Comprehensive Guide to Persistent Fatigue: Causes, Symptoms, and Management
Discover comprehensive insights into persistent fatigue, including its causes, signs, and effective management strategies. This detailed guide explains the complexities of chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS), helping readers recognize symptoms and seek appropriate treatment options to improve their quality of life.

Comprehensive Guide to Persistent Fatigue: Causes, Symptoms, and Management
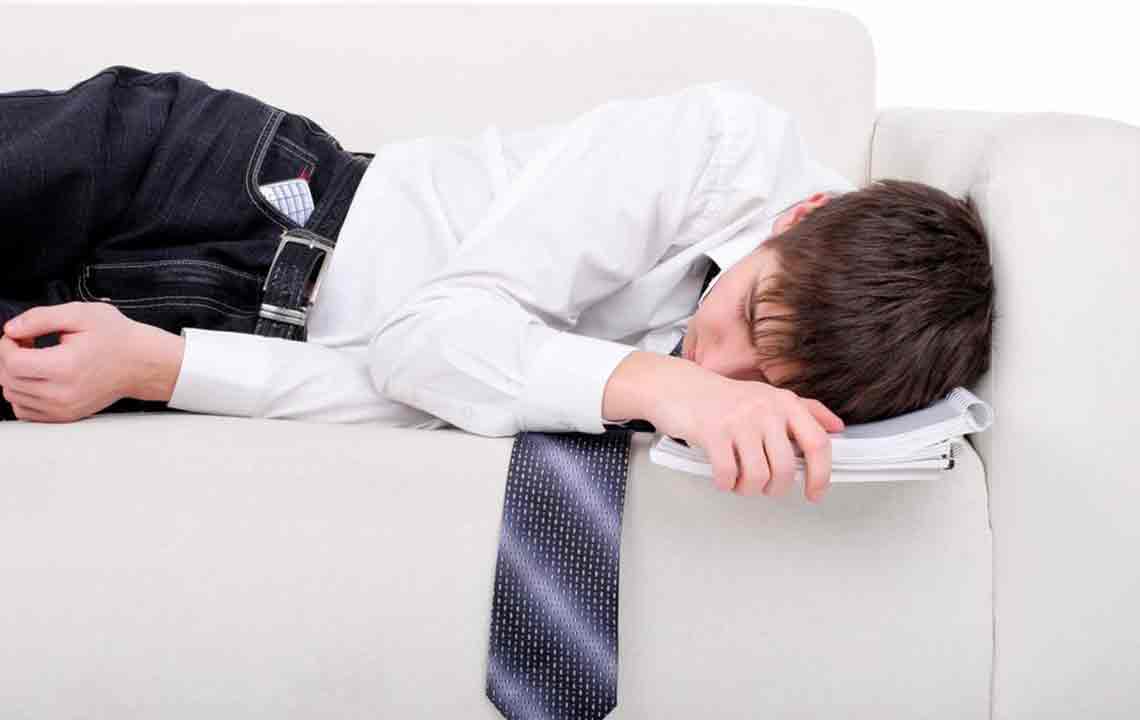
Are you feeling unusually drained, lacking energy despite enough sleep? Do you find yourself constantly battling a desire to nap or feeling exhausted even after resting? Persistent fatigue can significantly impact your daily life and may be a symptom of underlying health issues. Recognizing and understanding the causes and signs of prolonged tiredness is crucial for early diagnosis and effective management.
This condition often gets dismissed as simple tiredness or laziness, but persistent fatigue warrants attention. When tiredness persists for weeks or months and isn’t alleviated by rest, it could be indicative of a serious health disorder such as chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS), also known as myalgic encephalomyelitis (ME). Recognizing the symptoms early can help in seeking appropriate medical advice and improving your quality of life.
Chronic fatigue syndrome is a complex, debilitating condition characterized by profound and persistent tiredness that isn’t relieved even after adequate rest. Unlike common fatigue, which usually resolves with sleep or relaxation, CFS remains stubbornly present, disrupting daily activities and mental well-being.
While CFS cannot be attributed to any specific medical condition, its exact causes remain elusive. It predominantly affects women between their mid-20s and mid-40s but can also be diagnosed in children and adolescents. Its mysterious nature and overlapping symptoms with other illnesses make diagnosis challenging but vital for managing the condition effectively.
Understanding the Causes of Chronic Fatigue Syndrome
Deciphering what triggers CFS is a complex task, as no single definitive cause has been identified yet. Researchers believe a combination of factors may contribute to its development. Viral infections, immune system dysregulation, hormonal imbalances, and psychological stress are often suspected as potential triggers.
Various infectious agents have been linked to CFS, including viruses like Epstein-Barr virus, herpesvirus 6, Ross River virus, rubella, Coxiella burnetti, and mycoplasma. Many patients report episodes of illness due to these pathogens before experiencing persistent fatigue. Often, multiple infections over time increase the likelihood of developing CFS. This suggests that immune dysfunction plays a significant role in disease progression.
Hormonal fluctuations, especially involving the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, may also influence fatigue symptoms. Additionally, individuals with weakened immune responses or hormonal imbalances might be more predisposed to developing CFS.
Genetics and environmental factors such as stress, allergies, or exposure to toxins can further increase susceptibility. Women are approximately twice as likely to develop CFS compared to men, indicating a possible hormonal or genetic influence. Lifestyle factors, including poor sleep hygiene, high-stress levels, and mental health issues like depression, often exacerbate symptoms or trigger flare-ups.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Chronic Fatigue Syndrome
While symptoms vary between individuals, certain common signs suggestive of CFS include persistent fatigue that lasts for at least six months and is not relieved by sleep or rest. This fatigue often interferes with daily routines, work, and social interactions. Additional symptoms often accompanying the primary fatigue are as follows:
Memory lapses and concentration difficulties, often described as 'brain fog'
Unrefreshing sleep, where individuals wake up feeling tired regardless of sleep duration
Chronic sleep disturbances, including difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep
Unexplained muscle soreness and discomfort, which can be persistent
Joint pain without apparent swelling or redness
Frequent headaches, including migraines or tension headaches
Dizziness or lightheadedness, especially when standing up
Flu-like symptoms such as sore throat, swollen lymph nodes, and low-grade fever
Irregular heartbeats or palpitations
Multi-joint pain that shifts locations and varies in intensity
Prolonged exhaustion following mental or physical exertion
If you experience several of these symptoms for over six months alongside ongoing fatigue, consulting a healthcare professional is critical for diagnosis and management. Since there is no specific diagnostic test for CFS, doctors rely on symptom evaluation and ruling out other conditions such as hypothyroidism, fibromyalgia, multiple sclerosis, or autoimmune diseases.
During flare-ups, it’s advisable to avoid strenuous activities to prevent worsening symptoms. Many patients find that pacing their energy expenditure helps manage daily fluctuations. Psychological factors like depression, anxiety, social isolation, and lifestyle choices such as smoking or alcohol consumption can worsen CFS symptoms or complicate recovery. Personalized treatment plans focusing on symptom relief and lifestyle modifications are the cornerstone of managing this complex condition.
Current management strategies aim to improve quality of life through a combination of pharmacological, psychological, and lifestyle interventions. While there is no cure for CFS, many patients benefit from sympathetic therapies, graded exercise programs, cognitive-behavioral therapy, and recommendations to reduce caffeine, eliminate smoking, and limit alcohol intake. Recognizing early signs and adopting a supportive lifestyle can significantly alleviate the burden of this chronic condition.