Ultimate Guide to Healthy Eating for Diabetics: Tips, Food Choices, and Lifestyle Strategies
This comprehensive guide provides valuable insights into managing diabetes through proper dietary choices. It covers essential topics such as selecting lean proteins, healthy dairy options, whole grains, fruit moderation, vegetables for blood sugar control, and healthy fats. The article emphasizes portion control, meal planning, and lifestyle habits to help diabetics maintain stable blood glucose levels and improve overall health. With practical tips and detailed explanations, this guide aims to empower individuals to create a balanced, enjoyable diabetic-friendly diet that supports long-term wellness and prevents complications.

Comprehensive Strategies for Managing Diabetes through Diet
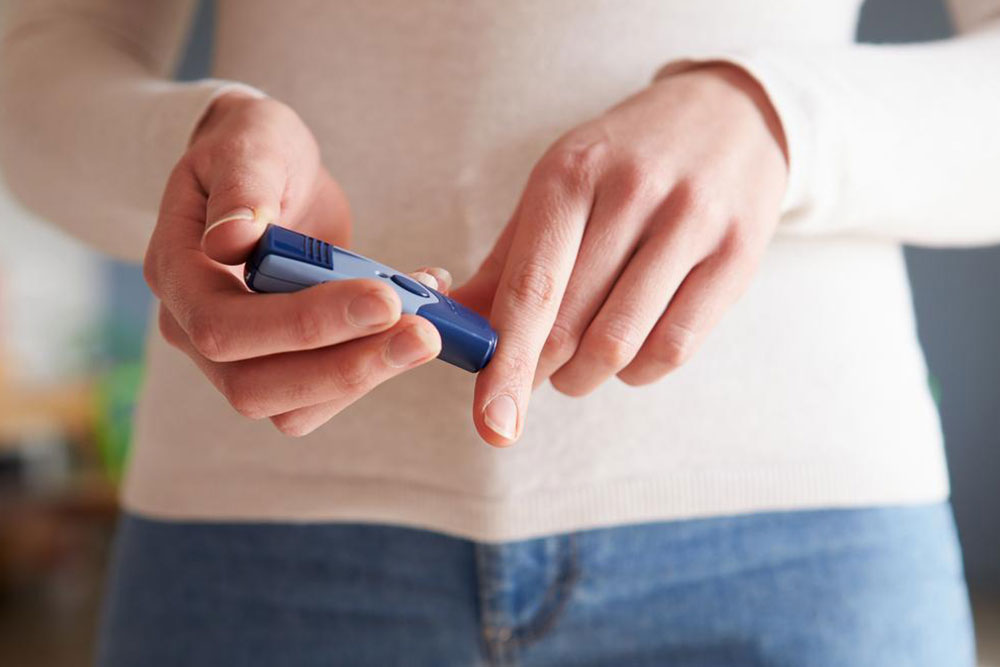
Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a chronic health condition characterized by elevated blood glucose levels due to the body's inability to produce or effectively use insulin. It has become one of the most widespread health concerns globally, particularly in developed countries like the United States. The increasing prevalence of diabetes is driven by rapid lifestyle changes, unhealthy dietary habits, sedentary behaviors, and obesity. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), over 30 million Americans suffer from diabetes, and many remain undiagnosed. Effective management of this condition is crucial to prevent complications such as cardiovascular disease, nerve damage, kidney failure, and vision loss.
Understanding the Importance of Proper Nutrition in Diabetes Management Properly managing diabetes involves a combination of medication, physical activity, and dietary modifications. Among these, diet plays a pivotal role. A well-balanced, nutritious diet can help stabilize blood sugar levels, reduce the risk of complications, and promote overall health. The key is to understand which foods are beneficial and which should be avoided or consumed in moderation. This comprehensive guide provides insight into making healthier food choices tailored for diabetics, ensuring they can enjoy varied, satisfying meals without compromising their health.
Choosing the Right Protein Sources
Proteins are essential for tissue repair, immune function, and muscle maintenance. For diabetics, selecting lean protein sources is especially important because they have minimal impact on blood sugar levels. According to guidelines from the American Diabetes Association, incorporating lean proteins such as fish, poultry, beans, and nuts into daily meals is highly recommended.
Opt for fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines, which are rich in omega-3 fatty acids that support heart health—a critical concern for diabetics. Skinless turkey and chicken are excellent options for poultry lovers, providing protein without the added saturated fat. Vegetarians and vegans can turn to plant-based proteins like lentils, chickpeas, kidney beans, black beans, and a variety of nuts and seeds, which also offer healthy fats and fiber.
It's advisable to limit or avoid processed meats such as hot dogs, bacon, and deli meats, as they tend to be high in saturated fats, sodium, and preservatives. These can contribute to insulin resistance and increase cardiovascular risks. Incorporating a variety of protein sources ensures nutrient diversity and helps maintain steady blood glucose levels.
Dairy and Milk Choices for Diabetics
Dairy products can be part of a healthy diabetic diet if chosen wisely. Unsweetened Greek yogurt, especially varieties without artificial sweeteners, offers a high protein content, probiotics, and minimal added sugars, making it a nutritious snack or breakfast option. Low-fat or fat-free dairy products such as milk, cheese, and yogurt help manage calorie and saturated fat intake, vital for heart health.
It's best to avoid sweetened dairy desserts like flavored yogurts, ice creams, and milkshakes, which often contain high amounts of added sugars. Reading nutrition labels diligently helps identify products with reduced sugar content. Additionally, opting for plant-based milk alternatives like almond, soy, or coconut milk can be suitable for those with lactose intolerance or seeking variety, but check for added sugars in these products as well.
Good Grain Choices: Whole vs. Processed
Carbohydrate management is central to diabetes control. The type of grains consumed significantly influences blood sugar response. Whole grains such as oats, quinoa, brown rice, millet, and whole wheat are rich in fiber, which slows digestion and absorption of glucose, leading to more stable blood sugar levels. These foods also provide essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that support overall health.
In contrast, refined grains—such as white bread, white rice, pastries, and many breakfast cereals—are heavily processed, stripped of their fiber and nutrients, and can cause rapid spikes in blood glucose. Limiting or avoiding foods made with white flour and instead choosing whole-grain alternatives helps maintain better glycemic control.
Fruits: Smart Choices for Blood Sugar Stability
Fruits contain natural sugars but are also packed with fiber, vitamins, and antioxidants. Fresh berries like strawberries, blueberries, raspberries, and blackberries are particularly beneficial due to their high fiber content, which helps temper blood sugar spikes. Other favorable options include guava, lemon, and cucumber, which are low in sugar and add variety to meals.
It’s important to consume high-sugar fruits like bananas, mangoes, grapes, and pineapples in moderation. Dry fruits such as raisins, dates, and apricots are concentrated sources of sugar and should be eaten sparingly. Packaged fruit juices are often loaded with added sugars and preservatives, so fresh fruit or infused water is a healthier alternative. Moderation and choosing lower-sugar options are key to incorporating fruit into a diabetic-friendly diet.
Vegetables for Blood Sugar Control
Vegetables are naturally low in carbohydrates and rich in dietary fiber, vitamins, minerals, and phytochemicals. Diabetics benefit from including a variety of high-fiber, low-carb vegetables such as leafy greens (spinach, kale, lettuce), broccoli, cauliflower, zucchini, and bell peppers in their meals. These vegetables can be used in salads, stir-fries, soups, and roasted dishes.
Starchy vegetables like potatoes, sweet potatoes, peas, corn, and carrots contain higher amounts of carbohydrates and can impact blood sugar levels. Though not necessary to eliminate these vegetables entirely, they should be consumed in smaller portions and less frequently. Combining vegetables with lean proteins and healthy fats can further help stabilize blood sugar levels.
The Role of Healthy Fats in a Diabetic Diet
Healthy fats are essential for overall wellness, hormone production, and satiety. Incorporating beneficial fats such as avocados, olive oil, nuts (almonds, walnuts, pecans), seeds (chia, flaxseed), and oily fish supports heart health, reduces inflammation, and can improve insulin sensitivity.
It's crucial to limit intake of unhealthy fats found in processed and fried foods, trans fats, and high-fat dairy like cheese, butter, and processed meats. These fats can promote insulin resistance and elevate LDL cholesterol, increasing the risk of cardiovascular disease. Emphasizing monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats as key components of meals optimizes health outcomes.
Tips for Effective Blood Sugar Management
Managing blood sugar levels requires more than just choosing the right foods; portion control and meal timing are equally important. Using smaller plates, measuring servings, and spacing meals evenly throughout the day help prevent blood sugar fluctuations. Incorporating physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding processed foods also contribute significantly.
Regular blood glucose monitoring enables diabetics to understand how different foods affect their levels, allowing for personalized adjustments. Additionally, staying hydrated, reducing alcohol intake, and managing stress are vital aspects of a holistic approach to diabetes control. Adopting these habits fosters a sustainable, healthful lifestyle that supports long-term well-being.
Final Thoughts
Living with diabetes requires a commitment to a nutritious, balanced diet and healthy lifestyle choices. Understanding which foods promote stable blood sugar and which can cause spikes helps diabetics make informed decisions. Combining a wholesome diet with regular exercise, adequate sleep, and stress management creates a comprehensive strategy for managing this chronic condition effectively. By making mindful choices every day, diabetics can enjoy a vibrant, healthy life while minimizing the risk of complications. Remember, consulting healthcare professionals or registered dietitians can provide personalized guidance suited to individual needs and preferences.