Comprehensive Guide to HIV/AIDS Diagnosis and Effective Treatment Strategies
This comprehensive guide explores the crucial processes involved in diagnosing HIV/AIDS and establishing effective treatment strategies. Detailing various testing methods such as antibody, RNA, antigen/antibody combination, rapid, and saliva tests, it emphasizes early detection's importance. The article also discusses key factors in treatment planning, including patient readiness, disease stage, and co-existing conditions. By understanding these aspects, healthcare providers can design personalized therapies aimed at controlling the infection, improving prognosis, and enhancing patient well-being. This detailed overview aims to support increased awareness and timely intervention for HIV/AIDS management.
Understanding HIV/AIDS Diagnosis for Optimal Treatment Outcomes
HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) often presents with subtle or non-specific symptoms, which can easily be mistaken for other illnesses. This makes early detection through precise medical testing crucial in managing the disease effectively. Accurate diagnosis not only helps in preventing the progression to AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome) but also enables timely initiation of effective treatment protocols, improving patient outcomes and quality of life.
Various diagnostic tests are utilized worldwide to identify HIV infection. These tests analyze different bodily fluids, such as blood and saliva, for specific markers associated with the virus. The results obtained from these tests are vital for physicians to craft personalized treatment plans, ensuring that patients receive the most appropriate care suited to their disease stage and overall health status.
Antibody Tests (Serological Tests)
These are among the most common initial screening tools used to detect antibodies produced by the immune system in response to HIV infection. These antibodies typically become detectable within 2 to 8 weeks following exposure, although in some cases, it can take longer. Tests such as ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) and immunoassays are highly reliable and widely used in clinical practice. Confirmatory testing is often performed if initial results are positive, helping to reduce false positives and ensure accurate diagnosis.
Another crucial diagnostic method is the RNA test, which detects the actual virus particles in the bloodstream. This test can identify infection as early as 10 to 12 days after exposure, making it highly effective during the early stages of infection. However, due to its higher cost, it is usually reserved for cases where early detection is necessary, such as in high-risk populations, or when symptoms closely mimic those of other illnesses like the flu. It provides vital information about the viral load, which is essential for tracking disease progression and treatment efficacy.
In addition to RNA testing, the Combination Antigen/Antibody Test is commonly used in screening for HIV. This test detects both HIV antibodies and antigens—the viral components that appear in blood within 2 to 4 weeks after infection. It is advantageous because it shortens the window period, allowing for more rapid and accurate early diagnosis. This combined testing approach enhances the ability to detect infections sooner and facilitates prompt intervention.
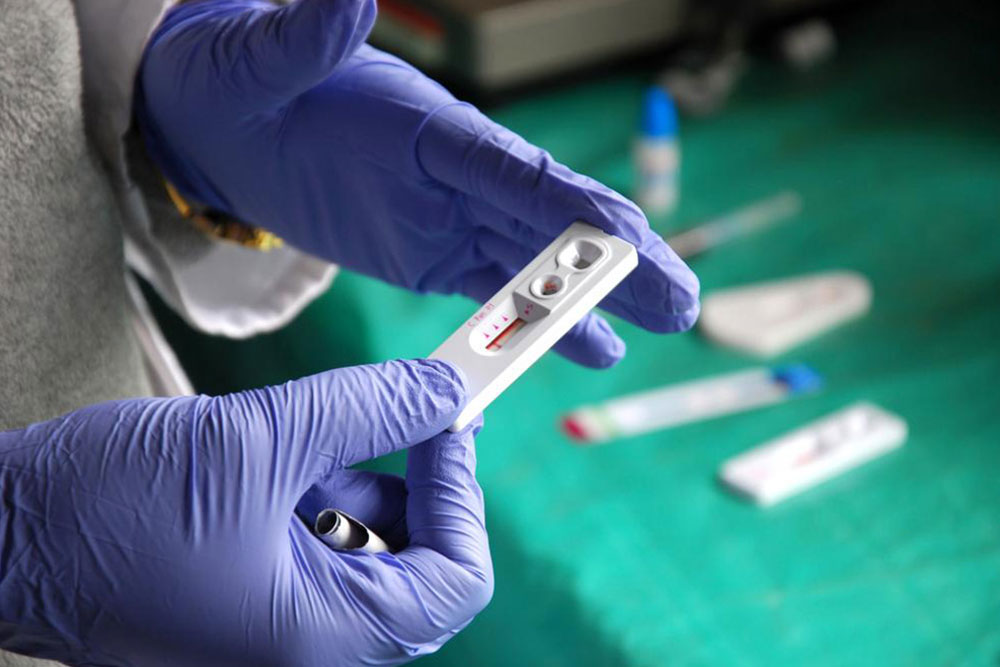
Rapid antigen tests offer a quick and efficient way to screen for HIV infection, especially in settings where immediate results are beneficial. These tests can deliver results within 20 minutes, making them suitable for clinics, community testing sites, and emergency settings. Although they are less sensitive than laboratory-based tests, positive results should always be confirmed with more definitive testing to ensure accuracy.
Saliva Tests
This non-invasive testing method involves collecting saliva samples using a cotton swab or pad. The sample is then analyzed in a laboratory, with results typically available within 2-3 days. Saliva tests are especially useful for initial screenings due to their simplicity, ease of use, and convenience, making them accessible to individuals hesitant about blood draws.
Key Considerations in Developing HIV Treatment Plans
When healthcare professionals devise a treatment strategy for HIV-positive individuals, they assess several vital factors to ensure the approach is personalized and effective:
The patient’s readiness, willingness, and psychological preparedness to start and adhere to therapy
The specific stage of the infection, ranging from acute to chronic phases
Any co-existing health conditions or comorbidities that might influence treatment choices
Following comprehensive testing and evaluation, healthcare providers develop a tailored management plan that may include antiretroviral therapy (ART), lifestyle modifications, regular monitoring, and support services. Early diagnosis and individualized treatment are key components in controlling the infection, preventing transmission, and maintaining a good quality of life for those living with HIV.