Comprehensive Guide to Eczematous Dermatitis: Types, Symptoms, and Effective Treatment Strategies
This comprehensive guide explores the various types of eczematous dermatitis, including atopic, contact, dyshidrotic, and other forms. It highlights key symptoms, common triggers, and effective treatment strategies such as moisturization, cold compresses, and avoiding irritants. Suitable for anyone affected by eczema, the article emphasizes early diagnosis and professional medical support to manage flare-ups and maintain healthy skin. Understanding these conditions is crucial for effective management and improving quality of life for eczema sufferers.
Comprehensive Guide to Eczematous Dermatitis: Types, Symptoms, and Effective Treatment Strategies
Skin conditions can be both uncomfortable and distressing, impacting daily life and overall well-being. Among these, eczema, also known as eczematous dermatitis, is a common chronic skin disorder characterized by redness, itching, and inflammation. This condition affects millions globally and manifests in various forms, each with unique features, triggers, and treatment needs. Understanding the different types of eczematous dermatitis, their signs, and how to manage them effectively is essential for anyone affected or caring for someone with this condition.
What Is Eczematous Dermatitis?
Eczema, medically termed eczematous dermatitis, is a broad category of skin inflammations distinguished by itchy, inflamed, and often dry or scaly skin. It is not contagious, meaning it cannot be transmitted from person to person through contact. The exact cause remains elusive, but it is believed to result from a combination of genetic predisposition, immune system responses, environmental factors, and skin barrier dysfunction. People with eczema tend to have sensitive skin that reacts to various irritants or allergens, leading to flare-ups.
The condition is often associated with other allergic conditions such as asthma, hay fever (allergic rhinitis), and food allergies, suggesting a common allergic or immune-mediated pathway. Though eczema is most common in children, adults can also develop various forms of the condition. Managing eczema involves understanding its different types, recognizing symptoms early, and applying appropriate treatment strategies to reduce discomfort and prevent complications.
Primary Types of Eczematous Dermatitis
Each type of eczematous dermatitis presents with distinct signs, triggers, and affected populations. Recognizing these differences aids in diagnosis and tailoring effective treatment plans.
Atopic Dermatitis
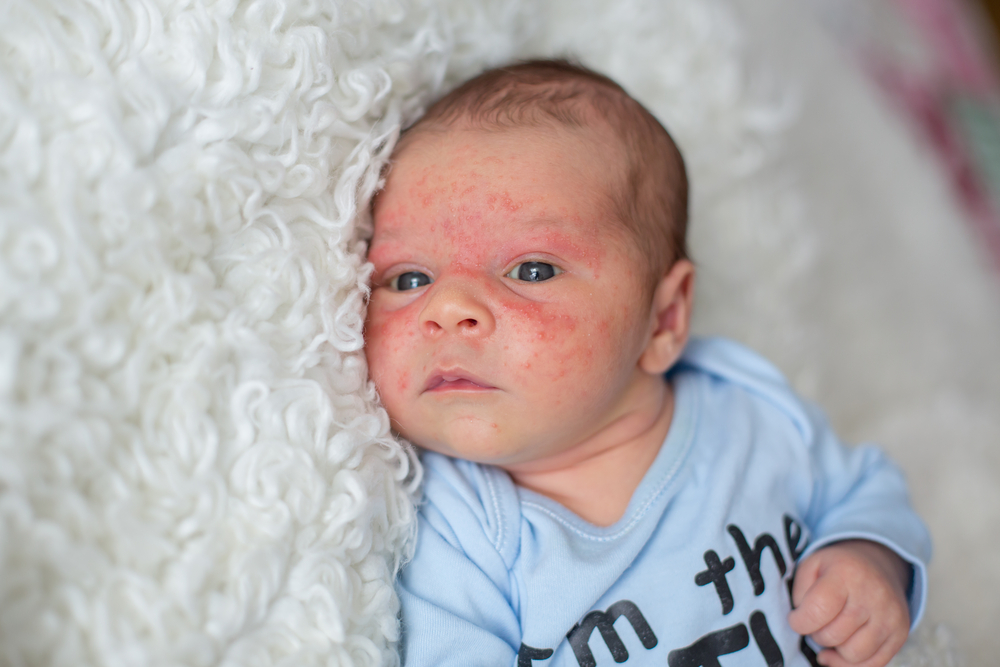
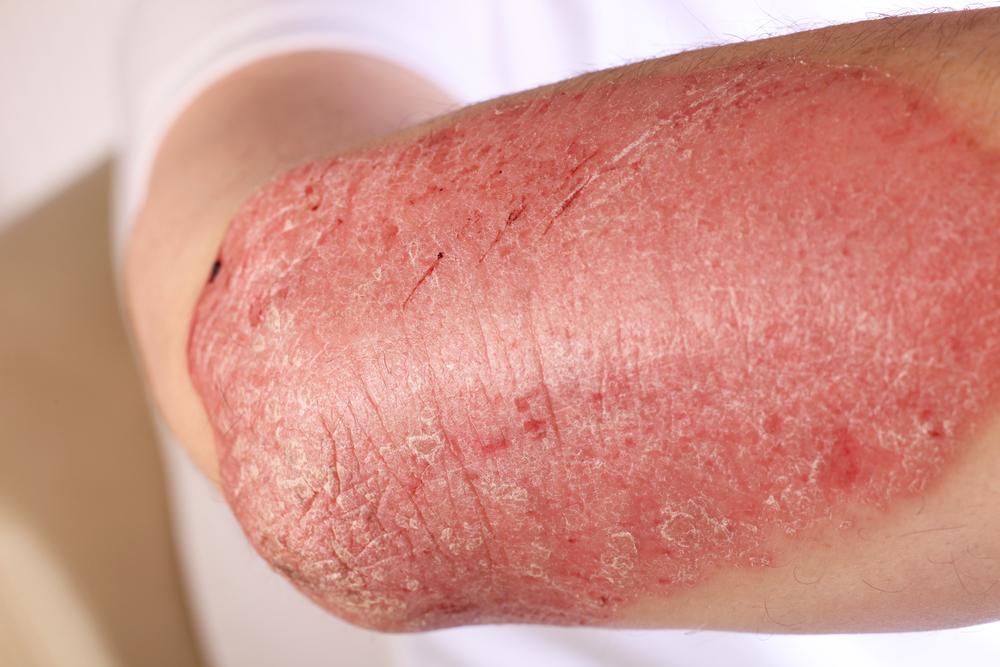
This is the most prevalent form of eczema, primarily affecting children but often improving or resolving by adulthood. Atopic dermatitis is strongly linked to other allergic conditions, including hay fever, asthma, and food allergies. It typically manifests as rashes on specific areas like the inside of elbows, behind the knees, and sometimes on the scalp or cheeks of infants.
Individuals with atopic dermatitis often experience intense itching, discomfort, and dry skin. The condition tends to flare periodically and can be exacerbated by irritants, stress, weather changes, or allergens.
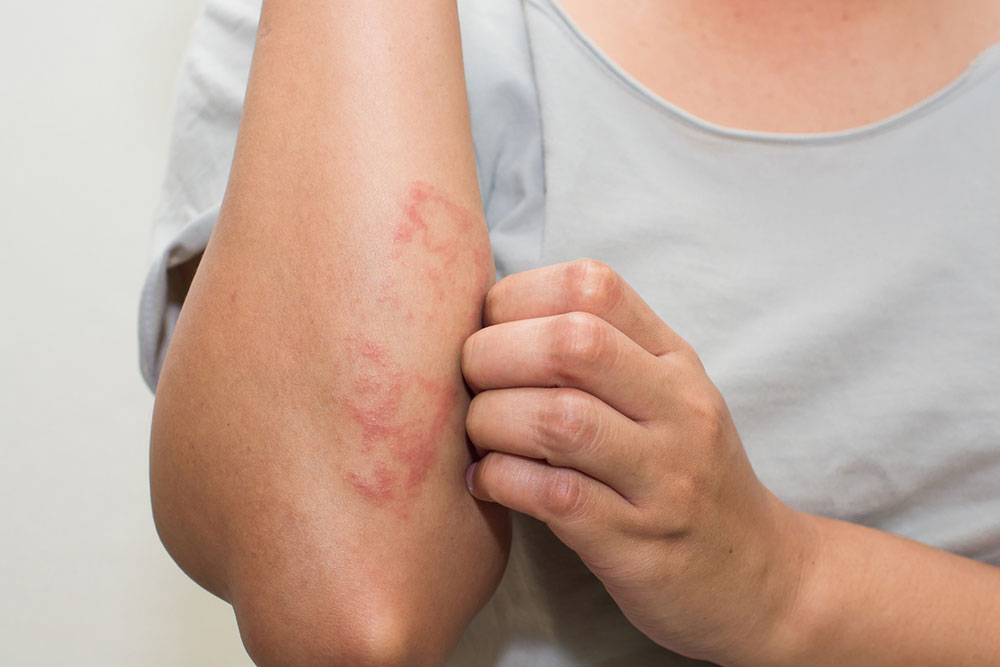
Contact Dermatitis
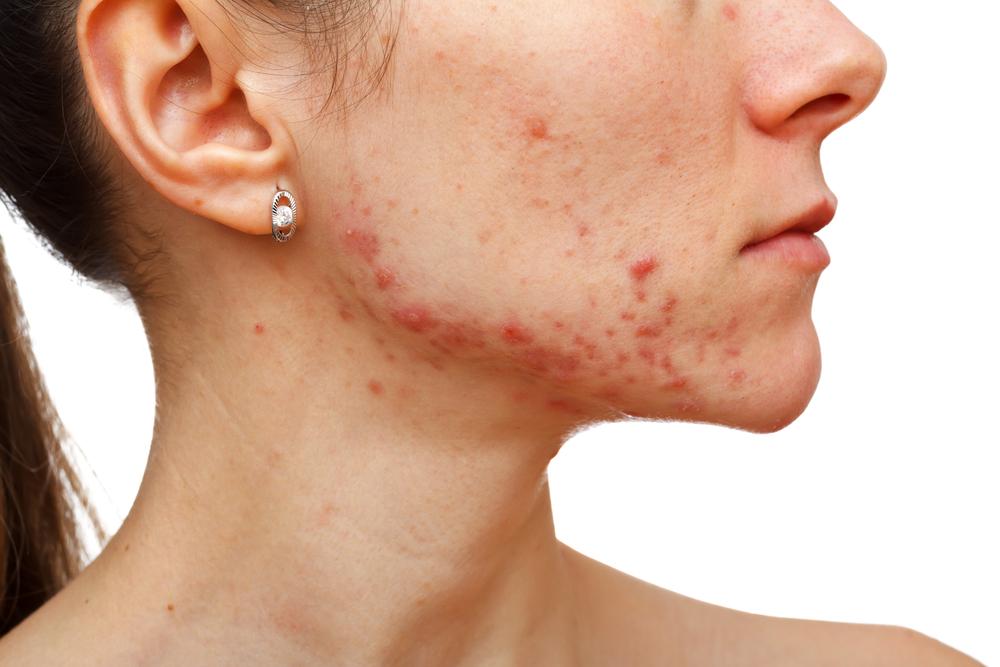
Contact dermatitis results from direct contact with irritants or allergens. It can be classified into allergic contact dermatitis, caused by an immune response to substances like nickel, certain fragrances, or latex, and irritant contact dermatitis triggered by exposure to harsh chemicals or detergents. This type causes redness, burning, itching, and sometimes blistering where the skin has come into contact with the offending substance.
Dyshidrotic Eczema
Originating more frequently in women, dyshidrotic eczema presents as small, itchy blisters mainly on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. These blisters can be painful and may lead to cracking and peeling of the skin, often causing discomfort during daily activities.
Hand Eczema
This form affects only the hands and is common among professionals who frequently handle chemicals, such as hairdressers, cleaners, and healthcare workers. Symptoms include redness, itching, cracked skin, and blisters, which can interfere with work and daily routines.
Neurodermatitis
Characterized by thickened patches and intense itching, neurodermatitis typically occurs on the limbs and neck. It often worsens during periods of relaxation or sleep and can lead to bleeding and secondary infections from scratching.
Nummular Eczema
Easy to identify by its round, coin-shaped patches, nummular eczema is highly itchy and tends to develop in outbreaks. Its distinct appearance makes it easier to differentiate from other types.
Stasis Dermatitis
Primarily affecting the lower legs, stasis dermatitis results from poor venous circulation, leading to fluid leakage and skin changes. Symptoms include swelling, redness, pain, and skin sores or ulcers, especially in individuals with varicose veins.
Effective Treatment Strategies for Eczematous Dermatitis
While eczema management varies depending on the type and severity, several general strategies can alleviate symptoms and prevent flare-ups.
Cold Compresses: Applying a cold, damp cloth to affected areas helps soothe itching and reduce inflammation, providing quick relief during flare-ups.
Baths with Baking Soda or Colloidal Oatmeal: These baths can help calm irritated skin, diminish itching, and soften scales. Use lukewarm water and avoid overly hot baths, which can dry the skin further.
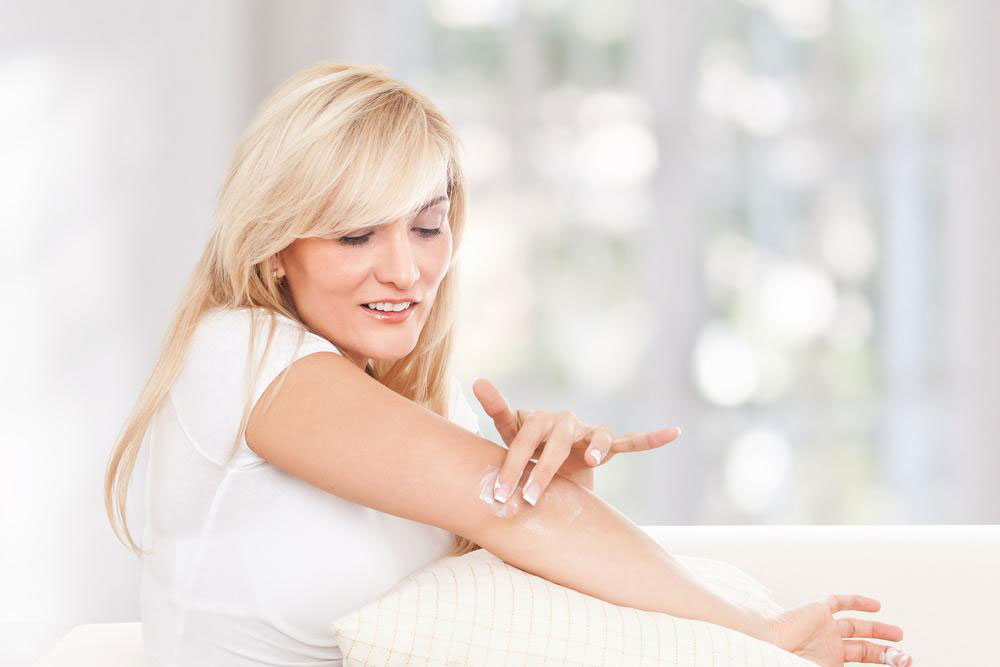
Moisturizing Regularly: Applying rich, oil-based moisturizers immediately after bathing creates a protective barrier, retaining moisture and reducing dryness. Suitable options include thick creams, ointments, or petroleum jelly.
Identifying and Avoiding Triggers: Keeping a diary to track flare-ups can help identify allergens or irritants like certain soaps, detergents, or fabrics.
Medical Consultation and Medication: For persistent or severe eczema, consulting a healthcare professional is essential. They may recommend topical corticosteroids, antihistamines, or other medications to control inflammation and itching.
Choosing Appropriate Clothing: Wearing loose, breathable garments made of soft cotton minimizes skin irritation and allows the skin to breathe, preventing worsening of symptoms.
In addition to self-care measures, ongoing medical treatment and skin care routines are crucial for managing eczema effectively. Early intervention can reduce severity, prevent infections, and improve quality of life. If you notice persistent symptoms, seek medical advice promptly for tailored treatment options and guidance on managing triggers.