Cutting-Edge Developments in HIV Management and Treatment Strategies
This article explores the latest advances in HIV treatment, focusing on post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP), antiretroviral therapy (ART), and the importance of early intervention. It delves into how modern medicine has made managing HIV more effective and tolerable, dispelling common myths and emphasizing proactive healthcare strategies. The comprehensive overview aims to inform readers about current HIV management practices, recent breakthroughs, and the critical role of early diagnosis and treatment in improving quality of life and reducing transmission risks.
Cutting-Edge Developments in HIV Management and Treatment Strategies
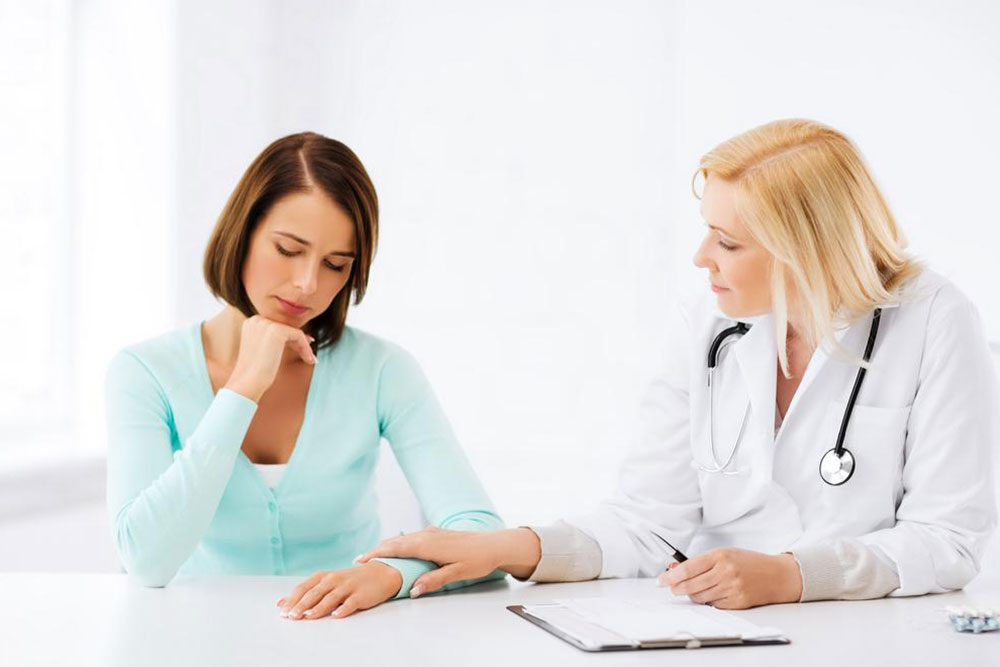
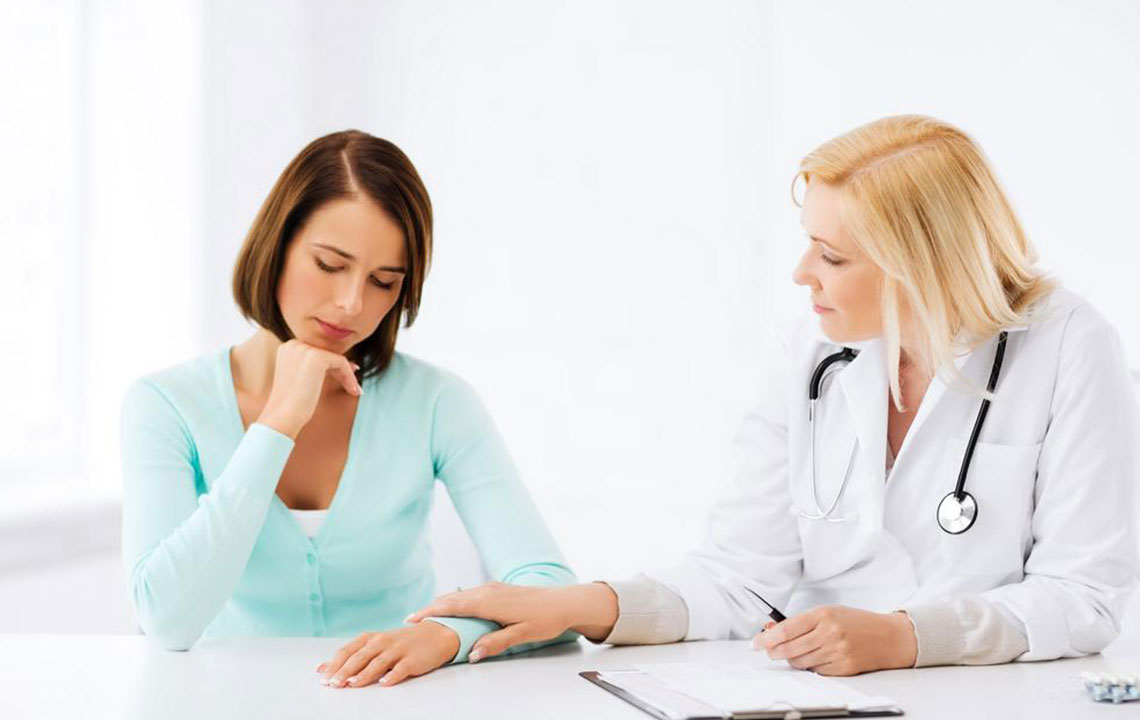
Accelerating medical responses to HIV exposure is essential for preventing the virus from taking hold within the body. One of the most critical early interventions is post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP), a treatment protocol that involves taking a combination of antiretroviral drugs within 72 hours after suspected exposure to HIV. The primary goal of PEP is to significantly reduce the risk of developing a full-blown infection, although it is not 100% effective and may cause temporary side effects such as nausea, fatigue, or gastrointestinal discomfort. Health professionals emphasize the importance of quick action and adherence to the medication schedule to maximize the effectiveness of PEP.
Understanding Antiretroviral Therapy (ART)
While a complete cure for HIV remains a future goal, advances in medical research have made it possible to effectively manage the virus through comprehensive therapies. Antiretroviral Therapy (ART) is the cornerstone of HIV treatment today. ART involves the daily administration of a combination of medications that work synergistically to suppress the replication of HIV within the body. The primary aim is to reduce the viral load — the amount of HIV present in the bloodstream — to undetectable levels. Achieving an undetectable viral load not only enhances the individual's health but also significantly reduces the risk of transmitting the virus to others, thereby playing a crucial role in public health efforts to curb the spread of HIV.
Debunking Common Myths About HIV Treatment
There is a widespread presence of misinformation about HIV treatment, often leading to misconceptions and unnecessary fears. One common misconception is that HIV patients need to take multiple pills multiple times a day; in reality, most patients now take a once-daily combination pill that includes multiple active ingredients, simplifying treatment regimens. There are six different classes of antiretroviral drugs, with over 30 available options, allowing healthcare providers to tailor therapy plans to individual needs and manage potential side effects effectively. Modern HIV medications are designed to be more tolerable, with side effects generally limited to mild issues such as stomach upset or fatigue, which tend to diminish over time. Although some risks—such as alterations in cholesterol levels or reductions in bone mineral density—exist, the overwhelming benefits of early initiation of ART far outweigh these concerns.
The Importance of Early Treatment Initiation
Timely starting of ART is crucial for optimal health outcomes. While some doctors historically delayed treatment until certain immune thresholds were reached, current medical guidelines strongly recommend early intervention. Initiating treatment promptly after diagnosis not only enhances long-term health prospects by preventing immune system deterioration but also reduces the likelihood of transmission to others. Advances in medical research and drug formulations have made early treatment safer and more manageable, empowering individuals living with HIV to maintain a high quality of life. Regular monitoring of CD4 counts and viral loads remains important in guiding clinical decisions and ensuring that therapy is effective and well-tolerated.
In summary, the landscape of HIV treatment has evolved remarkably over recent years. With current strategies centered around early diagnosis, prompt initiation of ART, and widespread education to dispel myths, people living with HIV can lead long, healthy lives. The development of newer antiretroviral drugs with fewer side effects and simplified dosing schedules continues to improve treatment adherence and overall health outcomes. While challenges remain in the pursuit of a complete cure, these medical advances represent significant progress towards controlling and eventually eradicating HIV/AIDS globally.