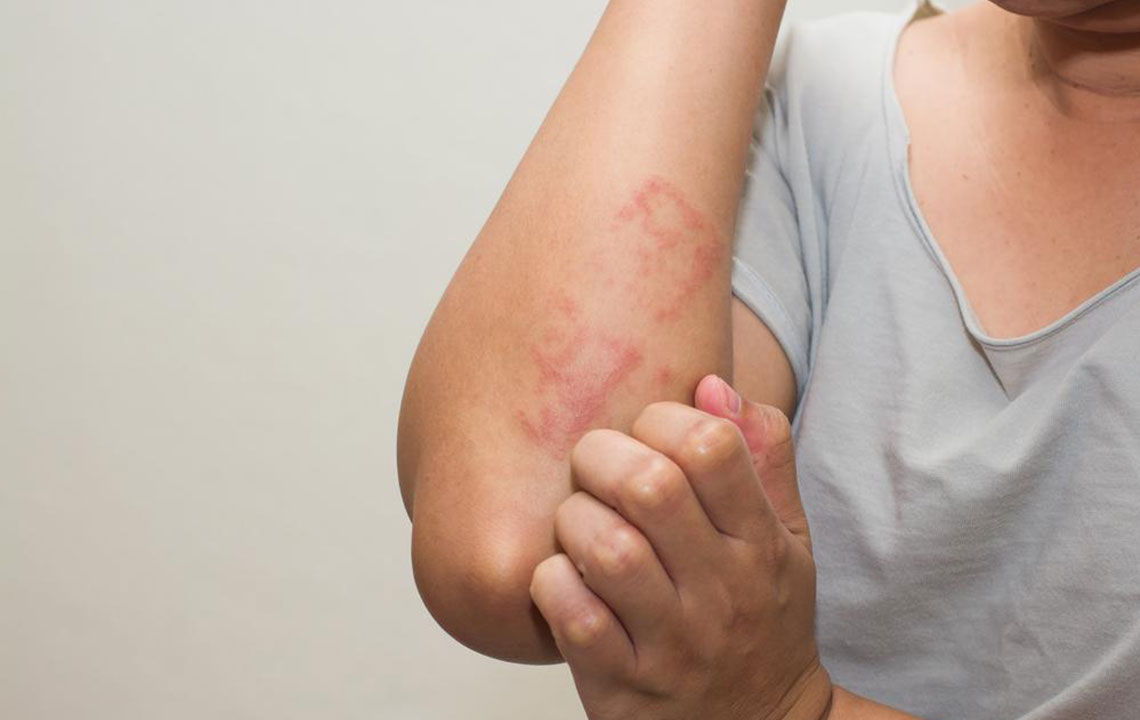
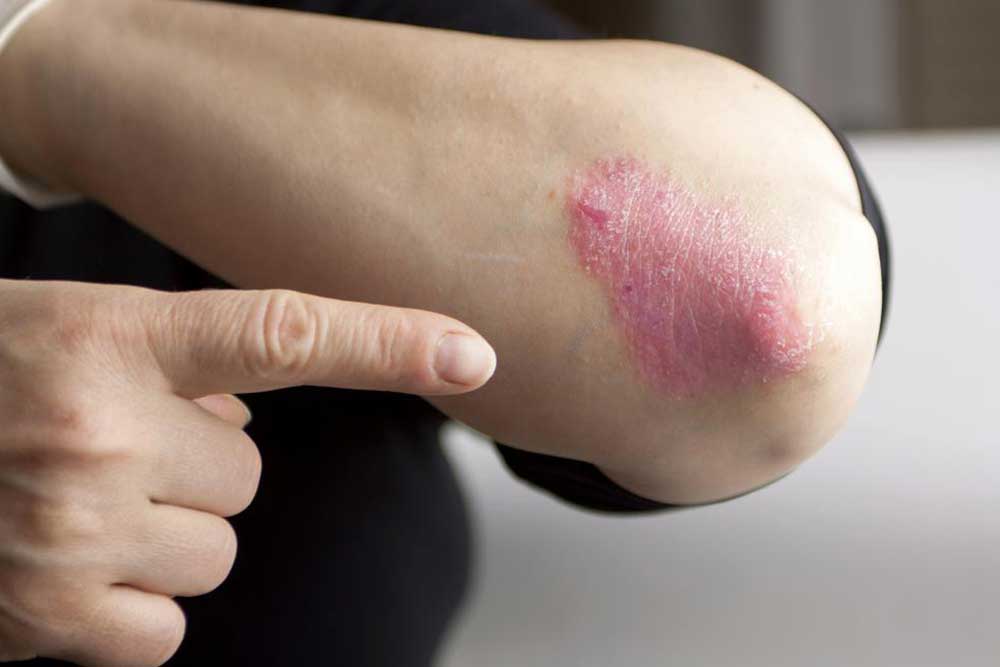
Psoriasis is a complex and chronic autoimmune skin disorder characterized by the rapid buildup of skin cells, leading to the formation of itchy, inflamed, and scaly patches on the skin's surface. This condition affects millions worldwide, impacting their quality of life through discomfort and often aesthetic concerns. While the exact root cause of psoriasis remains a subject of ongoing research, a variety of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors are known to influence its onset and severity. Importantly, psoriasis is non-contagious, meaning it cannot be transmitted from person to person through physical contact, which often eases concerns about spread among those affected.
Understanding the Causes and Triggers of Psoriasis
Identifying the factors that contribute to the development or worsening of psoriasis is crucial for effective management and treatment. Although psoriasis stems from immune system dysfunction — specifically, an overactive immune response causing skin cell proliferation — external and internal elements often trigger or exacerbate symptoms. Recognizing these triggers allows individuals to take preventative measures and seek appropriate treatment early.
Genetic Factors
A significant portion of psoriasis cases exhibits a hereditary component. Individuals with a family history of psoriasis are at a higher risk of developing the condition, as certain genes involved in immune regulation and skin cell production are inherited. This genetic predisposition can also influence the severity and frequency of flare-ups, making it essential for those with affected relatives to be vigilant of early symptoms and triggers.
Environmental and Lifestyle Factors
Emotional Stress and Psychological Triggers
Chronic stress, anxiety, and emotional upheavals are common psoriasis exacerbators. Stress can disrupt immune system functioning, leading to increased inflammation and more frequent or severe flare-ups. Techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, yoga, and regular physical activity are proven to mitigate stress levels, thereby often reducing the likelihood of psoriasis outbreaks.
Climate and Weather Conditions
Climate plays a vital role in psoriasis management. Cold, dry weather tends to dry out the skin, leading to cracking, inflammation, and worsening of lesions. Conversely, exposure to sunlight and moderate warmth can help improve symptoms by reducing inflammation. Regular exposure to natural sunlight, with appropriate skin protection to prevent burns, can be beneficial. Additionally, maintaining skin hydration through frequent moisturizing is essential in dry climates to shield against flare-ups.
Infections and Immune Challenges
Certain infections have been linked to triggering psoriasis episodes. For instance, bacterial and viral infections, including streptococcal pharyngitis, yeast infections, HIV, and thrush, can activate immune responses that precipitate or intensify skin lesions. Effective treatment of underlying infections often alleviates related skin symptoms. It is vital for individuals with psoriasis to monitor and manage infections promptly to prevent exacerbations.
Medications and Chemical Exposures
Some medications, such as beta-blockers, lithium, antimalarials, and corticosteroids, have been noted to induce or worsen psoriasis in susceptible individuals. Environmental exposures to harsh chemicals, fragrances, or skin irritants could also impair skin barrier function and act as triggers. Patients should discuss medication plans with their healthcare providers and consider alternative options if they notice worsening symptoms.
Diet and Lifestyle Choices
While diet's direct role remains under investigation, emerging evidence suggests that certain foods may influence inflammation and immune responses. Maintaining a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, such as omega-3 fatty acids, fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, may support skin health. Avoiding known dietary triggers like processed foods, excessive alcohol, and fried foods can also prevent flare-ups. Regular exercise and adequate sleep contribute to immune regulation and overall well-being.
To effectively manage psoriasis, awareness of these triggers is essential. Patients are advised to observe personal patterns, avoid known provocateurs, and consult healthcare professionals for personalized treatment plans. Topical treatments, phototherapy, systemic medications, and biologics are common therapeutic options tailored to individual needs. Complementary approaches, including stress reduction techniques, proper skin care, and lifestyle modifications, play crucial roles in enhancing disease control. Recognizing early signs of flare-ups, such as redness, itching, or scaling, enables prompt intervention, reducing the severity and improving long-term outcomes.
In conclusion, while psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune disorder without a definitive cure, understanding its key influences allows affected individuals to better manage their condition. Combining medical treatments with lifestyle adjustments can significantly decrease the frequency and intensity of flare-ups, leading to improved skin health and better quality of life. Staying informed about personal triggers and maintaining a proactive approach are central to living well with psoriasis.