Comprehensive Guide to Varicose Veins: Causes, Symptoms, Prevention, and Advanced Treatment Options
Learn everything about varicose veins, including their causes, symptoms, preventive strategies, and advanced treatment options. This comprehensive guide helps you understand how to manage and treat this common vascular condition effectively, ensuring healthier legs and improved well-being.

Varicose veins represent a common and often concerning vascular condition that affects a significant portion of the population worldwide. These enlarged, twisted veins are usually visible beneath the skin, primarily affecting the legs. While they may seem purely cosmetic at first, varicose veins can lead to discomfort, pain, and more serious health complications if left untreated. Understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and exploring effective treatment options are essential steps to managing this condition and improving overall vascular health.
What Are Varicose Veins?
Varicose veins are dilated, tortuous veins that develop when the valves inside the veins fail to function properly. Normally, veins carry deoxygenated blood back to the heart, assisted by valve mechanisms that prevent blood from flowing backward. When these valves become weakened or damaged, blood can pool within the veins, causing them to expand and become visible on the surface of the skin. The result is a characteristic appearance of bulging, bluish or purple veins that often twist and turn like cords beneath the skin.
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors contribute to the development of varicose veins. Age plays a significant role, as vascular tissues tend to weaken over time. Pregnancy is a common contributor due to hormonal changes and increased blood volume, which exert additional pressure on leg veins. Obesity also increases intra-abdominal pressure, straining the veins and promoting their dilation. Prolonged periods of standing or sitting hinder the blood flow in the legs, thereby increasing the risk. Genetic predisposition is another notable factor; if relatives have a history of varicose veins, the likelihood of developing them rises.
Symptoms and Signs
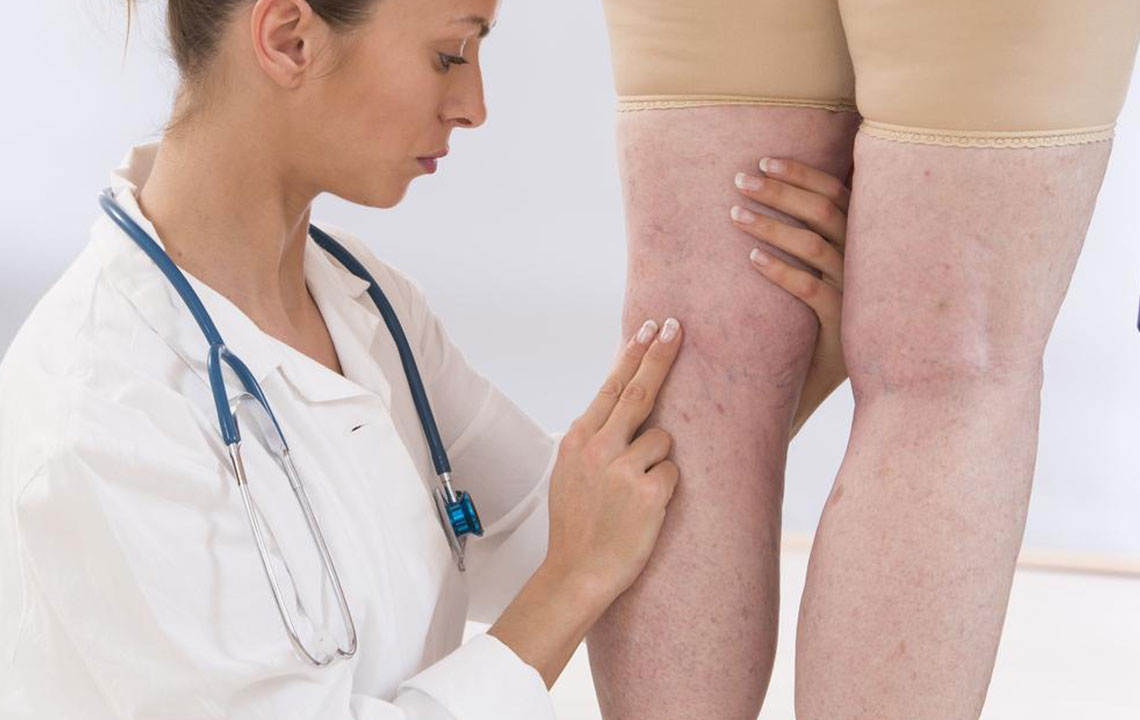
While some individuals may have no symptoms other than visible veins, many experience a range of discomforts. These include a dull ache, throbbing, or a feeling of heaviness in the legs—particularly after extended periods of standing or physical activity. Swelling around the ankles and calves may occur, especially after long days. Skin changes such as discoloration, dryness, or inflammation can develop over time. In advanced cases, ulcers may form near the ankles, which are slow to heal and require medical attention. Recognizing these symptoms early allows for timely intervention and prevents complications.
Diagnosis and Medical Evaluation
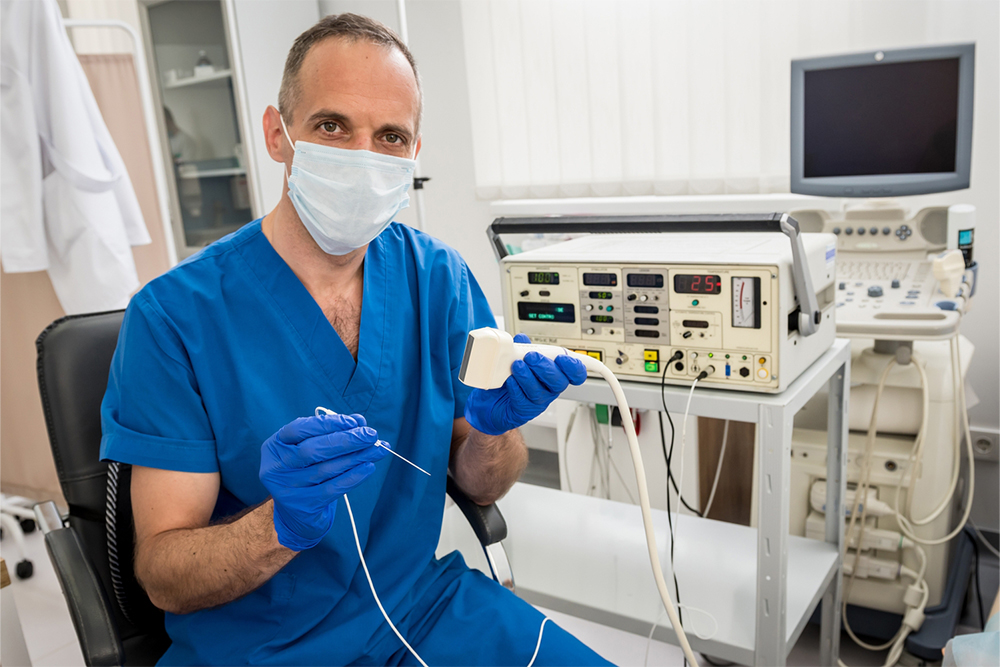
Diagnosis typically involves a detailed medical history and physical examination, focusing on the appearance of veins and related symptoms. To confirm the diagnosis and assess blood flow, healthcare providers often utilize duplex ultrasound imaging. This non-invasive test visualizes the veins and evaluates the function of valves, revealing areas of reflux or insufficiency. Accurate diagnosis is critical for developing an effective treatment plan tailored to the severity and extent of the condition.
Modern Treatment Options for Varicose Veins
Conservative Management and Lifestyle Changes
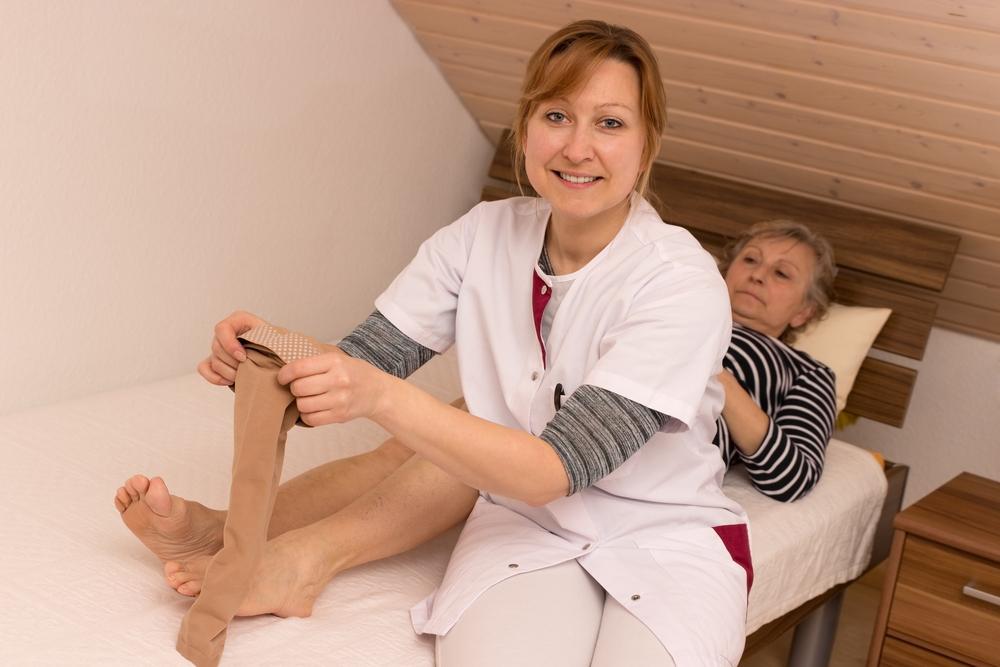
Initial management may include lifestyle modifications that reduce symptoms and prevent progression. Regular exercise such as walking, swimming, or cycling promotes healthy blood circulation. Maintaining a healthy weight alleviates pressure on the veins, while avoiding prolonged crossing of legs or standing in one place helps ensure unobstructed blood flow. Wearing compression stockings provides external support, compressing the veins and facilitating blood return to the heart. Elevating the legs periodically also relieves venous pressure, especially after long periods of activity.
Minimally Invasive Procedures
Advancements in medical technology have introduced minimally invasive procedures that effectively treat varicose veins with minimal discomfort and downtime. Laser ablation involves using laser energy to close affected veins, which are then naturally absorbed by the body. Sclerotherapy, another popular technique, entails injecting a sclerosant solution into the problematic veins, causing them to collapse and fade over time. Ultrasound-guided foam sclerotherapy is suitable for larger veins and involves injecting a foam sclerosant to ensure thorough treatment. These methods have high success rates and lower risk of complications compared to traditional surgery.
Surgical Interventions
For severe or stubborn cases, traditional surgical removal, such as vein stripping and ligation, may be necessary. This procedure involves tying off the problematic vein and extracting it through small incisions. While more invasive, surgery can provide definitive results, especially when other treatments are ineffective. Postoperative care involves leg elevation, compression therapy, and avoiding strenuous activities for a period to promote healing and prevent recurrence.
Preventive Measures and Self-Care Tips
Prevention remains a crucial aspect of managing varicose veins. Regular physical activity, especially exercises that strengthen the leg muscles, enhances overall venous health. Maintaining a healthy weight reduces undue pressure on the lower limbs. Avoiding prolonged periods of immobility—such as sitting or standing—by taking short breaks to walk or stretch can significantly improve blood flow. Wearing compression stockings during daily activities provides ongoing support, especially for individuals with a family history or early signs of vein issues.
When to Seek Medical Advice
Individuals experiencing persistent leg pain, swelling, skin discoloration, or ulcers should consult a healthcare professional promptly. Early diagnosis facilitates conservative management and less invasive treatments, reducing the risk of complications such as skin infections, bleeding, or chronic venous insufficiency. Regular follow-up with a vascular specialist ensures ongoing monitoring and adjustment of treatment plans as needed.
Conclusion
Varicose veins, though common, can lead to significant discomfort and potential health risks if left untreated. Understanding their causes and recognizing early symptoms empower individuals to seek timely medical intervention. With a spectrum of treatment options—from lifestyle modifications and compression therapy to advanced minimally invasive procedures and surgical interventions—most people can find relief and restore their leg health. Prioritizing preventive care and maintaining a healthy lifestyle remain the best strategies to reduce the incidence and impact of varicose veins, ultimately enhancing quality of life.